
(See related pages)
| Σ | The Greek symbol for sum. |
| abscissa | The x-axis. |
| absolute pressure | The pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. |
| absolute pressure scale | A pressure scale that designates the pressure exerted by a perfect vacuum as zero. |
| absolute systems | A coherent system that defines mass, length, and time; force is a derived quantity. |
| absolute temperature scale | A temperature scale that designates absolute zero as "zero degrees." |
| absolute zero | Temperature is reduced as low as possible and motion, although not at zero, is at its minimum. |
| acceleration | The rate at which velocity changes with respect to time. |
| accuracy | The extent to which the reported value approaches the "true" value and is free from error. |
| actuator | A mechanism that uses pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrical signals to activate equipment. |
| address | A numerical designation for a memory location. |
| algorithm | A sequence of actions that will solve a particular problem. |
| allowable stress | The maximum force per unit area that may be safely applied. |
| alternating current | Electric current that reverses direction periodically. |
| ampere | The base unit of electric current.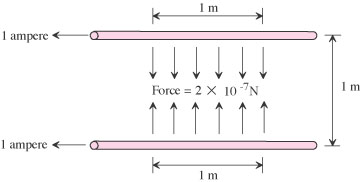 |
| amperes | The measure of current, defined as 1 coulomb per second (1 C/s). |
| amplifier | A device that allows a small amount of electrical energy to regulate a large amount of electrical energy. |
| amporphous | Noncrystalline. |
| analog | An electronic device that uses continuous values of voltages and currents. |
| analog computer model | An analog electronic circuit that simulates a physical system. |
| analysis | The process of defining and seeking an answer to a problem. |
| angular displacement | A vector describing the change in position of a rotating or orbiting body. |
| angular momentum | A vector quantity with magnitude equal to the mass moment of inertia times the angular velocity; describes the ability of a rotating or orbiting object to resist forces that would tend to change the rotation rate.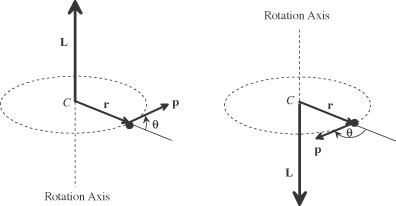 |
| anion | Negatively charged ion. |
| annuity | A series of equal payments occurring at equal time periods that last a finite length of time. |
| anode | A positively charged electrode. |
| application | A process whereby appropriate information is identified for the problem at hand. |
| application issue | The lack of clarity as to whether a particular act violates a law, rule, or policy. |
| Archimedes' principle | The total mass of a floating object equals the mass of the fluid displaced by the object. |
| assembly language | The use of Englishlike commands to generate machine language instructions. |
| atom | A single nucleus with its accompanying electrons. |
| atomic mass | The mass of 1 mole of molecules; commonly called atomic weight. |
| atomic number | The number of protons in an atom. |
| atomic weight | The weight of 1 mole of molecules; also called atomic mass. |
| attractive force | A force that causes two objects to move toward each other. |
| average acceleration | The rate that velocity changes during a finite time period. |
| average angular acceleration | During a finite time interval, the change in angular speed divided by the change in time. |
| average angular speed | During a finite time interval, the angular displacement of an object divided by time. |
| average velocity | The rate that position changes during a finite time period. |
| Avogadro's number | NA The number of atoms or molecules in 1 gram-mole. |
| axiom | An assumption that cannot be rigorously proved to be true, but seems to be true from experience or observation. |
| ballast | A device that regulates current in a fluorescent light. |
| base | Electrode that regulates current flow through a bipolar transistor. |
| base units | The units from which all other units in a measuring system are derived. |
| battery | A device that produces electricity from the chemical energy in the anodes and cathodes. |
| bell-shaped curve | A common expression referring to the normal distribution. |
| Bernoulli equation | The equation that describes the interconversion of pressure energy, gravitational potential energy, and kinetic energy for an incompressible fluid flowing at steady state. |
| binary | Base-2 number system. |
| bipolar transistor | A transistor that contains two pn junctions. |
| bit | A unit of information consisting of either 0 or 1. |
| blackbody | An object that completely absorbs light. |
| Boyle's law | The absolute pressure P and the volume V of a perfect gas are inversely proportional, provided the temperature T and number of moles n are constant.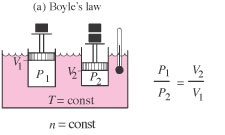 |
| brush | Electric contact that slides against a rotating component. |
| bushel | A British unit used to measure dry goods; equals 8 imperial gallons. |
| byte | Eight bits bundled together. |
| calorie | The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. |
| calorimeter | A device that measures heat effects. |
| candela | A base unit of luminous intensity. |
| capacitance | A measure of the amount of charge stored in a capacitor for a given voltage. |
| capacitor | A charge storage device that is constructed from two conducting plates separated by an insulating material. |
| capitalized costs | The amount of money needed to purchase equipment plus the principal needed to establish a perpetuity to replace the equipment when it wears out. |
| Carnot equation | The equation that describes the maximum amount of work Wmax that can be produced from a unit of high-temperature heat (Equation 11-13). |
| cathode | A negatively charged electrode. |
| cathode-ray tube | A device that produces visual images by bombarding a phosphor screen with high-velocity electrons. |
| cation | Positively charged ions. |
| Celsius temperature scale | A temperature scale in which the two reference points are the melting point of ice (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C). |
| central processing unit | The part of the computer that interprets and executes instructions. |
| central tendency | A "typical" value of a data set given by the mean, mode, or median. |
| centrifugal force | The influence on a rotating or orbiting body that directs it away from the center pivot point. |
| centripetal acceleration | Acceleration directed toward the center pivot point. |
| centripetal force | The influence on a rotating or orbiting body that causes it to accelerate toward the center pivot point. |
| Charles' law | Volume V and absolute temperature T are directly proportional, provided the pressure P and number of moles n are constant.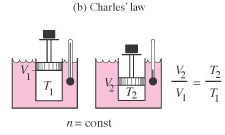 |
| check valve | A device that allows fluid to flow in one direction only. |
| chemical work | Work required to change chemistry or concentration. |
| chronological strategy | A strategy that gives a historical account of the topic. |
| circuit | Collection of electrical components wired together. |
| clock cycle | The speed at which the computer performs a single operation. |
| closed system | A system in which mass does not cross the boundary. |
| coefficient of kinetic friction | The ratio of the friction force between two bodies and the perpendicular force between the bodies when there is relative sliding motion between the two bodies. |
| coefficient of static friction | The ratio of the friction force between two bodies and the perpendicular force between the bodies at the instant when the bodies transition from being stationary to being set in relative sliding motion. |
| coherent | Photons that are in phase. |
| coherent light | Light in which the electrical energy peaks of the photons align. |
| coherent unit system | A unit system in which the numerical part of any conversion factor is 1. |
| collector | Electrode that receives electrons in a bipolar transistor. |
| commutator | Split slip ring that converts alternating current to direct current. |
| compound interest | The interest accumulated on unpaid interest as well as the original principal. |
| comprehension | The step in which the proper theory and data are used to actually solve the problem. |
| compressibility factor | Z A factor used to correct the perfect gas equation so it can describe real gases. |
| compression force | The force that causes the atoms of a structure to compact. |
| conceptual issue | The morality of an action is agreed upon, but there is uncertainty about how it should be codified into clearly defined law, rule, or policy. |
| concurrent engineering | A design approach in which specialists work together right at the beginning of a project. |
| conductor | Substance through which current readily flows. |
| conference proceedings | A collection of papers written by authors who speak at a meeting devoted to a particular topic. |
| conflict of interest | A situation in which an engineer's loyalties and obligations may be compromised because of self-interest or other loyalties and obligations. |
| conservation of mass | Mass can be neither created nor destroyed; also called conservation of matter. |
| conserved | A quantity that is neither generated or consumed. |
| conserved quantities | Quantities that are neither generated nor consumed. |
| constant-pressure heat capacity | The amount of heat that causes a 1° temperature change in a material maintained at constant pressure. |
| constant-volume heat capacity | The amount of heat that causes a 1° temperature change in a material maintained at constant volume. |
| continuous compound interest | A method in which the interest on unpaid interest and principal is assessed continuously rather than after finite time periods, such as monthly or annually. |
| control components | Devices that regulate current flow in an electrical circuit. |
| convergence | To tend toward a common solution. |
| conversion factor | A numerical factor that, through multiplication or division, converts a quantity expressed in one system of units to another system of units. |
| coulomb | For a 1-ampere current, the number of electrons that flow past a point during 1 second. |
| couple | Two forces have the same magnitude and act parallel to each other, but in opposite directions |
| critical point | The temperature and pressure where the density of the liquid and vapor phases become identical. |
| critical temperature | Tc The temperature where electrical resistance becomes zero. |
| crystalline | Molecules or atoms ordered into a repeating structure. |
| cube-square law | A law of nature that says as an object gets smaller, its volume decreases much faster than its area; therefore, the surface-area-to-volume ratio increases with smaller objects. |
| cubit | An ancient form of measure, equivalent to the length from a Pharaoh's elbow to the farthest fingertip of his extended hand. |
| cumulative frequency | The sum of the frequency in a given class plus the frequencies in all lower classes. |
| cumulative frequency polygon | A polygon plotted by connecting the midpoints of the cumulative frequency rectangles. |
| current | Flow of charge opposite to electron flow. |
| datum | A reference point used when making a measurement. |
| debate strategy | A strategy that describes the pros and cons of a particular approach. |
| Delphi technique | A technique in which the members of a group are intentionally separated and given the same problem. They return their solutions to the leader, the solutions are pooled, and the group members rate the ideas. |
| denary | Base-10 number system. |
| density | The amount of mass in a unit volume. |
| dependent variable | A variable that cannot be arbitrarily selected and is determined by the independent variable. |
| depletion layer | Zone of a pn junction where electrons from the n-type semiconductor occupy holes in the p-type semiconductor. |
| depreciation | A decrease in value because of age, wear, or market conditions. |
| descriptive statistics | Brief numerical descriptions of data. |
| detailed design | The step where highly detailed drawings and specifications are prepared for the best design option. |
| deviation | The difference between one number in a set and the mean of the set. |
| differential equation | An equation that contains one or more derivatives. |
| differential pressure | The difference between two pressures. |
| diffusion | A process in which chemical species A flows from a high concentration to a low concentration while dispersed in chemical species B. |
| diffusivity | The proportionality constant that describes the ability of chemical species A to diffuse through chemical species B. |
| digital | An electronic device that uses only discrete voltages and currents. |
| digital computer model | A program in a digital computer that simulates a physical system. |
| dimension | An abstract idea described by units of measure. |
| dimensional analysis | A process of determining the functional relationship between quantities by using the dimensions of each quantity. |
| dimensional homogeneity | The dimensions on the left-hand and right-hand sides of the equation must be the same. |
| diode | A device that allows current to flow in one direction only. |
| direct current | Electric current that flows in a single direction. |
| discrete components | Individual circuit elements. |
| displacement | A change in position. |
| distance | A nonnegative scalar that describes the length of a path. |
| diverge | To differ. |
| dope | Introduction of substances into semiconductor crystal, typically by diffusion. |
| drag | Resistance exerted on a body as it moves through a fluid. |
| drain | Electrode that receives electrons in a field-effect transistor. |
| driving force | An influence that causes change. |
| dynamics | The study of forces and moments on moving objects. |
| efficiency | Ratio of output to input. |
| elastic limit | The stress that initiates a permanent structural rearrangement. |
| electrical conductivity | The ability to conduct current. |
| electrical superconductors | Materials that have no electrical resistance. |
| electrical work | Energy required to move a charge across a voltage difference. |
| electric field | Region surrounding an electric charge that describes the force on a test sphere. |
| electricity | Study of charge and related phenomena. |
| electrochemistry | Chemical reactions driven by electrical energy. |
| electrodialysis | A process for separating ions by electrical energy. |
| electrolysis reactions | Chemical reactions that require an input of electrical energy. |
| electromagnetic force | A force that attracts two objects of opposite charge (or opposite magnetic poles) and repels two objects of like charge (or like magnetic poles). |
| electromagnetic radiation | Electric/magnetic energy emitted as photons. |
| electron | A negatively charged subatomic particle. |
| electroplating | A process in which metal ions react at a cathode to form elemental metals. |
| electroseparations | Separation process driven directly by electrical energy. |
| electrostatic force | A force of attraction or repulsion between electric charges. |
| eminent domain | The right of the government to take possession of private property for public use. |
| emitter | Source of electrons in a bipolar transistor. |
| empirical constant | The value of the constant is determined by experiment. |
| energy | A unit of exchange used by the scientific and engineering community to equate various phenomena. |
| energy efficiency | Ratio of energy output to energy input. |
| energy source | A device produces electrical energy from other forms of energy. |
| engineer | An individual who combines knowledge of science, mathematics, and economics to solve technical problems that confront society. |
| engineering analysis paper | A paper with a light grid pattern that can be used for graphing or drafting. |
| engineering design method | A procedure of synthesis, analysis, communication, and implementation used to design solutions to problems. |
| engineering economics | The discipline that translates engineering technology into a form that permits evaluation by businesses or investors. |
| engineering ethics | The set of behavioral standards that all engineers are expected to follow. |
| engineering notation | The use of leading zeros for decimal numbers less than 1. |
| enthalpy | H = U + PV |
| enthalpy H | Internal energy plus the product of pressure and volume. |
| entropy | A measure of the disorder of a system. |
| equilibrium conditions | Conditions that do not change as time passes. |
| Eratosthenes' sieve | An algorithm that finds all the prime numbers less than or equal to a user-specified integer. |
| error | The difference between the reported value and the true value. |
| ethical egoism | A moral theory stating that an act is moral provided you act in your enlightened self-interest. |
| ethics | The general and abstract concepts of right and wrong behavior culled from philosophy, theology, and professional societies. |
| etiquette | The codes of behavior and courtesy. |
| evaluation matrix | A mathematical evaluation that identifies the best solution by weighting desired properties on the basis of their relative importance. |
| excess reactant | A reactant that remains after other reactants are completely converted to product. |
| exponential equation | y - kBmx |
| extensive quantities | Quantities that depend on scale. |
| extrapolation | Extending beyond the data points.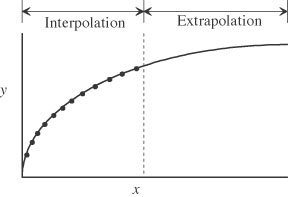 |
| factual issue | Uncertainty about morally relevant facts. |
| Fahrenheit temperature scale | A temperature scale in which the two reference points are the freezing point of water (32°F) and the boiling point of water (212°F). |
| Faraday's constant | The ratio of Avogadro's number to the coulomb. |
| feasibility study | The step of the engineering design method where ideas are roughed out. |
| field-effect transistor | A solid-state amplifier that regulates current flow by controlling the size of the depletion layer. |
| first law of thermodynamics | Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. |
| fission | The process whereby a heavy element is broken into lighter elements. |
| flip-flop | An electronic circuit that can store either of two stable states. |
| flowchart | A schematic that describes the sequential order in which the steps of a logarithm are done. |
| flow rate | The amount of flow past a fixed point in a given time. |
| fluids | Materials that flow when pressure is applied, including liquids, gases, vapors, and supercritical fluids. |
| fluorescent light | A device that converts electrical energy to light using fluorescence. |
| flux | The flow rate per cross-sectional area. |
| foci | The two points symmetrically located on the major axis of an ellipse either side of the center. |
| forbidden zone | Energy level that is forbidden to electrons. |
| force | The rate that momentum enters or leaves the system; the influence on a body that causes it to accelerate in the absence of any other counteracting forces. |
| free body diagram | A drawing of a system with forces acting on it. |
| frequency | The number of data points in a class. |
| frequency polygon | A polygon plotted by connecting the midpoints of histogram bars. |
| friction | Bonding between two surfaces that contact each other. |
| fuel cell | A device that converts the chemical energy of added reactants into electrical energy.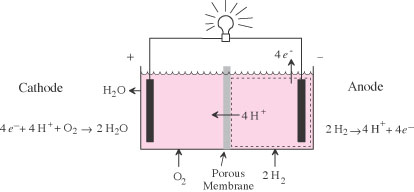 |
| fulcrum | The point or support on which a lever pivots. |
| fusion | The act of melting a solid. |
| gage pressure | The pressure relative to atmospheric air. |
| game theory | A tool for evaluating optimal behavior strategies. |
| gap | Energy level that is forbidden to electrons. |
| gas pressure | The pressure resulting from the impact of gas molecules on the container wall. |
| gate | Electrode that regulates the size of the depletion zone in a field-effect transistor. |
| Gay-Lussac's Law | The absolute pressure P and absolute temperature T are directly proportional, provided the volume and number of moles are constant.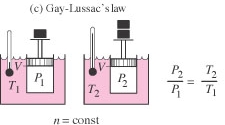 |
| general-to-specific strategy | A strategy that presents general information first, and then gives increasingly detailed information and specific examples. |
| generation | The amount of the counted quantity produced during the time interval within the system boundary. |
| generator | A device that produces electrical energy from a mechanical energy input. |
| global optimum | The best condition found without constraints. |
| glug | A derived unit for mass in the CGS gravitational system; rarely used. |
| Gramme machine | An early electric generator. |
| gram-molecule | The base unit of the amount of substance (usually referred to as mole); Avogadro's number. |
| gravimetric energy density | The total amount of energy that can be stored in a given mass. |
| gravimetric power density | The rate at which energy is released from a given mass. |
| gravitational systems | A coherent system that defines force, length, and time. Mass is a derived quantity. |
| gravity | An attractive force between two objects that have mass. |
| grid | A device that controls the flow of electrons in a tube amplifier. |
| half-life | The time it takes for half the radioactive particles to decay. |
| hands | A unit of length used to determine the height of a horse; equal to 4 inches. |
| happiness objective function | (Σ)(benefit) (importance) - (Σ)(harm) (importance) |
| hardware | A term for the computer and the associated peripherals, such as the printer, disk drives, and networks. |
| head | Pressure differences, velocities, and heights expressed as length. |
| heat | Energy flow resulting from a temperature driving force. |
| heat capacity | C The amount of heat per unit mass divided by the temperature change. |
| heat of vaporization | The heat required to convert a liquid to a vapor. |
| Hero's odometer | A 2000-year-old aid for computation that used rotating pegged wheels. |
| heterogeneous system | A system that has different properties, depending on what portion of the system is examined. |
| heuristic | The use of speculative strategies for solving a problem. |
| hexadecimal | Base-16 number system. |
| high-pass filter | A circuit that passes high-frequency signals, but not low-frequency signals. |
| histogram | A figure in which the frequency of each class of data is plotted as bars, and the bar lengths are proportional to the frequency. |
| hole | Absence of an electron. |
| homogeneous system | A system that has the same properties everywhere within the system. |
| hydraulic lift | A device used to lift automobiles at service stations. |
| hydraulic work | Energy required to flow a fluid across a pressure difference. |
| hydrostatic pressure | The pressure resulting from the weight of liquid or gas. |
| incandescent light | A device that converts electrical energy to light energy by heating a metal to very high temperatures. |
| incoherent light | Light in which the electrical energy peaks of the photons do not align. |
| independent variable | A variable that can be arbitrarily selected. |
| inductance | The quantitative factor that describes the "inertia" of an electrical circuit to resist changes in current. |
| inductor | A coil of wire. |
| inertial | Not accelerating. |
| infinitives | Verbs preceded by the word to. |
| inflation | An increase in the money supply relative to goods and services that results in a continuing rise in prices. |
| initial capital cost | The purchase price of a product. |
| input | The amount of the counted quantity passing through the system boundary into the system during the time interval. |
| installment loan | The payment of equal periodic amounts to repay a lump sum of money. |
| instantaneous acceleration | The rate that velocity changes during a differential time period. |
| instantaneous angular acceleration | During a differential time interval, the change in angular speed divided by the change in time. |
| instantaneous angular speed | During a differential time interval, the angular displacement of an object divided by time. |
| instantaneous velocity | The rate that position changes during a differential time period. |
| insulator | A material with a low electrical or thermal conductivity. |
| integer | A discrete number used for counting. |
| integrated circuit | A device in which circuit components are mounted directly onto a semiconductor crystal. |
| intensifier | A device that increases or decreases the pressure of a pulsating fluid. |
| intensive quantities | Quantities that are independent of scale. |
| interaction rules | Expected sets of behavior (etiquette, law, morals, and ethics) between the engineer, other individuals, and society as a whole. |
| intercept | The value where a line intersects a coordinate axis. |
| interconversion | Mutual conversion. |
| interest | The "rent" paid for borrowed money. |
| interest period | The length of time after which interest is due. |
| interest rate | The "rent" for borrowed principal expressed as a percentage of the principal per unit time. |
| interference pattern | Light patterns resulting from aligned or misaligned light wave peaks. |
| interferometer | A laboratory device used to observe interference patterns. |
| internal energy | The collection of microscopic kinetic and potential energies. |
| interpolating | To estimate a value of a function or series between two known values. |
| interpolation | Extending between the data points. |
| irreversible | A system which, when returned to its original state, causes a change in the surroundings. |
| isolated system | A system in which nothing crosses the boundary. |
| isotherm | Constant temperature. |
| iterative procedure | Repetition of a sequence of steps to solve a problem. |
| kelvin | The base unit of thermodynamic temperature. |
| Kelvin temperature scale | A thermodynamic temperature scale in which 0 K is defined as absolute zero and the temperature interval is the same as the Celsius scale. |
| kilogram | The base unit of mass. |
| kinetic energy | The energy associated with a moving mass. |
| kinetic friction | The frictional force tending to slow a body in motion. |
| Kirchhoff's current law | The total current flowing into a junction is equal to the total current flowing out of a junction. |
| laser | A device that emits monochromatic, coherent light. |
| laser light work | The energy required to produce laser light. |
| law | The system of rules established by authority, society, or custom. |
| law of diminishing returns | The concept that with small inputs, the output increases linearly, but with larger inputs, the output levels off.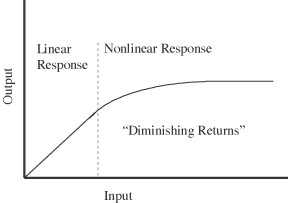 |
| law of inertia | An object in motion will maintain its velocity in the absence of any applied forces. |
| lead-acid battery | A secondary battery in which the anode is constructed of lead and the cathode is constructed of lead oxide. |
| least-squares linear regression | A rigorous mathematical procedure that is used to find a line that best fits all the data points.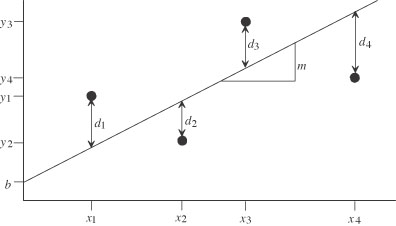 |
| legal rights | The "just claims" given to all humans within a government's jurisdiction. |
| length contraction | The observation that length contracts in the direction of travel. |
| life-cycle cost | The purchase price and additional costs such as labor, operation, insurance, and maintenance. |
| light-emitting diode | A pn junction that emits light when current flows through it. |
| limiting reactant | A reactant that is completely consumed before other reactants are converted to product. |
| linear interpolation | The approximation of a curve with a straight line.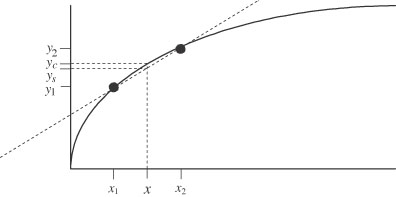 |
| linear momentum | A vector resulting from multiplying a mass by its velocity vector. |
| linear regression | The process of finding the equation of a straight line that best fits the data. |
| lines of force | Imaginary lines surrounding an electric charge that are parallel to the force on a test sphere. |
| load | Component of an electric circuit that converts electrical energy into another form of energy. |
| local area network | A system that links computers together and allows them to share files, programs, and use common input/output devices. |
| local optimum | The best condition found with constraints. |
| logarithm | The power to which a base must be raised to produce a given number. |
| log-log graph | A graph in which both axes are logarithmic. |
| loop | Closed path in a circuit. |
| low-pass filter | A circuit that passes low-frequency signals, but not high-frequency signals. |
| luminous intensity | The amount of light flux into a specified solid angle. |
| machine language | A series of binary numbers that directs the CPU. |
| magnetic field | Region surrounding a magnet that describes the force on a test magnet. |
| magnetic force | The force that exists between two magnetic poles. |
| manipulative models | A class of problems that have some physical entity that can be used to one's advantage in order to solve a problem. |
| mass moment of inertia | The mass of an orbiting particle times the orbital radius squared. |
| mathematical model | Mathematical formulas that describe a physical system. |
| mean | A number that typifies a set of data. |
| mean absolute deviation | The average of the absolute deviations. |
| mechanical advantage | The ratio of a machine's output force to the applied input force. |
| mechanical work | The energy associated with applying a force over a distance. |
| median | The middle value of sorted data. |
| memory | A specific part of a computer used solely to store numbers. |
| meter | The base unit of length. |
| mode | The value that appears most frequently in a data set. |
| model | A representation of a real physical system. |
| modulus of elasticity | The ratio of stress to strain. |
| mole | The base unit of the amount of substance; Avogadro's number. |
| molecular mass | The mass of 1 mole of molecules; commonly called molecular weight. |
| molecular weight | The weight of 1 mole of molecules; also called molecular mass. |
| molecules | A group of atoms held together by chemical bonds. |
| mole proportionality law | The volume V and number of moles n are directly proportional provided the pressure and volume are constant.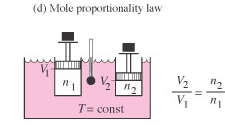 |
| moment | A right-angle force exerted at a distance from a central pivot point. |
| momentum | The mass of an object multiplied by its velocity. |
| monochromatic | Single color. |
| moral issue | An issue that can be resolved only by making a moral decision. |
| moral rights | The "just claims" that belong to all humans, regardless of whether these rights are recognized by government. |
| morals | The accepted standards of right and wrong that are usually applied to personal behavior. |
| moral theories | A framework for making moral and ethical decisions. |
| motivational strategy | A strategy that describes a problem, offers a solution, and motivates the client to act. |
| motor | A device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. |
| mug | A derived unit for mass in the MKS gravitational system; rarely used. |
| multiplicand | The number that is to be multiplied by another. |
| muon | Subatomic particle. |
| Napier's bones | A set of ivory rods used to perform multiplication quickly. |
| neutron | A subatomic particle with no charge. |
| Newton's first law | In the absence of a net force the momentum of an object does not change. |
| Newton's second law | A net force changes the momentum of an object. |
| Newton's third law | The force on one body is equal and opposite to the force on the second body; isolated forces cannot exist. |
| node | Point connecting two or more wires in a circuit. |
| nomenclature | A system of names used in arts and science. |
| nominal group technique | A technique in which a leader poses a problem to a group and each group member then works on the problem and comes up with ideas. The ideas are discussed and then ranked. |
| noncoherent unit system | A unit system in which the numerical part of conversion factors differs from 1. |
| normal distribution | A bell-shaped curve given by Equation 9-12. |
| n-type semiconductor | Semiconductor doped with Group V elements. |
| octal | Base-8 number system. |
| opalescent | A milky iridescence like that of an opal. |
| open system | A system in which mass crosses the boundary. |
| operating system | The fundamental interface through which the user loads instructions on the CPU, routes output to a printer, or saves work for later use. |
| ordinate | The y-axis. |
| osmotic pressure | The pressure required to force the solvent through a semipermeable membrane separating two solutions with different concentrations of solute. |
| parallelepiped | A solid with six parallelogram faces that are parallel to the opposite face. |
| parallel processing | The simultaneous work of multiple computers on a single problem. |
| particle | An object that has mass confined to a single point with no volume. |
| particle accelerator | A machine that accelerates particles to extremely high velocities that approach the speed of light. |
| path quantities | Quantities that depend on path. |
| percentiles | The percentage of data points that are below a particular data point. |
| perfect gas | A hypothetical gas in which the volume of the individual atoms (molecules) is negligible compared to the total volume of the container and there are no forces between the atoms (molecules); also called an ideal gas. |
| perfect gas equation | The relationship between temperature, pressure, volume, and the number of moles of low-density gas; also called the ideal gas equation. |
| perihelion | The point where the Earth is nearest the sun. |
| period | The time it takes to complete 1 revolution. |
| perpetuity | A constant payment occurring at equal time intervals for an infinite length of time. |
| phase diagram | A diagram that indicates the stable phase or state of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. 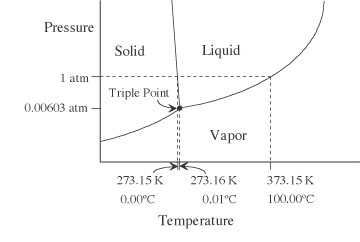 |
| photon | A "packet" of light. |
| photons | Packets of electromagnetic radiation. |
| photovoltaic cell | A device that directly converts light energy into electrical energy. |
| physical model | A physical representation of a complex system. |
| placebo | A pill with no medicine. |
| Planck's constant | 6.6260755 x 10-34 J/s |
| plane angle | In a circle, the length of the swept circumference divided by the radius.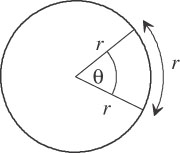 |
| pn junction | Interface of p-type and n-type semiconductors. |
| Poiseuille equation | The equation that describes the laminar flow rate of a viscous fluid through a pipe of a given length and diameter resulting from an applied pressure (Equation 12-8). |
| population | The complete set of individuals, items, or data. |
| position | A place or location within a reference frame. |
| potential energy | Energy associated with position. |
| poundal | A unit of force in the FPS absolute system. |
| power | Energy per unit time. |
| power equation | y - kxm |
| precision | The extent to which the measurement may be repeated and the same answer obtained. |
| preliminary design | The step of the engineering design method where some of the more promising ideas are explored in more detail. |
| pressure | A force exerted on an area. |
| primary battery | A battery that cannot be recharged. |
| primary colors | Red, blue, and green colors from which all other colors are produced. |
| principal | The amount of money borrowed. |
| printed circuit board | An electrically insulating board onto which electrical components are assembled and wired together. |
| problem solving | A process in which an individual or a team applies knowledge, skills, and understanding to achieve a desired outcome in an unfamiliar situation. |
| problem-to-solution strategy | A strategy that describes the problem and offers a variety of solutions. |
| program counter | The storage of the memory location of the next instruction. |
| properties of matter | Descriptions of materials, such as temperature, pressure, specific volume, specific internal energy, and specific enthalpy. |
| proportional limit | The greatest stress that a material will sustain while maintaining a linear relationship between stress and strain. |
| proton | A positively charged subatomic particle. |
| p-type semiconductor | Semiconductor doped with Group III elements. |
| PV flow work | The energy that enters or leaves a system resulting from the volume and pressure of a fluid. |
| Pythagorean theorem | The sum of the squares of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. |
| qualitative model | A non-numerical description of a physical system. |
| quanta | Discrete increment. |
| quantum mechanics | Atomic-scale physics. |
| quincunx | A device in which marbles drop at the top center, contact pegs, and sort into chutes (Figure 9-6). |
| rad | The abbreviation for radian. |
| random error | An error that does not result from a measurement method that is inherently wrong. |
| range | The difference between the largest value (maximum) and the smallest value (minimum). |
| Rankine temperature scale | A thermodynamic temperature scale in which 0°R is defined as absolute zero and the temperature interval is the same as the Fahrenheit scale. |
| rate | The amount of change per unit time. |
| rate processes | Processes where fluxes occur as a result of driving forces. |
| raw data | Data that have not been processed. |
| reactants | Chemical species that are converted into other chemical species. |
| real number | A number that is used to measure continuous quantities. |
| rectifier | A circuit that converts alternating current to direct current. |
| rectilinear graph | A graph in which both axes are linear. |
| reductionism | The ability to logically break a problem into pieces. |
| redundancy | The use of multiple components in which each has the same capabilities. |
| reference frame | A portion of the universe which the observer defines as stationary. |
| regression | Going backward from the data to the equation. |
| relative cumulative frequency | The accumulated sum of the relative frequencies. |
| relative frequency | The number of data points within a given class (frequency) divided by the total number of data points. |
| relativistic transformations | A set of equations that relates the position and time in one reference frame to another reference frame. |
| relativity | Einstein's theory stating that there is no preferred reference frame and that the speed of light in free space is constant regardless of the reference frame. |
| relay | A device in which electrical energy opens or closes a switch. |
| repetition structures | Program structures that can loop as long as a condition is true, but break out of the loop once it is false, or loop a specified number of repetitions. |
| repulsive force | A force that pushes two objects apart. |
| resistance | The driving force divided by the flow rate. |
| resistor | A device that converts electrical energy directly to heat. |
| rest mass | The mass of a stationary object. |
| reversible | A system which, when returned to its original state, does not cause a change in the surroundings. |
| rights analysis | A moral theory that equally respects each human being. |
| rigid body | An idealized object with both mass and dimensions, with the restriction that the components of the object do not move with respect to each other. |
| rounding error | Rounding in intermediate calculations which results in an incorrect final answer. |
| safety factor | The ratio of the minimum load that would cause failure divided by the actual peak load. |
| sample | A set of data drawn from a population that is analyzed to estimate the characteristics of the population. |
| scalar | A quantity completely described by its magnitude; has no direction. |
| scientific notation | Numbers expressed in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10. |
| second | The base unit of time. |
| secondary battery | A battery that can be recharged. |
| second law of thermodynamics | Naturally occurring processes are directional. |
| selection structures | Program structures that have a decision point where a condition is evaluated. |
| semiconductor | Substance through which current flows moderately well. |
| semilog graph | A graph in which one axis is logarithmic and the other is linear. |
| sequential engineering | An approach in which specialists work in a compartmentalized manner. |
| sequential structures | Program structures that perform sequentially. |
| server | A computer that is used for routing communication between multiple computers and is a centralized repository for files and programs. |
| shaft work | Energy from a rotating shaft. |
| shear force | The force that tends to cause atoms of a structure to slide past each other. |
| SI base units | The unit of length (meter), unit of mass (kilogram), unit of time (second), unit of electric current (ampere), unit of thermodynamic temperature (kelvin), unit of amount of substance (mole), and unit of luminous intensity (candela). |
| significant figure | An accurate digit, excluding the zero required to place the decimal point. |
| simple interest | The interest payment is based only on the original principal and not unpaid interest. |
| single-cycle process | A process that causes a system to return to its original state. |
| SI supplementary units | The mathematical definitions needed to define both base and derived units. |
| SI system of units | The metric system. |
| slide rule | A simple device that uses logarithms to perform multiplication and division. |
| slip ring | Rotating component through which electrical contact is made. |
| slope | Rise over run. |
| slug | A derived unit for mass in the USCS gravitational systems; widely used in engineering. |
| software | A collection of instructions that directs computer hardware to perform specific tasks. |
| solenoid | Wire coil. |
| solid angle | In a sphere, the swept area divided by the radius squared.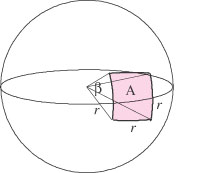 |
| solidus | Oblique stroke: /. |
| space-time coordinates | A coordinate system that describes where and when. |
| spaghetti code | Computer code characterized by many "go to" statements that direct the flow to various parts of the program. |
| spatial strategy | A strategy that describes the component parts of an object. |
| specific heat of combustion | Energy released from combusting a unit quantity of fuel. |
| specific quantities | Quantities formed by dividing an extensive quantity by mass or moles. |
| specific quantity | The amount of something per unit mass. |
| speed | A scalar describing the magnitude of the velocity vector. |
| spring force | The force that results when a spring is compressed or stretched. |
| standard deviation | The square root of the average squared deviation (Equations 9-8 and 9-9). |
| standard normal distribution | The relative frequency given by Equation 9-13. |
| starter | A circuit that vaporizes mercury in a fluorescent light. |
| state | A quantity that is independent of path. |
| state energy | Energy that does not depend on path. |
| state quantities | Quantities that are independent of path. |
| static friction | The bonding between two bodies at rest. |
| statics | The study of forces and moments on stationary objects. |
| statistical inference | To draw conclusions from data. |
| statistical quality control | The use of statistical methods to assess the quality of a product or process. |
| statistics | Scientific methods for collecting, organizing, summarizing, presenting, and analyzing data as well as making conclusions based on the data. |
| steady-state system | A system that does not change with respect to time. |
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | 5.67051 x 10-8 J/(s.m2.K4) |
| stoichiometric | Quantitative relationship that describes the amount of products resulting from the complete conversion of reactants. |
| stone | A unit of weight in Great Britain; equal to 14 pounds. |
| strain | The change in length per unit of original length caused by the application of a force. |
| strong force | A force that acts at very short distances and is responsible for holding atomic nuclei together. |
| structured code | Computer code characterized by statements that are logically organized. |
| supercritical fluid | A gas with liquid-like densities in which the pressure and temperature are above the critical point. |
| superfluid | A fluid with no viscosity that can flow without a pressure difference. |
| surroundings | Everything in the universe except the system. |
| switch | A device that mechanically opens or closes a circuit. |
| synthesis | The act of creatively combining smaller parts to form a coherent whole. |
| system | A subset of the universe we wish to study. |
| systematic error | An error that results from a measurement method that is inherently wrong. |
| technical journal | A publication devoted to a single topic. |
| temperature | A measure of the degree of random atomic motion. |
| temperature interval | The difference between two temperatures. |
| temperature scale | Formed by placing two reference points on the mercury-in-glass thermometer and evenly subdividing the points into temperature intervals. |
| tension force | The force that tends to cause atoms of the structure to separate. |
| test sphere | Charged sphere used to test electric fields. |
| thermal conductivity | The proportionality constant that describes the ability of heat to flow through a material. |
| thermionic effect | The phenomenon that allows electrons to be emitted from a high-temperature surface. |
| thermodynamics | The science that describes what is possible and what is impossible during energy conversion processes. |
| thermodynamic temperature scales | Temperature scale that is linearly proportional to the thermal energy of an ideal gas; also called absolute temperature scales. |
| thermoelectric cooler | A heat pump that is powered by electrical energy, without moving parts. |
| thermoelectric generator | A device that converts thermal energy directly to electrical energy. |
| thermoscope | A device used by Galileo to measure temperature. |
| time dilation | The observation that time slows as speed increases. |
| torque | A vector quantity that describes a twisting force. |
| transcendental functions | Mathematical functions represented by an infinite series. |
| transformer | A device that increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current. |
| transistor | A solid-state amplifier. |
| triple point | Condition where liquid, solid, and vapor are in equilibrium. |
| ulitarianism | A moral theory that seeks to create the most good for the most people. |
| ultimate strength | The highest stress obtained prior to failure. |
| uncertainty | The result from random errors and describes the lack of precision. |
| unit | A quantity used as a standard of measurement. |
| universal accounting equation | Final amount - initial amount = input - output + generation - consumption |
| universal gas constant | The proportionality constant in the perfect gas equation. |
| unsteady-state system | A system that changes with respect to time. |
| valence electrons | Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. |
| van der Waals equation | An equation used to calculate the compressibility factor Z. |
| vaporization | The change of liquid to vapor. |
| vapor pressure | The pressure of the vapor in equilibrium with the liquid or the solid. |
| variance | The standard deviation squared (Equation 9-10). |
| vector | A quantity with a magnitude and a direction. |
| velocity | A vector describing the time rate of change for the position of a body. |
| velocity magnitude | The magnitude of the velocity vector. |
| virtual storage | A programming technique in which programs and data are swapped out of active memory into peripheral storage devices. |
| viscosity | A measure of the "thickness" of a fluid. |
| voltage | Work required to move a test sphere toward a charge, expressed per unit of charge on the test sphere. |
| volumetric energy density | The total amount of energy that can be stored in a given volume. |
| vulcanized | To improve the strength and resiliency of a polymer such as rubber or plastic by combining it with sulfur (or some other type of agent). |
| weak force | A force involved in radioactive decay. |
| whistle blowing | The act of informing authorities of harmful, dangerous, or illegal activities. |
| word charts | A chart that conveys information using short phrases or single words. |
| work | The energy flow across a system boundary resulting from any driving force other than temperature. |
| yield strength | The intersection of the stress-strain curve and a line that passes through 0.002 strain and is parallel to the linear portion of the stress-strain curve. |