| Chapter 23. Monopoly#1: Calculating Total Profit Using a Graph
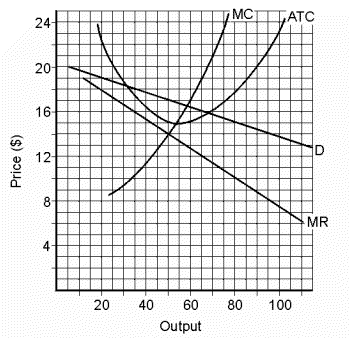
The analysis we use for the monopolist is identical to that which we used for the perfect competitor. I'd like you to look at Figure 23.1 and then write down the firm's output, price, and ATC.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30187/image14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30187/image14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a>
Figure 23.1
The firm's output is 50 (where MC = MR), its price is $17 (read off the demand curve), and its ATC is $15 (at an output of 50). Now substitute these numbers in the formula and solve for total profit.
Solution:| Total Profit | = | Output (Price - ATC) | | = | 50 ($17 - $15) | | = | 50 ($2) | | = | $100 |
#2: Calculating Total Loss Using a Graph
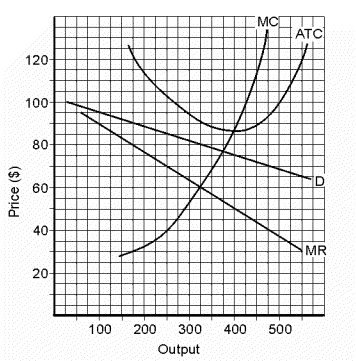
Use the data in Figure 23.2 to find the total loss (or negative total profit) taken by this company.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30187/image15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30187/image15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a>
Figure 23.2
Solution:| Total Profit | = | Output (Price - ATC) | | = | 325 ($80 - $90) | | = | 325 (-$10) | | = | -$3,250 |
|



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education

 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education