 |
| 1 |  | 
Explain why the walls of the ventricles are thicker than the walls of the atria. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
In most tissues, peak blood flow occurs during systole and decreases during diastole. In heart tissue, however, the opposite is true, and peak blood flow occurs during diastole. Explain why this difference occurs. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
A patient has tachycardia. Would you recommend a drug that prolongs or shortens the plateau of cardiac muscle cell action potentials? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Endurance-trained athletes often have a decreased heart rate compared to that of a nonathlete when both are resting. Explain why an endurance-trained athlete's heart rate decreases rather than increases. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
A doctor lets you listen to a patient's heart with a stethoscope at the same time that you feel the patient's pulse. Once in a while you hear two heartbeats very close together, but you feel only one pulse beat. Later, the doctor tells you that the patient has an ectopic focus in the right atrium. Explain why you hear two heartbeats very close together. The doctor also tells you that the patient exhibits a pulse deficit (i.e., the number of pulse beats felt is fewer than the number of heartbeats heard). Explain why a pulse deficit occurs. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Heart rate and cardiac output were measured in a group of nonathletic students. After 2 months of aerobic exercise training, their measurements were repeated. It was found that heart rate had decreased, but cardiac output remained the same for many activities. Explain these findings. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Explain why it's sufficient to replace the ventricles, but not the atria, in artificial heart transplantation. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
During an experiment in a physiology laboratory, a student named Cee Saw was placed on a table that could be tilted. The instructor asked the students to predict what would happen to Cee Saw's heart rate if the table were tilted so that her head was lower than her feet. Some students predicted an increase in heart rate, and others claimed it would decrease. Can you explain why both predictions might be true? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
After Cee Saw is tilted so that her head is lower than her feet for a few minutes, the regulatory mechanisms that control blood pressure adjust so that the heart pumps sufficient blood to supply the needs of her tissues. If she is then tilted so that her head is higher than her feet, gravity causes blood to flow toward her feet, and the blood pressure in the carotid sinus and aortic arch decreases. The decrease in blood pressure is detected by the baroreceptors in these vessels and activates baroreceptor reflexes. The result is increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart and an increase in the heart rate. The increased heart rate functions to increase the blood pressure to its normal value. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
A friend tells you that her son had an ECG and it revealed that he has a slight heart murmur. Should you be convinced that he has a heart murmur? Explain. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Predict the effect of an incompetent aortic semilunar valve on stroke volume, the volume of blood in the left ventricle at the end of diastole, and on heart sounds? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
An experiment on a dog was performed in which the mean arterial blood pressure was monitored before and after the common carotid arteries were partially clamped (at time A). The results are graphed below:
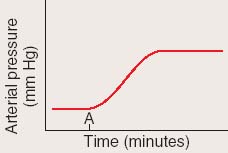 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234434/eq_ch20_q12_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234434/eq_ch20_q12_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a>
Explain the change in mean arterial blood pressure.
|
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
During hemorrhagic shock (caused by loss of blood) the blood pressure may fall dramatically, although the heart rate is elevated. Explain why the blood pressure falls despite the increase in heart rate. |
|  | |
|
|

