 |
1 |  | 
NMR relies on? |
|  | A) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds. |
|  | B) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds in conjugated p systems. |
|  | C) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of any atom. |
|  | D) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms. |
|  | E) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms, exciting their spin state. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
Which of the following statements about shielding is false? |
|  | A) | shielding is an increased effect of the external magnetic field due to the induced magnetic field in the molecule. |
|  | B) | shielding is a decreased effect of the external magnetic field due to the induced magnetic field in the molecule. |
|  | C) | shielding determines the chemical shift of the atom. |
|  | D) | the standard reference for measuring shielding effects is TMS. |
|  | E) | deshielding shifts the signal or peak downfield |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Electronegative atoms? |
|  | A) | shield adjacent protons shifting the peak upfield. |
|  | B) | deshield adjacent protons shifting the peak downfield. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Alkenes and arenes protons are? |
|  | A) | shielded due to the induced magnetic field of the p electrons. |
|  | B) | deshielded due to the induced magnetic field of the p electrons. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
Which of the following statements about proton NMR is false? |
|  | A) | the number of peaks indicates the number of hydrogen atoms. |
|  | B) | the multiplicity (or splitting pattern) indicates the number of vicinal protons. |
|  | C) | the chemical shift indicates the local chemical environment (i.e. the presence of electronegative atoms and/or p bonds). |
|  | D) | the intensity, or area, of the peak indicates the number of each type of proton. |
|  | E) | the number of peaks indicates the number of chemically distinct protons. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
Which statement about spin-spin coupling is false? |
|  | A) | spin-spin coupling occurs between vicinal protons. |
|  | B) | spin-spin coupling results in a peak being split in n+1 peaks (where n is the number of vicinal protons). |
|  | C) | the coupling constant, J, is the separation between peaks that are split by spin-spin coupling. |
|  | D) | spin-spin coupling is observable for protons separated by 4 bonds. |
|  | E) | protons that have the same chemical shift do not split each other's signals. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
Groups of peaks can indicate specific functional groups.
What would a quartet at 3.5 ppm and a triplet at 1.8 ppm indicate? |
|  | A) | a -CH(CH3)2 group. |
|  | B) | a -CH2CH3 group. |
|  | C) | a -C(CH3)3 group. |
|  | D) | a -CH2CH2CH3 group. |
|  | E) | a -O-CH2CH3 group. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Acidic protons (those on acids, alcohols, and amines) do or do not couple with their vicinal protons? |
|  | A) | they do not. |
|  | B) | they do. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
The chemical shifts (in ppm) for 13C-NMR for the following types of carbon atoms are?
alcohol, alkene, arene, acid, aldehyde |
|  | A) | 50-65, 100-150, 110-175, 160-185, 190-220. |
|  | B) | 220-190, 160-185, 110-175, 100-150, 50-65. |
|  | C) | 100-150, 50-65, 160-185, 110-175, 190-220. |
|  | D) | 100-150, 50-65, 110-175, 160-185, 190-220. |
|  | E) | 50-65, 100-150, 160-185, 110-175, 190-220. |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
In the following 13C-NMR the peak at 168 ppm is?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane carbon. |
|  | B) | a carbon attached to an electronegative atom. |
|  | C) | an sp2 hybridized carbon. |
|  | D) | an aromatic carbon. |
|  | E) | a carbonyl carbon in an acid or ester. |
|  | F) | a carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde or ketone. |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
In the following 13C-NMR the peak at 60 ppm is?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane carbon. |
|  | B) | b. a carbon attached to an electronegative atom. |
|  | C) | an sp2 hybridized carbon. |
|  | D) | an aromatic carbon. |
|  | E) | a carbonyl carbon in an acid or ester. |
|  | F) | a carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde or ketone. |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
In the following 13C-NMR the peaks at 130 ppm are?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane carbon. |
|  | B) | a carbon attached to an electronegative atom. |
|  | C) | an sp2 hybridized carbon. |
|  | D) | an aromatic carbon. |
|  | E) | a carbonyl carbon in an acid or ester. |
|  | F) | a carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde or ketone. |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
In the following 13C-NMR the peaks taken together suggest this compound is an...?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_1013.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (36.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane. |
|  | B) | an alkene. |
|  | C) | an aromatic ether. |
|  | D) | an aromatic ester. |
|  | E) | an aromatic ketone. |
|  | F) | an aromatic aldehyde. |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
In the following decoupled 1H-NMR there are how many unique types of H atoms?
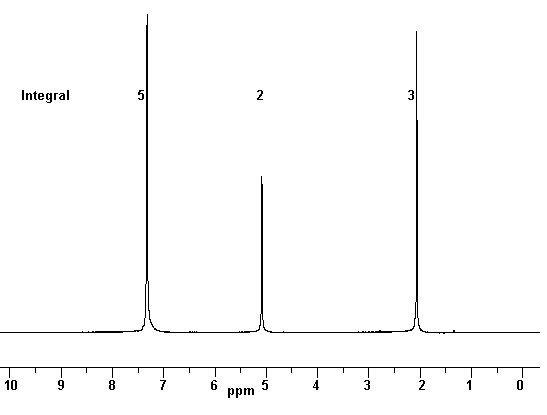 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_14.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_14.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 1 |
|  | B) | 2 |
|  | C) | 3 |
|  | D) | 4 |
|  | E) | 5 |
|  | F) | 6 |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
In the following 1H-NMR the peak at 12 ppm suggest what functional group?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_15.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (38.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_15.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (38.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an aldehyde. |
|  | B) | an acid. |
|  | C) | an ether. |
|  | D) | an alkyl halide. |
|  | E) | an alcohol. |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
In the following 1H-NMR the peaks at 7 - 8 ppm suggest what functional group?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_16.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_16.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | a monosubstituted aromatic ring. |
|  | B) | an ortho-disubstituted aromatic ring. |
|  | C) | an meta-disubstituted aromatic ring. |
|  | D) | an para-disubstituted aromatic ring. |
|  | E) | an ortho-trisubstituted aromatic ring. |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
IR spectroscopy relies on?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_17.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (30.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_17.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (30.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds. |
|  | B) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds in conjugated p systems. |
|  | C) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of any atom. |
|  | D) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms. |
|  | E) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms, exciting their spin state. |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
Combinations of peaks in the IR can give indications of what functional group is present. What functional group would correspond to the following combination of peaks?
3500 cm-1 (w) and 1690 cm-1 (s) (w = weak, s = strong) |
|  | A) | an acid. |
|  | B) | an ester. |
|  | C) | an amine. |
|  | D) | an amide. |
|  | E) | an ether. |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
Combinations of peaks in the IR can give indications of what functional group is present. What functional group would correspond to the following combination of peaks?
3300 cm-1 (s,b) and 1650 cm-1 (s) (b = broad, s = strong) |
|  | A) | a phenol. |
|  | B) | an ester. |
|  | C) | an amide. |
|  | D) | an amine. |
|  | E) | an ether. |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
The following IR is of an?
IMAGE |
|  | A) | an alkane. |
|  | B) | an alkene. |
|  | C) | an alcohol. |
|  | D) | an acid. |
|  | E) | an ester. |
|  | F) | an aromatic ester. |
 |
 |
21 |  | 
The following IR is of an?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_21.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (48.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_21.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (48.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane. |
|  | B) | an alkene. |
|  | C) | an alcohol. |
|  | D) | an acid. |
|  | E) | an ester. |
|  | F) | an aromatic ester. |
 |
 |
22 |  | 
The following IR is of an?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_22.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (47.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_22.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (47.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane. |
|  | B) | an alkene. |
|  | C) | an alcohol. |
|  | D) | an acid. |
|  | E) | an ester. |
|  | F) | an aromatic ester. |
 |
 |
23 |  | 
The following IR is of an?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_23.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072828374/211137/13_23.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | an alkane. |
|  | B) | an alkene. |
|  | C) | an alcohol. |
|  | D) | an acid. |
|  | E) | an ester. |
|  | F) | an aromatic ester. |
 |
 |
24 |  | 
UV spectroscopy relies on? |
|  | A) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds. |
|  | B) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds in conjugated p systems. |
|  | C) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of any atom. |
|  | D) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms. |
|  | E) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms, exciting their spin state. |
 |
 |
25 |  | 
UV light excites? |
|  | A) | vibrational motions of atoms. |
|  | B) | nuclear spin states. |
|  | C) | core electrons to excited states. |
|  | D) | valence electrons to excited states. |
|  | E) | p electrons to the LUMO. |
 |
 |
26 |  | 
Which statement is incorrect about the wavelength of UV light and the size of the conjugated system? |
|  | A) | the electron excitation is a p to p* transition. |
|  | B) | lmax shifts by about 36 nm for each additional double bond in the p system. |
|  | C) | the conjugated system that is responsible for absorbing UV light is referred to as a chromophore. |
|  | D) | longer conjugated systems absorb light at longer wavelengths. |
|  | E) | longer conjugated systems absorb light at shorter wavelengths. |
 |
 |
27 |  | 
The absorbency of UV light is related to concentration via? |
|  | A) | Markovnikov's rule. |
|  | B) | Zaitsev's rule. |
|  | C) | Newton's third Law. |
|  | D) | Beer's Law. |
|  | E) | Planck's constant. |
 |
 |
28 |  | 
The correct form for Beer's law is? |
|  | A) | e = cl / A. |
|  | B) | e = Al / c. |
|  | C) | e = A / cl. |
|  | D) | A = cl / e. |
|  | E) | A = e / cl. |
 |
 |
29 |  | 
MS relies on? |
|  | A) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds. |
|  | B) | the absorption of energy by chemical bonds in conjugated p systems. |
|  | C) | the production of a radical cation. |
|  | D) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms. |
|  | E) | the absorption of energy by the nucleus of some atoms, exciting their spin state. |
 |
 |
30 |  | 
The molecular ion peak in MS is? |
|  | A) | the M+ peak. |
|  | B) | the peak with the largest relative intensity. |
|  | C) | the M+2 peak. |
|  | D) | the M+4 peak. |
|  | E) | the peak with the greatest mass to charge ratio (m/z). |
 |
 |
31 |  | 
A MS with M+ and M+2 peaks with a ratio of 1:0.3 contains? |
|  | A) | carbon isotopes. |
|  | B) | one Cl atom. |
|  | C) | two Cl atoms. |
|  | D) | one Br atom. |
|  | E) | two Br atoms. |
 |
 |
32 |  | 
A MS with M+, M+2, and M+4 peaks with a ratio of 1:2:1 contains? |
|  | A) | carbon isotopes. |
|  | B) | one Cl atom. |
|  | C) | two Cl atoms. |
|  | D) | one Br atom. |
|  | E) | two Br atoms. |
 |
 |
33 |  | 
The MS can be used to determine all of the following except? |
|  | A) | indicate the presence of isotopes. |
|  | B) | structural features of the compound. |
|  | C) | the exact structure of the compound. |
|  | D) | the molecular formula. |
|  | E) | the molecular weight. |
 |
 |
34 |  | 
The index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) is used to? |
|  | A) | indicate the presence of isotopes. |
|  | B) | determine possible structural features in the molecule. |
|  | C) | determine the exact structure of the compound. |
|  | D) | determine the molecular formula. |
|  | E) | determine the molecular weight. |
 |

