(See related pages)
LIFE-LONG LEARNING MODULE DWhat's Happening in Your World Today? It's amazing how fast "new" technology becomes commonplace. It wasn't very long ago that cell phones were unheard of and DVDs were just a distant dream. Now both are part of the fabric of our lives. There are many such inventions either on the drawing board or in the early stages of production that will become an integral part of our existence in the near future. Computers are no longer gadgets that tie us to a desk. We can move around all over the world with them and soon we'll even wear them in our clothing. We already wear watches that are much more than time pieces and we can get gizmos that will tell us whether someone is lying to us or not. With their escape from the desktop to the world outside, computers have become more sturdy, able to take weather and severe treatment that they never could in the past. As part of the go-anywhere computer trend, computers are becoming truly ubiquitous, showing up in hallways and malls in the form of Web stations. In the home we can have smart refrigerators and photo frames. Appliances and even decorative frames are fulfilling their respective roles in ways only dreamt of before now. Computer games, once available only in video arcades have come to our phones and PDAs. Not only that, but we can play with thousands, even hundreds of thousands of people we may never have met. Little mechanical and cuddly toys now incorporate robots that create a whole new world of adventure and opportunity for creativity. Virtual reality enables us to interact with the computer beyond the keyboard and screen. We can actually experience the virtual world inside the computer. We can go there to have fun or to practice surgery or flying airplanes. As part of this environment, we will shortly be able to truly feel objects in the virtual world as though they were real through haptic feedback. New technology is improving the quality of our lives in other ways giving doctors the ability to look inside us without first cutting us open. It's allowing medical staff to learn the correct procedures to take during an emergency. It's helping the blind to see and the deaf to communicate. If we didn't know better we might think that we're living in a wondrous magical kingdom. You can read more about these topics by just clicking on the links below:
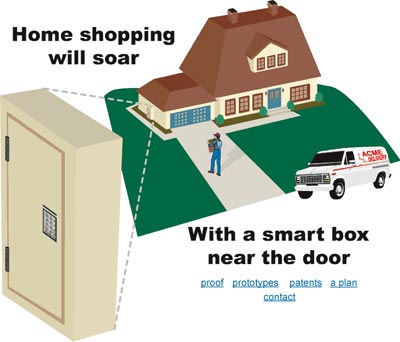
Portable and Wearable Computing The trend in computing, for decades now, has been more power packed into smaller and more diverse places. Cars are being sold with various microprocessors controlling everything from headlights to cruise control. Look around your home. You'll no doubt see the effects of the computer age everywhere, in your phone, answering machine, microwave, entertainment system, watch, and perhaps your lighting system and garage doors. Apart from the usual portable computer gadgets like phones and PDAs, there are other more novel accessories. For example, you can get an alarm system that attaches to a child and alerts you if the child moves beyond a pre-specified distance from you. In light of all these new gadgets, it's small wonder that computers have now made it to your clothes. In the future we will see jackets that adjust the temperature according to the weather, keeping us cool in summer and warm in winter. Wearable Computers Would you like to have a computerized jacket? If so, you might be interested in the Burton Amp jacket, "the world's first electronic jacket with an integrated Apple iPod." Using the same type of technology, you'll soon be able to get a jacket that will have ribbons and textile cable that will carry audio signals to your ear so that you can operate a cell phone from your jacket sleeve. If headgear incorporating a screen in front of your eyes, called a video headset, is more your style, you have several types to choose from. You can get glasses for gaming, 3-D movies, and so on. Another type is designed for creating virtual reality environments to let people see more at trade shows, to distract patients who are undergoing lengthy procedures, or to watch movies. Having a tiny screen inches from your eye feels like you're watching a 50-ft screen. See MobileMag, GT Wearables, and Wearable Internet Resources for more information. Wrist watches are closer to wearable computers nowadays than to the simple time pieces of yesterday. Today's watches incorporate phone books, voice dialing, calendars, SMS (smart messaging service), personal data storage, and GPS systems. Check out Samsung's GPRS writswatch and Casio's Color Wrist Camera watch for examples of what's available. Portable Lie Detectors Would you like to be able to tell is someone is lying to you? If so, you're not alone. Insurance companies, for example, could save a lot of money if they could tell early on which claims are fraudulent. The Digilog company offers insurance companies a system that incorporates the Israeli-based Makh-Shevet software Truster that detects, from "microtremors" in the voice, whether someone is lying or not. If you'd like to have that capability, you can get a portable gizmo called Handy Truster for under $25. Internet and Household Appliances Why shouldn't our information appliances and our traditional household appliances merge to improve our lives? That's the question that manufacturers of traditional household machines of various kinds are asking. Even the manufacturers of objects, like photo frames, that didn't used to be gadgets, are included. The answer seems to be that there's no reason they can't. Computers are even playing an increasingly significant role in physical protection of our belongings. Sophisticated security systems that, heretofore, were only possible for those with a lot of money, are now available to the rest of us. We can install cameras and connect them to the Internet so that we can see, from anywhere on earth, what's going on at home. We can track our packages as they travel to us and keep them protected if they arrive before we do. SmartBox Lock Box A SmartBox is a way of making sure that anything delivered to your home is safe until you arrive. A delivery person arriving with a package for you must have the right code to open the SmartBox and deposit your package. With the package inside and the box locked again your package is safe from inclement weather and unwanted attention from others until you get home. At SmartBox's Web site, you can look at the prototype, diagrams (including the one below), and photos.
Rugged Computers Not everyone uses computers in climate-controlled comfortable rooms. Some computers must be used under difficult conditions where there's torrential rain or a sand storm. There are computers built precisely for these types of conditions, which are used primarily by the military and in industrial settings. Miltope is a company that builds computers that stand up to punishing conditions. The company has notebook computers, for example, that stand up to rain, sand, salt fog, and fungus, and will survive being dropped from a height of several feet. Terralogic is another company that sells tough computers to the police, military and government agencies. Along with computers this company has PDAs and tablet-PCs that stand up to heavy rain, along with hard disks that are shock resistant and are protected from damage due to dust and humidity. Smart Refrigerators You may not yet be able to buy a refrigerator that reorders milk and eggs when you run out, but refrigerators are already on the market that do more than keep food cold. Electrolux, a Swedish company, has announced its MMX Fridge that allows owners with cell phones with MMS (multimedia messaging service) remotely snap a picture of their fridge's interior. This would allow you to "have a look" in your refrigerator when you're in the grocery store. Two other companies that have smart refrigerators are LG Electronics and Samsung. Samsung's smart refrigerator costs more than $6,000, but for that price it will detect the shelf life of your food and inform you about anything past it use-by date. It also displays on the door a list of items stored in the fridge. LG Electronics' Internet Refrigerator has an LCD touchscreen display embedded into the door for high-speed Internet surfing and shopping. Here you can check e-mail, download files, or watch TV. A remote control makes the process even easier. You can also leave video messages for other household members, get a list of what's in the fridge, store nutritional information, and consult an electronic calendar. Smart Photo Frames If you watch Oprah, you may have seen her segment on My Favorite Things. In that list is a smart photo frame that changes photos every day. The one from Ceiva can display up to 20 photos at a time either in single-view or slide-show format. The viewing area is about 5 inches by 7 inches. You need to setup the system at Ceiva's Web site. You can lock, delete, upload, or send photos and adjust the settings. Then, every night, you get a new set of photos to view the next day. Web Stations Web stations are stand-up computers that you use to check e-mail and surf the Web. They don't usually have MS Office or other application software. You often see such Web stations scattered around university campuses. They're used by students to make a quick check of e-mail between classes or quickly check a Web site. Companies such as StreetSpace are designing durable, rugged Web stations that will withstand vandals and weather for the commercial market (see a picture of this model below). These would be in malls and in coffee shops. StreetSpace's Web station has a drink tray so that you can drink while you surf. It also has stereo headphones in case you get a singing e-mail.
Web-Based Building Security Systems If you'd like to be able to check in at home while you're away, you might want to look into Web-based security systems like the one from Panasonic that lets you set up several cameras that are trained on various parts of your home and yard. Then you can just get onto the Web with your notebook computer, PDA or cell phone, and switch between camera views to see what's going on. As well as being able to watch your home from afar, you can also turn on the lights, adjust the climate controls, or change the pictures in your smart photo frame. If you have a second home or a cottage by the lake, this is an ideal system, since it allows you to prepare ahead of your arrival. For more information see the Custom Retailer and many other Web sites. Some people use their cell phones more to play games than to talk. Games are also one of the popular features on PDAs. Many more are hobby gamers who use their computers or specialized systems to play. Perhaps you'd prefer your entertainment system separate from items you use for work. In that case, you can choose from a variety of gaming consoles that play games, CD music, and DVD movies. If you'd rather take your entertainment on the go. Handheld gaming systems and MP3 players might be a good choice for you. In case you're looking for other forms of technology entertainment, we've listed cool "techno-gadgets" as well. On the Web you can find information on items such as Sony's AIBO, programmable AI bugs, and remote control devices that you don't really need but are fun to play with. Computer Games Computer games are big business. Every week new games are introduced so there's no way we can keep you informed on all the new games out there. But we can point you to where you can get information you need. Here are some valuable Web sites to keep you informed about new games. While you're at the Web sites above, read game reviews to find out what other "gamers" are saying. You can also check out these game review sites: Games can be expensive. New games can cost $50 or more. We'd recommend trying demos or shareware versions of games before deciding if you want to buy them. Here are some hyperlinks to check for games: Web Games Many of the newer games have a multiplayer feature. This means that you can play with other people who have the game over the Internet. Games like Battlefield 1942, Unreal Tournament, Return to Wofenstein, and old favorites like Quake III, Counterstrike, and Tribes 2 allow you to work with other people to accomplish goals. But there are thousands of games that don't require anything more than a Web browser and an Internet connection for you to compete with people from around the world. Web gaming sites are popular because you can play a quick game of chess, pool, or even Monopoly when you have a few spare minutes (and even when you don't). Some Web sites such as Yahoo! have an extensive collection of games in categories such as Board Games, Card Games, and Fantasy Sports games. Most of these sites only require you to register to play. In addition to Yahoo!, here are some Web gaming sites to check out: Game mods (modifications) are becoming hot. Many of them completely overhaul the original game into something totally new. Urban Terror is one such mod in the Quake III arena. Below are some sites that offer game mods. Many games sites also offer patches and charge a small monthly subscription fee for this service. PDA and Cell Phone Games Of course, you don't need a computer to play games anymore. You can find games designed for your PDA. Make sure to check the available memory and operating system of your PDA before downloading any of the games below. You need to make sure your PDA can run the game you select and install. If you have a Java-enabled cell phone you can play games on it. Some popular ones are Zodiac and N-Gage. Of course, the screen size, resolution, and small keys limit what games you can play, but engineers are working on solving these problems:
Gaming Computers Many people who play games, or gamers, have computers that can handle the intense multimedia and processing requirements of today's newer games. These high-end computers, called "gaming rigs", incorporate hardware that makes your system a true multimedia powerhouse. Large monitors, "tons" of RAM, dual processors, and high-end sound systems are standard fare. While some people build these computer systems from scratch, there are companies that will build one for you. Here are a few of them: Even though your computer might not be similar to one of the ones listed above, that doesn't mean you can't play games. Here are the minimum requirements for a basic gaming rig:
Video and Sound Cards Many gamers believe that video cards and RAM, in that order, are the most important features. The two leaders in video cards are Nvidia and ATI. A fast hard disk — 7,200 rpm would be good — is also crucial. For really great sound, as always, you need good equipment. To start with, you'll need a good sound card. For example, Creative Labs and Terratec are companies that make good sound cards. Next on the list is a good set of speakers – preferably surround sound. For games and movies check out Logitech, and for something with high-end sound for music try Behringer. Other Gaming Hardware Some gaming systems are as powerful as multipurpose computers. For example, the XBox contains hardware of a computer including a CPU, 20 GB hard drive and networking capabilities in the form of an Ethernet port that allows 2 XBoxes to be networked together with a router or hub, allowing 16 people to play the game simultaneously. With Xbox Live, you can network 2 or more XBoxes together via the Internet so that you can play with others around the globe. You can also use your Xbox as a DVD or CD player, so that you can have background music while you play. You don't need a computer to play intense video games. Since the days of Atari gaming consoles have been a big part of the gaming scene. Consoles give big bang for the buck because they use specialized hardware for 3-D graphics processing. Modestly priced consoles are sometimes even comparable to expensive PCs. Today's newer consoles allow you to play intense video games, listen to music CDs, and watch DVD movies. We've included hyperlinks to the newest gaming consoles. Even though the games come on CDs, these won't work in your computer. They are designed for specific gaming consoles. For example, a Playstation 2 game won't work in the Xbox. Make sure that you only use games designed for your particular gaming console: Of course, gaming consoles still require a television or multimedia system. They're not all that portable. If you want to take games with you, you'll need a handheld device. Some of these devices will work with a gaming console as well. For example, the Nintendo Gameboy Advance allows you to interface with your Nintendo Gamecube and share games. Other handheld devices combine more than just entertainment. They allow you to talk with friends with instant messages, surf the Web, send e-mail, and, of course, play games: Finally, if games aren't your forte, but you'd still like to watch movies or listen to music on the go, MP3 and multimedia players might be for you. Many of the newer devices also can be used as backup storage for important files. Technology allows you to listen to your favorite music, watch a video clip, and store your term paper all on the same device: Techno-Gadgets Of course, you can choose from a variety of entertainment devices that don't fit under the heading of gaming, but are still a lot of fun to play with. Expect to see more of these techno-gadgets with each advance in technology and computing power. Here are a few of our favorites: Robots You've most likely heard about worker robots like the Roomba (see the picture below from the Web site) that vacuums for you inside the house and the Robomower that mows the lawn outside, while you sit back and sip a drink on the sidelines.
Undoubtedly, you've also come across Aibo, the robot dog that can sit up and roll over and so on. But there are lots of other robotic toys on the market, too. There are crawling robot babies, robot dogs, and little Roboteers for the younger set. Then there's Clinch, the robot that picks up what you dropped. You should be six years old or older to play with that one. For older kids there are robot kits that let you learn while you play – surely one of the best ways to gain knowledge. Below are some Web sites that you can check out for robot toys. Virtual Reality And Perceptual User Interfaces Did you know that humans have been using a keyboard and a mouse to interact with computers for almost 20 years? Before that we simply used a keyboard. With all the advances in computing technology, most of us still point, click, and type to work or play on our computers. Many companies and researchers are finding new ways for us to interact with computers. Maybe you'd like to feel how "heavy" a file is as you move it across your desktop. Perhaps you'd like to sit down at a table to talk with friends hundreds of miles away instead of typing messages in chat software. Or maybe you'd like to simply talk to your computer to tell it what to do. All of these become possible with advances in virtual reality and perceptual user interfaces. Check out the Department of Energy's Sandia National Laboratories Web site to see how VR training is helping emergency personnel learn how to respond to terrorist attacks. You can read more about VR–type applications in the Life-Enhancing section of this Lifelong Learning Module. Virtual Reality Virtual reality (VR) is used in games and other entertainment. But, VR also has a serious side. It's used to train military and commercial pilots. It's used to help people get over phobias and to train medical students. In the textbook we discuss VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language). VRML is a technology that you can use to create a virtual world in which users have the illusion that they are physically participating. All you need is a Web browser, a plug-in, and a little programming to create your own world. For the most part, VRML applications still rely on you to use a keyboard, mouse, and a monitor to experience them. While VRML is a readily available and affordable technology, most Virtual Reality (VR) applications aren't. There are various VR systems that range in price from a few hundred to thousands of dollars. Many don't readily work with your computer. Still, VR promises to bring us new ways of interacting with a computing environment other than click, point, and type. One of the key components of VR systems is their ability to involve more than one sense (sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound). Let's explore some of the levels of VR you can experience. Each VR system increases in the number of senses involved, as well as price. Entry-Level VR System A VRML interface can be considered an entry-level VR system. Other types of entry-level systems would be those that still depend on the monitor, keyboard, and mouse, but use software that makes you feel like you're there. Games such as Sierra's Half-Life bring a level of interactivity that makes you think you're taking part in a realistic experience. While games make up a large portion of this level, there are other applications you can use on your computer. To use this software all you need is a computer similar to the basic gaming rig. Here are some examples of software you can use: Basic-Level VR System Think of a basic level VR system as a "pumped-up" entry-level VR system. If you want to run your own basic VR system, you'll need a fast and powerful computer - faster than the basic gaming rig. You'll also need to add a few more devices to increase the level of interactivity and senses involved. A basic level VR system includes input devices like a Microsoft Sidewinder force feedback joystick or Logitech's iFeel mouse. Both devices react to what happens in the VR environment. This is called "haptic feedback." Haptic feedback provides touch feedback to you as you experience an environment. This might mean an intense rumbling sensation when you rev a virtual car's engine or a sense of heaviness as you move a large object in the VR world. Basic level VR systems also change the way you see the information on the screen. You might use a head mounted display (HMD). Instead of looking at a monitor, you're able to see the world in 360 degrees as you rotate your head. New affordable VR devices are becoming available each day. Many are designed for your computer and gaming console systems because there's an existing market for these devices. We've listed a few below: Advanced-Level VR Systems Most of us can't afford to purchase an advanced level VR system. These complex systems have multiple computers, expensive multimedia equipment, and specialized sensory devices to immerse you in the experience. Many new thrill rides are in this category. You can experience roller coaster rides, high-speed chases, or even deep sea diving without ever leaving your chair: VR is used for more than entertainment. NASA researchers can explore and experiment in VR representations of different worlds and doctors can practice complex surgical procedures on virtual patients. Many researchers use an environment called a CAVE. This is an enclosed space that creates a world around you that you can interact with. It's not as complex as the holodeck on Star Trek, but give technology some time. Here are Websites of researchers using advanced-level VR systems: Perceptual User Interfaces While VR environments focus on changing the way you interact with the computer, perceptual user interfaces (PUI) focus on how the computer can better interact with you. PUIs are still very much in the research stage. There aren't any released yet for consumer use. However, imagine your computer knew when you entered the room and sat down to work. It immediately turns on and starts reading your e-mail to you. In the middle of a message your phone rings and you reach to answer it. Immediately your computer stops reading and waits for you to end your conversation. Microsoft research is doing much work with PUIs. Perhaps we'll see them soon in the next version of the Windows OS: We know it won't be long until you start seeing more PUI equipped computers and other devices. Some of the areas where progress has already been made is in eye-tracking systems and haptic ("feel") feedback and speech recognition. Eye-Tracking Systems Eye-tracking software lets a computer know exactly where you're looking. This type of technology has many possible areas of application. It can be used to evaluate advertisements and Web surfing and many other forms of human behavior study. Apart from analysis applications, it can also be used to interact with computers. For example, instead of, or in addition to, more traditional input devices like keyboards and mice. It could be used by handicapped people who don't have full use of their hands or people who temporarily need a hands-free input device. Haptic Feedback "Haptic" is a term meaning "related to the sense of touch." It means that the user has the sensation of actually coming into physical contact with the model – it's not real, of course, but it feels real. This can be used for gaming, as previously discussed, medical training, and all sorts of other virtual reality applications. Speech Recognition Apple's latest operating system, Mac OS X can understand requests like "open the April sales file." Apple claims that you don't have to train the software and that you can use continuous speech as you do when talking naturally. Apple has embarked on the journey that all computers will take at some point, that is, the process of making computers talk, listen, and understand. For PCs, you can get several speech recognition systems. Dragon Naturally Speaking is one example, and is one of the most popular speech recognition systems. Like other speech recognition software this package allows you to dictate letters, use the computer without your hands, and helps you to avoid repetitive strain injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome. As mobile devices become more and more popular, speech recognition for people on the go will become more important and, hopefully, more sophisticated. Life-Enhancing and Life-Saving Technologies Technology is fun, time-saving, convenient, and also essential to our safety. Heart transplants wouldn't be possible without computer technology. Neither would the operations that separate conjoined twins. Less dramatically, but just as important, technology is used to detect and predict health problems so that they can be addressed before they get to the lethal stage. Disabled people benefit from computerized aids too. Computers with scanners and special software can read text to blind people. Computers can speak for those who can't and see for those who are blind. Here you can read about a few of these developments and start to envision what might be. After all, that's how human advancement comes about. Virtual Journeys inside Your Intestines If you're one of the 8 million people who have colonoscopies every year, you know that it consists of scope being pushed into your large intestine by a doctor who spends about a half an hour looking around in there for problems. A virtual colonoscopy, on the other hand consists of a CT scan of the abdomen, and within minutes, your doctor has enough images of your insides and you can go home. Software takes those CT images and makes a 3-D image of your colon. Then the doctor travels virtually around your colon looking for polyps or cancer (sort of like a video game where you travel the halls looking for the baddies). If there's a problem anywhere between your mouth and the end of your 20-ft small intestine, a new "camera pill" pill saves you from more invasive investigative techniques. Here's how it works: You get a pill to swallow, but it's no ordinary pill - it has a battery-powered camera on one end. The pill then travels down your esophagus, into your stomach, and then goes through your small intestine. The journey takes about 2 hours, during which time the camera pill takes pictures at the rate of about 2 per second, which it beams to a recording device that you wear on your waist (like a Walkman). The camera pill then continues its journey, exiting from your rectum about 24 hours later. You bring the recording device back to the doctor, who then views the images and can tell whether medical intervention is necessary. Read more at Given Imaging's Web site. Given Imaging is the manufacturer of the camera pill. You can see how the camera pill is constructed by visiting Baylor University's Web site. Researchers are working on ways to equip the camera pill with a very small motor that could be powered from the outside to travel around the large intestine. They also envision a time where the camera pill would also be equipped with retractable blade that could excise polyps on the spot.
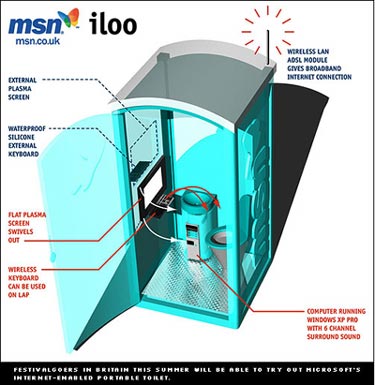
New Eyes and Better Navigation for the Visually Impaired New hope for people without eyes or with damage to the optic nerve - two of the situations for which doctors can do little. It involves special glasses that incorporate a camera that sees an image. The image is then transmitted to a small computer that the blind person wears on his/her belt. The computer is also connected to a flexible plastic card, about the size of a large postage stamp, that's implanted on the visual cortex of the blind person's brain allowing him/her to "see." The research is still in the experimental stage, and the images are crude, but the technology holds great promise for the visually impaired. "Drishti," the Sanscrit word for vision, is the name of a new system that combines a GPS receiver and a spatial database incorporated into a wearable computer to allow the visually impaired to navigate city streets. Drishti takes voice requests from the user, determines current location with the GPS system, and audibly responds with directions to the desired destination. The system "sees" the user's location in relation to obstacles like walkways, streets, and so on. The system was developed by Sever Moore, a University of Florida master's degree student. Future versions of the system will allow the user to input and store more information about his/her surroundings for future reference. Find more information at IEEE's Web site. Electronic Glove that Translates Sign Language The AcceleGlove is the invention of Jose Hernandez-Rebollar, a doctoral student at George Washington University. The glove translates the hand movements of American Sign Language (ASL) into speech and text. ASL is the fourth most used language in the United States, since 28 million people in this country suffer from some form of hearing loss. The AcceleGlove uses sensors to determine the movement, position and orientation of hand and fingers. Then the computer the glove is connected to searches for the letter, word, or phrase associated with the hand movement. The system could also be used to teach ASL. Look for this product to be on the market sometime in 2004. Read more at Gizmodo. Virtual Triage for Medical Students The process of learning necessarily involves making mistakes. In most situations, that's not so bad, but in medicine it can literally kill. To help medical students learn advanced life support skills and assessment, the University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita Campus, has a human simulator called "Ernie." Ernie is operated by a notebook computer and teaches students to intubate, perform a bronchoscopy, insert an IV, inject medication, and even defribrillate. It can even simulate swelling in a patient's pharynx or tongue during intubation. Ernie's lungs rise and fall when breathing is restored, and can even be attached to monitors that display his life signs. Other such training systems can react to more than 80 types of injected drugs. In very sophisticated virtual reality emergency rooms, student can use a triage simulator (head gear and gloves) to practice triage at major disasters such as train wrecks or multi-vehicle road accidents. While in this virtual reality environment, medical students can learn to assess the situation, identify the most severely wounded, and prioritize the order of medical care. Read more in the AMAC Reporter. Smart Highways and Intelligent Transportation Systems In Blacksburg, VA, is a "smart highway" that can provide drivers with rain, snow, and ice on demand. It's a $33 million project to help develop safer vehicles to save lives and cut travel time. Equipped with hundreds of embedded sensors, monitored by video cameras, and lined with towers that can create hazardous conditions, the 1.7 mile road is the world's first all-weather test facility for intelligent transportation systems (ITS). ITS is a federally funded program launched to try and cope with the huge volume of traffic currently on the roads and the projected 60% increase over the next 20 years. The government is serious about the ITS project. Between 1998 and 2002 the project was funded to the tune of more than $1 billion with funding increasing steadily year by year to $232 in 2003. Separate components of ITS are being installed already. In Boston, MA, traffic is being routed away from busy I-90 to the new tunnel. The tunnel has a system of underground wires. If a vehicle slows down or breaks down, the wires signal one of the 54 tunnel cameras to zoom in on the vehicle. Lane change information and other traffic reports appear on electronic signs. Even a power failure can't shut down the tunnel, there's an emergency lighting system with three back-up systems. See the BostonChannel.com for a video about the I-90 extensions. Potty-Based Web Surfing Going from the sublime to the ridiculous, a MSN UK is marketing a port-a-potty that has Internet access. It's been described as a "WWW.C," a reference to the British term W.C., or water closet, meaning toilet. It's official name is iLoo (loo being British slang for toilet) and allows you to surf while you take care of business. Microcoft UK is even negotiating with toilet paper manufacturers to print toilet paper with Web addresses.
|