 |
| 1 |  | 
RNA polymerase I synthesizes tRNA using a DNA template. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The primary function of basal transcription factors is to assist in associating RNA polymerase with the promoter element. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Transcriptional repressors are homodimers; transcriptional activators are heterodimers. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The Myc transcription factor functions to cause proliferation in specific cell types by associating with Max to form heterodimers. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Mutations in the GAL80 gene in yeast result in the continuous expression of the GAL1, GAL7, and GAL10 genes, even in the absence of galactose. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The association of DNA with histones to form chromatin increases transcription. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
A variation that does not involve a change in DNA sequence but can be passed from one generation to another is an epigenetic condition. |
|  | A) | True. |
|  | B) | False. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Alteration of codons can occur during:
|
|  | A) | transcriptional silencing |
|  | B) | mRNA editing |
|  | C) | ubiquitination |
|  | D) | methylation |
|  | E) | quenching |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
__________ involves addition of chemical groups to bases in DNA.
|
|  | A) | transcriptional silencing |
|  | B) | mRNA editing |
|  | C) | ubiquitination |
|  | D) | methylation |
|  | E) | quenching |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Hypercondensation of heterochromatin can result in:
|
|  | A) | transcriptional silencing |
|  | B) | mRNA editing |
|  | C) | ubiquitination |
|  | D) | methylation |
|  | E) | quenching |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Alteration of the properties of one transcription factor by another is an example of:
|
|  | A) | transcriptional silencing |
|  | B) | mRNA editing |
|  | C) | ubiquitination |
|  | D) | methylation |
|  | E) | quenching |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Targeting of a protein for degradation is accomplished by:
|
|  | A) | transcriptional silencing |
|  | B) | mRNA editing |
|  | C) | ubiquitination |
|  | D) | methylation |
|  | E) | quenching |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Beta-globin is coordinately regulated with other genes by:
|
|  | A) | basal factors |
|  | B) | locus control region |
|  | C) | imprinting |
|  | D) | iron response element |
|  | E) | proteasome |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Gene silencing that is heritable is an example of:
|
|  | A) | basal factors |
|  | B) | locus control region |
|  | C) | imprinting |
|  | D) | iron response element |
|  | E) | proteasome |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
An example of a regulatory RNA sequence is:
|
|  | A) | basal factor |
|  | B) | locus control region |
|  | C) | imprinting |
|  | D) | iron response element |
|  | E) | proteasome |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differs most with respect to: |
|  | A) | codon usage |
|  | B) | mRNA processing |
|  | C) | induction of genes by small molecules |
|  | D) | RNA polymerase binding to promoters |
|  | E) | regulation of DNA by binding of proteins |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
DNA binding is mediated by:
|
|  | A) | zinc finger motifs |
|  | B) | helix-turn-helix motifs |
|  | C) | helix-loop-helix motifs |
|  | D) | a & b |
|  | E) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Which of the following are basal transcription factors?
|
|  | A) | Dsx-F/Dsx-M |
|  | B) | Myc/Max |
|  | C) | TAFs/TBP |
|  | D) | Jun/Fos |
|  | E) | Sxl/string |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Eukaryotic cells are able to carefully regulate precise levels of transcription in specific genes encoding structural proteins through:
|
|  | A) | complex enhancer elements that can associate with multiple activator and repressor proteins |
|  | B) | production of different types of sigma factors |
|  | C) | attenuation |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|  | E) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Mutations altering the amount of protein synthesized from a reporter construct could occur where?
|
|  | A) | the reporter gene |
|  | B) | cis-acting DNA elements |
|  | C) | trans-acting protein genes |
|  | D) | a & c |
|  | E) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
Which sequence is most likely to be a eukaryotic promoter?
|
|  | A) | GTACAGTCATCCCGTC |
|  | B) | CTTGCTATACCATTCG |
|  | C) | AAATCTACTACGATTAG |
|  | D) | CGGTATATATCGTACG |
|  | E) | TCCTATAGAGCGATTGA |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
Which of the following is true of enhancer DNA sequences?
|
|  | A) | they contain the TATA box regulatory element |
|  | B) | they lose function if their nucleotide sequence is inverted |
|  | C) | they must be near the gene they regulate |
|  | D) | they may increase or decrease gene transcription levels |
|  | E) | they may contain only single regulatory elements |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
You add an inhibitor of polyadenylase to growing cells. What is the result?
|
|  | A) | stability of all mRNA transcripts decreases |
|  | B) | stability of most mRNA transcripts decreases |
|  | C) | rRNA synthesis ceases |
|  | D) | stability of all mRNA transcripts increases |
|  | E) | stability of most mRNA transcripts increases |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
Which of the following is not a mechanism for post-transcriptional modification controlling gene expression?
|
|  | A) | polyadenylation |
|  | B) | methylation |
|  | C) | 5' capping |
|  | D) | mRNA editing |
|  | E) | all are post-transcriptional modifications |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
Order the following stages in the cascade of sex determination in Drosophila: - Dsx-F/M synthesis
- sex-specific tissue development
- regulation of sxl
- sex chromosome:autosome ratio determination
- regulation of tra
|
|  | A) | BAECD |
|  | B) | DCEAB |
|  | C) | EADBC |
|  | D) | BDCEA |
|  | E) | DEACB |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
A mutation in the Myc gene that eliminates the dimerization domain would result in:
|
|  | A) | induction of cell proliferation genes |
|  | B) | repression of cell proliferation genes |
|  | C) | inability to form Myc-Max heterodimers |
|  | D) | inability to form Myc-Myc homodimers |
|  | E) | b and c |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
A null mutation in the IRE-binding protein would result in:
|
|  | A) | destabilization of transferrin receptor mRNA |
|  | B) | translation of ferritin mRNA in absence of iron |
|  | C) | repression of both transferrin and ferritin transcription |
|  | D) | a and b |
|  | E) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
You wish to localize the activation domain within your transcriptional activator protein. You attempt this by using recombinant DNA technology to fuse different regions of the gene encoding your protein to a portion of the bacterial lexA repressor gene that encodes a well-defined DNA-binding domain. You make sure these constructs are also fused to a promoter, so that transcript and then protein product is made. Each three-part fusion construct is then placed into cells in which the lexA-binding site has been placed upstream of a reporter gene that can then signal that the segment from the region under analysis does (or does not) have a complete activation domain. The regions of your gene you are testing and the results are shown below (lines indicate DNA retained in construct):
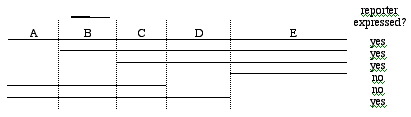 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
Which region contains the complete activation domain?
|
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|  | E) | E |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
What mode of inheritance does the pedigree below illustrate?
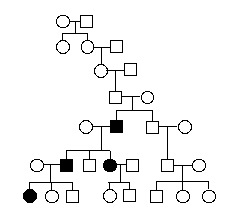 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (12.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | X-linked |
|  | B) | autosomal dominant |
|  | C) | autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance |
|  | D) | paternal imprinting |
|  | E) | maternal imprinting |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
Assume that the pedigree below illustrates a pattern of paternal imprinting of a rare disease:
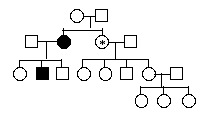 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072919302/56747/chap17mc_image3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
If "A" represents the normal, functional allele of the imprinted gene segregating in this pedigree and "a" represents a non-functional deletion, what is the most likely genotype of the individual marked with an asterisk?
|
|  | A) | AA |
|  | B) | Aa |
|  | C) | aa |
|  | D) | AA or Aa |
|  | E) | Aa or aa |
|
|
 |
| 31 |  | 
In Drosophila, alternative splicing plays an important role in sex determination. Predict the effect of a mutation in the tra gene that eliminates the splice acceptor site at the end of intron 1.
|
|  | A) | All flies will be females, regardless of X:A ratio. |
|  | B) | All flies will be males, regardless of X:A ratio. |
|  | C) | XX flies will be female, XY flies will be male |
|  | D) | XX flies will be male, XY flies will be female |
|  | E) | splicing will be random; there will be a mixture of male and female flies, but there will be no correlation between X:A ratio and sex. |
|
|

