 |
| 1 |  | 
Consider the following information for a simultaneous-move game:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a>
The one-shot, Nash equilibrium to the simultaneous-move advertising game is for |
|  | A) | Firm A to advertise and Firm B not to advertise. |
|  | B) | both firms not to advertise. |
|  | C) | both firms to advertise. |
|  | D) | Firm A not to advertise and Firm B to advertise. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Consider the following information for a simultaneous-move game:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a>
If the two firms plan to be in business for 20 years, then the Nash equilibrium is for |
|  | A) | each firm to advertise in early years, but not advertise in later years. |
|  | B) | both firms to advertise in every year. |
|  | C) | neither firm to advertise in early years, but to advertise in later years. |
|  | D) | both firms to not advertise in any year. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Consider the following information for a simultaneous-move game:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chap10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (130.0K)</a>
If both firms play the advertising game year-after-year into the unforeseeable future, then a Nash equilibrium when the interest rate is zero is for |
|  | A) | both firms to not advertise until the rival does, and then to advertise forever. |
|  | B) | Firm A to never advertise when Firm B does. |
|  | C) | both firms to never advertise. |
|  | D) | both firms to advertise until the rival does not advertise, and then not advertise forever. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A coordination problem usually occurs in situations where there is |
|  | A) | no Nash equilibrium in a game. |
|  | B) | more than one Nash equilibrium. |
|  | C) | no dominant strategies for both players. |
|  | D) | a unique, but undesirable Nash equilibrium. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
When a player randomizes over several available actions to make her current action less predictable, then a ______________________ strategy has been played. |
|  | A) | dominant strategy. |
|  | B) | secure strategy. |
|  | C) | mixed strategy. |
|  | D) | trigger strategy. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Refer to the following normal form game of price competition.
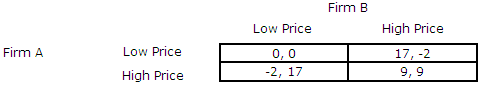 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a>
Suppose the game is infinitely repeated, and the interest rate is 10%. Both firms agree to charge a high price, provided no player has charged a low price in the past. If both firms stick to this agreement, then the present value of Firm A's payoffs are: |
|  | A) | $0.82. |
|  | B) | $9. |
|  | C) | $99. |
|  | D) | $187. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Refer to the following normal form game of price competition.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a>
Suppose that Firm B deviates from a trigger strategy to support a high price. What is the present value of Firm B's payoff from cheating? |
|  | A) | $187. |
|  | B) | $107. |
|  | C) | $17. |
|  | D) | $0. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Refer to the following normal form game of price competition.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073523224/986795/Chapter10_img2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (145.0K)</a>
What is the maximum interest rate that can sustain collusion? |
|  | A) | 24.3%. |
|  | B) | 12.5%. |
|  | C) | 78.5%. |
|  | D) | 112.5%. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
A secure strategy is one that |
|  | A) | guarantees the highest payoff given the worst possible scenario. |
|  | B) | results in the highest payoff regardless of the opponent's action. |
|  | C) | is contingent on the past play of a game in which a particular past action causes a different action by a player. |
|  | D) | a player randomizes over several available actions to make her current action less predictable. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Game theory is best applied to analysis of |
|  | A) | only pricing behavior of oligopoly firms. |
|  | B) | only output choices of oligopoly firms. |
|  | C) | any economic environment where a small number of agents interact. |
|  | D) | any academic discipline, but economics. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Which of the following is true? |
|  | A) | All secure strategies result in a Nash equilibrium. |
|  | B) | All perfect equilibria are Nash equilibria. |
|  | C) | All Nash equilibria are perfect equilibrium. |
|  | D) | Both A and C. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
When analyzing the behavior of an oligopoly firm, which of the following is crucial for the success of game-theoretic analysis? |
|  | A) | Payoffs do not need to reflect the true payoffs of the oligopolists, they just need to be greater than or equal to zero. |
|  | B) | Assume that oligopolists always move sequentially. |
|  | C) | Constructing the payoffs of the oligopolists to be interdependent is important as the payoff of one player usually affects the payoff of the other players. |
|  | D) | Assume that oligopolists always move simultaneously. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Management and a labor union are bargaining over how much of a $150 surplus to give to the union. The $150 is divisible up to one cent. The players have one shot to reach an agreement. Management has the ability to announce what it wants first, and then the labor union can accept or reject the offer. Both players get zero if the total amounts asked for exceed $150. Which of the following is true? |
|  | A) | There are multiple Nash equilibria. |
|  | B) | ($150, $0) is the unique Nash equilibrium. |
|  | C) | There is a unique subgame perfect equilibrium. |
|  | D) | Both A and C. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Which of the following is a correct statement regarding the industry structure and conduct variables that influence collusion in pricing games? |
|  | A) | Collusion is easier when there are fewer firms in the industry. |
|  | B) | Firms learn from experience how other firms will behave in the market, so market history can affect the ability to support collusion. |
|  | C) | The ability to practice price discrimination can effectively enhance the punishment mechanisms supporting collusive agreements. |
|  | D) | All of the responses are correct. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Tacit collusion in an infinitely repeated game is easier to sustain when |
|  | A) | there are many players involved. |
|  | B) | the interest rate is lower. |
|  | C) | the present value of cheating is higher. |
|  | D) | A and C. |
|
|

