 |
| 1 |  | 
Which compound is being reduced in this reaction?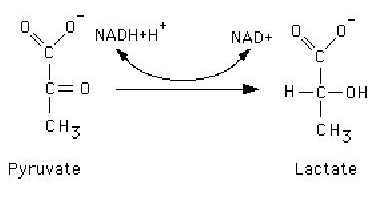 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Pyruvate |
|  | B) | Lactate |
|  | C) | NAD+ |
|  | D) | NADH+H+ |
|  | E) | Not enough information to tell |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which compound is being oxidized in this reaction?? <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Pyruvate |
|  | B) | Lactate |
|  | C) | NAD+ |
|  | D) | NADH+H+ |
|  | E) | Not enough information to tell |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following is/are true about enzymes
I. All enzymes are proteins.
II. All proteins are enzymes. |
|  | A) | I only is true. |
|  | B) | II only is true. |
|  | C) | Both I and II are true. |
|  | D) | Neither I nor II are true. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
If the Keq for an enzymatic reaction is greater than 1,
I. the reaction will be endergonic.
II. the reaction cannot occur without the input of energy. |
|  | A) | I only is true. |
|  | B) | II only is true. |
|  | C) | Both I and II are true. |
|  | D) | Neither I nor II are true. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
A complex enzyme is broken down into its constituent parts: apoenzyme and cofactor. Portions of the separate parts are heated for 3 minutes at 100°C. Various combinations are tested for their ability to perform the enzymatic function. Which of the following combinations would still be functional? |
|  | A) | Unheated apoenzyme and heated cofactor |
|  | B) | Heated apoenzyme and heated cofactor |
|  | C) | Unheated apoenzyme and unheated cofactor |
|  | D) | Heated apoenzyme and unheated cofactor |
|  | E) | More than one of the above combinations would function. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
An enzyme that is always produced, regardless of the presence of substrates or the end products, is called |
|  | A) | a constitutive enzyme. |
|  | B) | an isoenzyme. |
|  | C) | a repressible enzyme. |
|  | D) | an allosteric enzyme. |
|  | E) | a regulator enzyme. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
About 7.3 kcal/mole are released when |
|  | A) | NAD+ is reduced to NADH. |
|  | B) | ATP hydrolysis is coupled to sucrose synthesis. |
|  | C) | the terminal phosphate bond of ATP is broken by hydrolysis. |
|  | D) | a phosphoester bond of ATP is formed. |
|  | E) | glucose is converted to CO2 and H2O. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
In the following reaction, which component is being reduced?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy |
|  | A) | C6H12O6 |
|  | B) | O2 |
|  | C) | CO2 |
|  | D) | H2O |
|  | E) | energy |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
In the following reaction, which component is being oxidized?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy |
|  | A) | C6H12O6 |
|  | B) | O2 |
|  | C) | CO2 |
|  | D) | H2O |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Adenosine triphosphate is a type of |
|  | A) | fatty acid. |
|  | B) | amino acid. |
|  | C) | enzyme. |
|  | D) | steroid. |
|  | E) | nucleotide. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
A substrate binds to its enzyme at a location called the ______ site. |
|  | A) | coenzyme |
|  | B) | substrate |
|  | C) | active |
|  | D) | polypeptide |
|  | E) | cofactor |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The vitamin niacin is part of the ______ molecule. |
|  | A) | ferredoxin |
|  | B) | iron-sulfur |
|  | C) | pyridoxal phosphate |
|  | D) | pyrophosphate |
|  | E) | NAD+ |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Denaturation of an enzyme refers to the |
|  | A) | proper arrangement of the enzyme in a metabolic pathway. |
|  | B) | improper arrangement of the enzyme in a metabolic pathway. |
|  | C) | loss of the enzyme's proper shape. |
|  | D) | formation of the enzyme's proper shape. |
|  | E) | formation of a new isozyme for that enzyme. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
ATP is required to do |
|  | A) | chemical work. |
|  | B) | transport work. |
|  | C) | mechanical work. |
|  | D) | all of the above types of work. |
|  | E) | none of the above, another compound provides the necessary energy. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
The ability of Vibrio fischeri to convert chemical energy directly into radiant energy in bioluminescence is an example of __?___ at work. |
|  | A) | Shelford's law of tolerance |
|  | B) | Leibig's law of the minimum |
|  | C) | the first law of thermodynamics |
|  | D) | Heisenberg's principle of uncertainty |
|  | E) | the third law of thermodynamics |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
An exergonic reaction is one that |
|  | A) | requires energy in order to proceed. |
|  | B) | releases energy for work. |
|  | C) | gives off much heat. |
|  | D) | wastes energy. |
|  | E) | none of the above, there is no such thing as an exergonic reaction. |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
An endergonic reaction is one that |
|  | A) | requires energy in order to proceed. |
|  | B) | releases energy for work. |
|  | C) | gives off much heat. |
|  | D) | wastes energy |
|  | E) | none of the above, there is no such thing as an endergonic reaction. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
The reaction A + B -------> AB takes place slowly at 20°C unless either compound X or Y is present. Compound X is a metallic catalyst for the reaction and Y is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction. Ten ml of solution A and B is placed in each of four test tubes to which varying amounts of X or Y are added as follows.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q02.jpg','popWin', 'width=385,height=129,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q02.jpg','popWin', 'width=385,height=129,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a>
If A and B are heat stable at 100°C and the reaction occurs at that temperature, the reaction is probably |
|  | A) | greatest in tube I. |
|  | B) | greatest ln tube II. |
|  | C) | greatest in tube III. |
|  | D) | greatest in tube IV. |
|  | E) | equal in all tubes. |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
The vitamin riboflavin is part of the ______ molecule. |
|  | A) | ferredoxin |
|  | B) | FAD |
|  | C) | pyridoxal phosphate |
|  | D) | pyrophosphate |
|  | E) | NAD+ |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Hydrogen and oxygen release enormous amounts of energy when they react -- witness the Hindenberg explosion. Yet, hydrogen and oxygen can be mixed together in a balloon and nothing will happen. Why? |
|  | A) | Competitive inhibitors are blocking the reaction from occurring in the active site. |
|  | B) | There must be contaminating elements in the balloon that prohibit the reaction from occurring. |
|  | C) | The energy of activation to form the transition-state complex is too high to allow the reaction to occur without assistance. |
|  | D) | The person mixing the oxygen and hydrogen in the balloon must have done something wrong. |
|  | E) | The transition-state complex has too low an energy barrier. |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
The fact that beta-oxidation (breakdown) of fatty acids occurs in the mitochondria whereas fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix is an example of regulation of enzymatic activity by the __?__ mechanism. |
|  | A) | compartmentation |
|  | B) | induction |
|  | C) | repression |
|  | D) | competitive inhibition |
|  | E) | non-competitive inhibition |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
Compare the entities I and II
I. The affinity of an enzyme for its substrate when the enzyme has a Km of 0.50M.
II. The affinity of an enzyme for its substrate when the enzyme has a Km of 0.05M. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | II is greater than I. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
Compare the entities I and II
I. The ability of a competitive inhibitor to bind to an active site in an allosterically controlled enzyme.
II. The ability of a non-competitive inhibitor to bind to an active site in the same allosterically controlled enzyme. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | II is greater than I. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
Compare the entities I and II
I. The ability of NADH+H+ to be reduced.
II. The ability of NAD+ to be reduced. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | II is greater than I. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
Compare the entities I and II
I. The ability of FADH to be oxidized.
II. The ability of FAD to be oxidized. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | II is greater than I. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
Compare the entities I and II
I. The Vmax of an enzyme without a competitive inhibitor
II. The Vmax of an enzyme with a competitive inhibitor |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | II is greater than I. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
To a living organism, which of the following has the greatest amount of available energy per molecule? |
|  | A) | ATP |
|  | B) | ADP |
|  | C) | AMP |
|  | D) | H2O |
|  | E) | CO2 |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
The reaction A + B -------> AB takes place slowly at 20°C unless either compound X or Y is present. Compound X is a metallic catalyst for the reaction and Y is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction. Ten ml of solution A and B is placed in each of four test tubes to which varying amounts of X or Y are added as follows.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q02.jpg','popWin', 'width=385,height=129,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20543/quiz08q02.jpg','popWin', 'width=385,height=129,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a>
If A and B are heat stable at 20°C and the reaction occurs at that temperature, the reaction is probably |
|  | A) | greatest in tube I. |
|  | B) | greatest ln tube II. |
|  | C) | greatest in tube III. |
|  | D) | greatest in tube IV. |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
Which of the following is the best evidence for the lock and key theory of enzyme action? |
|  | A) | All isolated enzymes have been identified as proteins. |
|  | B) | Compounds similar in structure to the substrate inhibit enzyme activity. |
|  | C) | Enzymes are found in living organisms and speed up certain reactions. |
|  | D) | Enzymes speed up reactions by definite amounts. |
|  | E) | Enzymes determine the direction of a reaction. |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
The ability of CTP to bind to aspartate carbamoyltransferase and shut down the synthesis of more CTP is an example of |
|  | A) | enzyme induction. |
|  | B) | enzyme repression. |
|  | C) | feedback inhibition of enzyme activity. |
|  | D) | channeling. |
|  | E) | compartmentation. |
|
|

