
(See related pages)
| §83(b) election | a special tax election that employees who receive restricted stock or other property with ownership restrictions can make to accelerate income recognition from the normal date when restrictions lapse to the date when the restricted stock or other property is granted. The election also accelerates the employer’s compensation deduction related to the restricted stock or other property. |
| §1231 assets | depreciable or real property used in a taxpayer’s trade or business owned for more than one year. |
| §1231 look-back rule | a tax rule requiring tax payers to treat current year net §1231 gains as ordinary income when the taxpayer has deducted a §1231 loss as an ordinary loss in the five years preceding the current tax year. |
| §1245 property | tangible personal property and intangible property subject to cost recovery deductions. |
| §1250 property | real property subject to cost recovery deductions. |
| §162(m) limitation | the $1 million deduction limit on nonperformance based salary paid to certain key executives. |
| §179 election | an incentive for small businesses that allows them to immediately expense a certain amount of tangible personal property placed in service during the year. |
| §197 purchased intangibles | intangible assets that are purchased that must be amortized over 180 months regardless of their actual useful lives. |
| §263A Cost (or UNICAP) | certain book expenses that must be capitalized into inventory for tax purposes. |
| §291 depreciation recapture | the portion of a corporate taxpayer’s gain on real property that is converted from §1231 gain to ordinary income. |
| §338 election | an election by a corporate buyer of 80-percent-or-more of a corporation’s stock to treat the acquisition as an asset acquisition and not a stock acquisition. |
| §338(h)(10) election | a joint election by the corporate buyer and corporate seller of the stock of a subsidiary of the seller to treat the acquisition as a sale of the subsidiary’s assets by the seller to the buyer. |
| §481 adjustment | a change to taxable income associated with a change in accounting methods. |
| §7520 rate | an interest rate set at 120 percent of the applicable federal midterm rate (published monthly by the Treasury) and used to calculate the value of temporal interests. |
| 12-month rule | regulation that allows prepaid business expenses to be currently deducted when the contract does not extend beyond 12 months and the contract period does not extend beyond the end of the tax year following the year of the payment. |
| 30-day letter | the IRS letter received after an audit that instructs the taxpayer that he or she has 30 days to either (1) request a conference with an appeals officer or (2) agree to the proposed adjustment. |
| 90-day letter | the IRS letter received after an audit and receipt of the 30-day letter that explains that the taxpayer has 90 days to either (1) pay the proposed deficiency or (2) file a petition in the U.S. Tax Court to hear the case. The 90-day letter is also known as the statutory notice of deficiency. |
| 704(b) capital accounts | partners’ capital accounts maintained using the accounting rules prescribed in the Section 704(b) regulations. Under these rules, capital accounts reflect the fair market value of property contributed to and distributed property from partnerships. |
| Abandoned spouse | a married taxpayer who lives apart from his or her spouse for the last six months of the year (excluding temporary absences) and who maintains a household for a qualifying child. |
| Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) | the depreciation system enacted by Congress in 1981 that is based on the concept of set recovery periods and accelerated depreciation methods. |
| Accelerated death benefits | early receipt of life insurance proceeds that are not taxable under certain circumstances, such as the taxpayer is medically certified with an illness that is expected to cause death within 24 months. |
| Accountable plan | an employer’s reimbursement plan under which employees must submit documentation supporting expenses to receive reimbursement and reimbursements are limited to legitimate business expenses. |
| Accounting method | the procedure for determining the taxable year in which a business recognizes a particular item of income or deduction thereby dictating the timing of when a taxpayer reports income and deductions. |
| Accounting period | a fixed period in which a business reports income and deductions, generally referred to as a tax year. |
| Accrual method | a method of accounting that generally recognizes income in the period earned and recognizes deductions in the period that liabilities are incurred. |
| Accrued market discount | a ratable amount of the market discount at the time of purchase (based on the number of days the bond is held over the number of days until maturity when the bond is purchased) that is treated as interest income when a bond with market discount is sold before it matures. |
| Accumulated adjustments account (AAA) | an account that reflects the cumulative income or loss for the time the corporation has been an S corporation. |
| Accumulated earnings and profits | undistributed earnings and profits from years prior to the current year. |
| Accumulated earnings tax | a tax assessed on corporations that retain earnings without a business reason to do so. |
| Acquiescence | issued after the IRS loses a trial-level or circuit court case when the IRS has decided to follow the court’s adverse ruling in the future. It does not mean that the IRS agrees with the court’s ruling. Instead, it simply means that the IRS will no longer litigate this issue. |
| Acquisition indebtedness | debt secured by a qualified residence that is incurred in acquiring, constructing, or substantially improving the residence. |
| Acquisition subsidiary | a subsidiary used by the acquiring corporation in a triangular merger to acquire the target corporation. |
| Action on decision | an IRS pronouncement that explains the background reasoning behind an IRS acquiescence or nonacquiescence. |
| Active participant in a rental activity | an individual who owns at least 10% of a rental property and participates in the process of making management decisions, such as approving new tenants, deciding on rental terms, and approving repairs and capital expenditures. |
| Ad valorem tax | a tax based on the value of property. |
| Adjusted basis | see adjusted tax basis. |
| Adjusted current earnings (ACE) | a version of a corporation’s current year earnings that more closely represents a corporation’s economic income for the year than do regular taxable income or alternative minimum taxable income. |
| Adjusted gross estate | gross estate reduced by administrative expenses, debts of the decedent, and losses, and state death taxes. |
| Adjusted gross income (AGI) | gross income less deductions for AGI. AGI is an important reference point that is often used in other calculations. |
| Adjusted tax basis | the taxpayer’s acquisition basis (for example, cost) plus capital improvements less depreciation or amortization. |
| Adjusted taxable gifts | cumulative taxable gifts from previous years other than gifts already included in the gross estate valued at date of gift values. |
| After-tax rate of return | a taxpayer’s before-tax rate of return on an investment minus the taxes paid on the income from the investment. The formula for an after-tax rate of return that is taxed annually is the before-tax rate of return × (1 - marginal tax rate) [i.e., r = R × (1 - t)]. A tax payer’s after-tax rate of return on an investment held for more than one tax period is r = (FV/I) 1/n - 1, where r is the after-tax rate of return, FV is the after-tax future value of the investment, I is the original investment amount, and n is the number of periods the investment is held. |
| Aggregate approach | a theory of taxing partnerships that ignores partnerships as entities and taxes partners as if they directly owned partnership net assets. |
| Alimony | a support payment of cash made to a former spouse. The payment must be made under a written separation agreement or divorce decree that does not designate the payment as something other than alimony, the payment must be made when the spouses do not live together, and the payments must cease no later than when the recipient dies. |
| All-events test | requires that income or expenses are recognized when (1) all events have occurred that determine or fix the right to receive the income or liability to make the payments and (2) the amount of the income or expense can be determined with reasonable accuracy. |
| All-inclusive income concept | a definition of income that says that gross income means all income from whatever source derived. |
| Allocate | as used in the sourcing rules, the process of associating a deduction with a specific item or items of gross income for purposes of computing foreign source taxable income. |
| Allocation | the method of dividing or sourcing nonbusiness income to specific states. |
| Allowance method | bad debt expense is based on an estimate of the amount of the bad debts in accounts receivable at year-end. |
| Alternative minimum tax | a tax on a broader tax base than the base for the “regular” tax; the additional tax paid when the tentative minimum tax (based on the alternative minimum tax base) exceeds the regular tax (based on the regular tax base). The alternative minimum tax is designed to require taxpayers to pay some minimum level of tax even when they have low or no regular taxable income as a result of certain tax breaks in the tax code. |
| Alternative minimum tax adjustments | adjustments (positive or negative) to regular taxable income to arrive at the alternative minimum tax base. |
| Alternative minimum tax base (AMT base) | alternative minimum taxable income minus the alternative minimum tax exemption. |
| Alternative minimum tax exemption | a deduction to determine the alternative minimum tax base that is phased out based on alternative minimum taxable income. |
| Alternative minimum tax system | a secondary or parallel tax system calculated on an alternative tax base that more closely reflects economic income than the regular income tax base. The system was designed to ensure that taxpayers generating economic income pay some minimum amount of income tax each year. |
| Alternative valuation date | the date nine months after the decedent’s date of death. |
| Amortization | the method of recovering the cost of intangible assets over a specific time period. |
| Amount realized | the value of everything received by the seller in a transaction (cash, FMV of other property, and relief of liabilities) less selling costs. |
| Annotated tax service | a tax service arranged by code section. For each code section, an annotated service includes the code section; a listing of the code section history; copies of congressional committee reports that explain changes to the code section; a copy of all the regulations issued for the specific code section; the service’s unofficial explanation of the code section; and brief summaries (called annotations) of relevant court cases, revenue rulings, revenue procedures, and letter rulings that address issues specific to the code section. |
| Annual exclusion | amount of gifts allowed to be made each year per donee (regardless of the number of donees) to prevent the taxation of relatively small gifts ($14,000 per donee per year in 2013). |
| Annualized income method | a method for determining a corporation’s required estimated tax payments when the taxpayer earns more income later in the year than earlier in the year. Requires corporations to base their first and second required estimated tax installments on their income from the first three months of the year, their third installment based on their taxable income from the first six months of the year, and the final installment based on their taxable income from the first nine months of the year. |
| Annuity | a stream of equal payments over time. |
| Applicable tax rate | the tax rate or rates used to measure a company’s deferred tax asset or liability. In general, it is the enacted tax rate that is expected to apply to taxable income in the period in which the deferred tax asset or liability is expected to be recovered or settled. For U.S. tax purposes, the applicable tax rate is the regular tax rate. |
| Apportion | as used in the sourcing rules, the process of calculating the amount of a deduction that is associated with a specific item or items of gross income for purposes of computing foreign source taxable income. |
| Apportionment | the method of dividing business income of an interstate business among the states where nexus exists. |
| Arm’s-length amount | price in transactions among unrelated taxpayers, where each transacting party negotiates for his or her own benefit. |
| Arm’s-length transaction | transactions among unrelated taxpayers, where each transacting party negotiates for his or her own benefit. |
| Articles of incorporation | a document, filed by a corporation’s founders with the state describing the purpose, place of business, and other details of the corporation. |
| Articles of organization | a document, filed by a limited liability company’s founders with the state, describing the purpose, place of business, and other details of the company. |
| Asset and liability approach | the approach taken by ASC Topic 740 that focuses on computing a company’s current taxes payable (refundable) and deferred tax assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. The income tax provision recorded on the income statement is the amount needed to adjust the beginning of the year balance sheet amounts to the end of the year balance sheet amounts. |
| Assignment of income doctrine | the judicial doctrine holding that earned income is taxed to the taxpayer providing the service, and that income from property is taxed to the individual who owns the property when the income accrues. |
| At-risk amount | an investor’s risk of loss in a worst-case scenario. In a partnership, an amount generally equal to a partner’s tax basis exclusive of the partner’s share of nonrecourse debt. |
| At-risk rules | tax rules limiting losses flowing through to partners or S corporation shareholders to their at-risk amount. |
| Average tax rate | a taxpayer’s average level of taxation on each dollar of taxable income. Specifically, 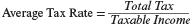 |
| Bargain element (of stock options) | the difference between the fair market value of the employer’s stock and the amount employees pay to acquire the employer’s stock. |
| Barter clubs | organizations that facilitate the exchange of rights to goods and services between members. |
| Basis | a taxpayer’s unrecovered investment in an asset that provides a reference point for measuring gain or loss when an asset is sold. |
| Before-tax rate of return | a taxpayer’s rate of return on an investment before paying taxes on the income from the investment. |
| Beneficiary | person for whom trust property is held and administered. |
| Bond | a debt instrument issued for a period of more than one year with the purpose of raising capital by borrowing. |
| Bonus depreciation | additional depreciation allowed in the acquisition year for new tangible personal property with a recovery period of 20 years or less. |
| Bond discount | the result of issuing bonds for less than their maturity value. |
| Bond premium | the result of issuing bonds for more than their maturity value. |
| Book equivalent of taxable income | a company’s pretax income from continuing operations adjusted for permanent differences. |
| Book or financial reporting income | the income or loss corporations report on their financial statements using applicable financial accounting standards. |
| Book–tax difference | a difference in the amount of an income item or deduction item taken into account for book purposes compared to the amount taken into account for the same item for tax purposes. |
| Boot | property given or received in an otherwise nontaxable transaction such as a like-kind exchange that may trigger gain to a party to the transaction. |
| Bracket | a subset (or portion) of the tax base subject to a specific tax rate. Brackets are common to graduated taxes. |
| Branch | an unincorporated division of a corporation. |
| Bright line tests | technical rules found in the tax law that provide the taxpayer with objective tests to determine the tax consequences of a transaction. |
| Brother-sister controlled group | a form of controlled group consisting of two or more corporations if five or fewer individuals collectively own more than 50 percent of the voting power or stock value of the corporation on the last day of the year. |
| Built-in gain | the difference between the fair market value and tax basis of property owned by an entity when the fair market value exceeds the tax basis. |
| Built-in gains tax | a tax levied on S corporations that were formerly C corporations. The tax applies to net unrealized built-in gains at the time the corporation converted from a C corporation to the extent the gains are recognized during the first 10 years (first 7 years for asset sales in 2010; first 5 years for asset sales in 2011) it operates as an S corporation (the built-in gains tax recognition period). The applicable tax rate is 35 percent. |
| Built-in gains tax recognition period | the first 10 years a corporation operates as an S corporation after converting from a C corporation. |
| Built-in loss | the difference between the fair market value and tax basis of property owned by an entity when the tax basis exceeds the fair market value. |
| Bunching itemized deductions | a common planning strategy in which a taxpayer pays two year’s worth of itemized expenses in one year to exceed the standard deduction in that year. |
| Business activity | a profit-motivated activity that requires a relatively high level of involvement or effort from the taxpayer to generate income. |
| Business income | income derived from business activities. |
| Business purpose doctrine | the judicial doctrine that allows the IRS to challenge and disallow business expenses for transactions with no underlying business motivation. |
| Business tax credits | nonrefundable credits designed to provide incentives for taxpayers to hire certain types of individuals or to participate in certain business activities. |
| Bypass provision | a provision in the will of a deceased spouse that transfers property to nonspousal beneficiaries to maximize the value of the decedent’s unified credit. |
| Bypass trust | a trust used in lieu of a bypass provision to transfer property to nonspousal beneficiaries to maximize the value of the unified credit of the first spouse to die. |
| C corporation | a corporate taxpaying entity with income subject to taxation. Such a corporation is termed a “C” corporation because the corporation and its shareholders are subject to the provisions of subchapter C of the Internal Revenue Code. |
| Cafeteria plan | an employer plan that allows employees to choose benefits from a menu of nontaxable fringe benefits or receive cash compensation in lieu of the benefits. |
| Capital account | an account reflecting a partner’s share of the equity in a partnership. Capital accounts are maintained using tax accounting methods or other methods of accounting, including GAAP, at the discretion of the partnership. |
| Capital asset | in general, an asset other than an asset used in a trade or business or an asset such as an account or note receivable acquired in a business from the sale of services or property. |
| Capital gain property | any asset that would have generated a longterm capital gain if the taxpayer had sold the property for its fair market value. |
| Capital interest | an economic right attached to a partnership interest giving a partner the right to receive cash or property in the event the partnership liquidates. A capital interest is synonymous with the liquidation value of a partnership interest. |
| Capital loss carryback | the amount of a corporation’s net capital loss from one year that it uses to offset net capital gains in any of the three preceding tax years. |
| Capital loss carryover | the amount of a corporation’s or an individual’s net capital loss from one year that it may use to offset net capital gains in future years. |
| Capitalization | recording an expenditure as an asset on the balance sheet rather than expensing it immediately. |
| Carryover basis | the basis of an asset the transferee takes in property received in a nontaxable exchange. The basis of the asset carries over from the transferor to the transferee. |
| Cash method | the method of accounting that recognizes income in the period in which cash, property, or services are received and recognizes deductions in the period paid. |
| Cash surrender value | the amount, if any, the owner of a life insurance policy receives when the policy is cashed in before the death of the insured individual. |
| Cash tax rate | the tax rate computed by dividing a company’s taxes paid during the year by its pretax income from continuing operations. |
| Casualty | an unexpected, unforeseen event driven by forces outside the control of the taxpayer (such as “fire, storm, or shipwreck” or other event or theft) that damages or destroys a taxpayer’s property. |
| Casualty loss | a loss arising from a sudden, unexpected, or unusual event such as a “fire, storm, or shipwreck” or loss from theft. |
| Ceiling | limitations that are maximum amounts for adjustments to taxable income (or credits). The amounts in excess of the ceiling are either lost or carried to another tax year. |
| Certainty | one of the criteria used to evaluate tax systems. Certainty means taxpayers should be able to determine when, where, and how much tax to pay. |
| Certificate of deposit | an interest-bearing debt instrument offered by banks and savings and loans. Money removed from the CD before maturity is subject to a penalty. |
| Certificate of limited partnership | a document limited partnerships must file with the state to be formerly recognized by the state. The document is similar to articles of incorporation or articles or organization. |
| Character of income | determines the rate at which income will be taxed. Common income characters (or types of income) include tax exempt, ordinary, and capital. |
| Charitable contribution deduction modified taxable income | taxable income for purposes of determining the 10% of taxable income deduction limitation for corporate charitable contributions. Computed as taxable income before deducting (1) any charitable contributions, (2) the dividends received deduction, (3) net operating loss carrybacks, and (4) the domestic production activities deduction. |
| Circular 230 | regulations issued by the IRS that govern tax practice and apply to all persons practicing before the IRS. There are three parts of Circular 230: Subpart A describes who may practice before the IRS (e.g., CPAs, attorneys, enrolled agents) and what practicing before the IRS means (tax return preparation, representing clients before the IRS, etc.). Subpart B describes the duties and restrictions that apply to individuals governed by Circular 230. Subpart C explains disciplinary proceedings for practitioners violating the Circular 230 provisions. |
| Citator | a research tool that allows one to check the status of several types of tax authorities. A citator can be used to review the history of the case to find out, for example, whether it was subsequently appealed and overturned, and to identify subsequent cases that cite the case. Citators can also be used to check the status of revenue rulings, revenue procedures, and other IRS pronouncements. |
| Civil penalties | monetary penalties imposed when tax practitioners or taxpayers violate tax statutes without reasonable cause—for example, as the result of negligence, intentional disregard of pertinent rules, willful disobedience, or outright fraud. |
| Claim of right doctrine | judicial doctrine that states that income has been realized if a taxpayer receives income and there are no restrictions on the taxpayer’s use of the income (for example, the taxpayer does not have an obligation to repay the amount). |
| Cliff vesting | a qualified plan provision allowing for benefits to vest all at once after a period of time has passed. |
| Collectibles | a work of art, a rug or antique, a metal or gem, a stamp or coin, an alcoholic beverage, or other similar items held for investment for more than one year. |
| Combined controlled group | a form of a controlled group consisting of three or more corporations each of which is a member of either a parent-subsidiary or brother-sister controlled group and one of the corporations is the parent in the parent-subsidiary controlled group and also is in a brother-sister controlled group. |
| Commercial domicile | the state where a business is headquartered and directs operations; this location may be different from the place of incorporation. |
| Commercial traveler exception | a statutory exception that exempts nonresidents from U.S. taxation of compensation from services if the individual is in the United States 90 days or less and earns compensation of $3,000 or less. |
| Common-law states | the 41 states that have not adopted community property laws. |
| Community-property states | nine states (Arizona, California, Idaho, Louisiana, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin) that automatically equally divide the ownership of property acquired by either spouse during a marriage. |
| Community property systems | systems in which state laws dictate how the income and property is legally shared between a husband and a wife. |
| Commuting | traveling from a personal residence to the place of business. |
| Complex trust | a trust that is not required by the trust instrument to distribute income currently. |
| Conglomerate | a group of corporations in different businesses under common ownership. |
| Consolidation | the combining of the assets and liabilities of two or more corporations into a new entity. |
| Constructive dividend | a payment made by a corporation to a shareholder that is recharacterized by the IRS or courts as a dividend even though it is not characterized as such by the corporation. |
| Constructive ownership | rules that cause stock not owned by a taxpayer to be treated as owned by the taxpayer for purposes of meeting certain stock ownership tests. |
| Constructive receipt doctrine | the judicial doctrine that provides that a taxpayer must recognize income when it is actually or constructively received. Constructive receipt is deemed to have occurred if the income has been credited to the taxpayer’s account or if the income is unconditionally available to the taxpayer, the taxpayer is aware of the income’s availability, and there are no restrictions on the taxpayer’s control over the income. |
| Continuity of business enterprise (COBE) | a judicial (now regulatory) requirement that the acquiring corporation continue the target corporation’s historic business or continue to use a "significant" portion of the target corporation’s historic business assets to be tax-deferred. |
| Continuity of interest (COI) | a judicial (now regulatory) requirement that the transferors of stock in a reorganization collectively retain a continuing ownership (equity) interest in the target corporation’s assets or historic business to be tax-deferred. |
| Contribution to capital | a shareholder’s or other person’s contribution of cash or other property to a corporation without receipt of an additional equity interest in the corporation. |
| Controlled foreign corporation | a foreign corporation that is more than 50 percent owned by U.S. shareholders. |
| Controlled group | a group of corporations owned by the same individual shareholders; it can either be brother-sister corporations or parent-subsidiary corporations. |
| Convenience | one of the criteria used to evaluate tax systems. Convenience means a tax system should be designed to facilitate the collection of tax revenues without undue hardship on the taxpayer or the government. |
| Corporation | business entity recognized as separate entity from its owners under state law. |
| Corpus | the principal or property transferred to fund a trust or accumulated in the trust. |
| Correspondence examination | an IRS audit conducted by mail and generally limited to one or two items on the taxpayer’s return. Among the three types of audits, correspondence audits are generally the most common, the most narrow in scope, and least complex. The IRS typically requests supporting documentation for one or more items on the taxpayer’s return (e.g., documentation of charitable contributions deducted). |
| Cost depletion | the method of recovering the cost of a natural resource that allows a taxpayer to estimate or determine the number of units that remain in the resource at the beginning of the year and allocate a pro rata share of the remaining basis to each unit of the resource that is extracted or sold during the year. |
| Cost recovery | the method by which a company expenses the cost of acquiring capital assets. Cost recovery can take the form of depreciation, amortization, or depletion. |
| Coupon rate | the interest rate expressed as a percentage of the face value of the bond. |
| Covenant not to compete | a contractual promise to refrain from conducting business or professional activities similar to those of another party. |
| Criminal penalties | penalties commonly charged in tax evasion cases (i.e., willful intent to defraud the government). They are imposed only after normal due process, including a trial. Compared to civil cases, the standard of conviction is higher in a criminal trial (beyond a reasonable doubt). However, the penalties are also much higher, such as fines up to $100,000 for individuals plus a prison sentence. |
| Current earnings and profits | a year-to-year calculation maintained by a corporation to determine if a distribution is a dividend. Earnings and profits is computed for the current year by adjusting taxable income to make it more closely resemble economic income. |
| Current gifts | gifts completed during the calendar year that are not already exempted from the gift tax. |
| Current income tax expense or benefit | the amount of taxes paid or payable (refundable) in the current year. |
| Current tax liability or asset | the amount of taxes payable or refundable in the current year. |
| De minimis fringe benefit | a nontaxable fringe benefit that allows employees to receive occasional or incidental benefits tax free. |
| Debt basis | the outstanding principal of direct loans from an S corporation shareholder to the S corporation. Once taxpayers deduct losses to the extent of their stock basis, they may deduct losses to the extent of their debt basis. When the debt basis has been reduced by losses, it is restored by income/gain allocations. |
| Deductible temporary differences | book-tax differences that will result in tax deductible amounts in future years when the related deferred tax asset is recovered. |
| Deductions | amounts that are subtracted from gross income in calculating taxable income. |
| Deductions above the line | for AGI deductions or deductions subtracted from gross income to determine AGI. |
| Deductions below the line | from AGI deductions or deductions subtracted from AGI to calculate taxable income. |
| Deductions for AGI | deductions that reduce AGI. |
| Deductions from AGI | deductions subtracted from AGI to calculate taxable income. |
| Deferral items, deferred income, or deferrals | realized income that will be taxed as income in a subsequent year. |
| Deferral method | recognizes income from advance payments for goods by the earlier of (1) when the business would recognize the income for tax purposes if it had not received the advance payment or (2) when it recognizes the income for financial reporting purposes. |
| Deferred like-kind exchange | a like-kind exchange where the taxpayer transfers like-kind property before receiving the like-kind property in exchange. The property to be received must be identified within 45 days and received within 180 days of the transfer of the property given up. |
| Deferred tax asset | the expected future tax benefit attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. |
| Deferred tax liability | the expected future tax cost attributable to taxable temporary differences. |
| Defined benefit plan | employer-provided qualified plans that spell out the specific benefit employees will receive on retirement. |
| Defined contribution plan | employer-provided qualified plans that specify the maximum annual contributions employers and/or employees may contribute to the plan. |
| Definitely related deductions | deductions that are associated with the creation of a specific item or items of gross income. |
| Dependency exemption | a fixed deduction allowed for each individual who qualifies as a “dependent” of the taxpayer. |
| Dependent | a person for whom a taxpayer may claim a dependency exemption. To qualify as a dependent a person must be a qualifying child or qualifying relative of the taxpayer. |
| Dependent care benefit | a nontaxable fringe benefit that allows employees to receive up to $5,000 of care for children under age 13 or for a spouse or other dependent with physical needs. |
| Depletion | the cost recovery method to allocate the cost of natural resources as they are removed. |
| Depreciation | the cost recovery method to allocate the cost of tangible personal and real property over a specific time period. |
| Depreciation recapture | the conversion of §1231 gain into ordinary income on a sale (or exchange) based on the amount of accumulated depreciation on the property at the time of sale or exchange. |
| Determination letters | rulings requested by the taxpayer, issued by local IRS directors, and generally not controversial. An example of a determination letter is the request by an employer for the IRS to rule that the taxpayer’s retirement plan is a “qualified plan.” |
| DIF (Discriminant Function) system | the DIF system assigns a score to each tax return that represents the probability that the tax liability on the return has been underreported (a higher score = a higher likelihood of underreporting). The IRS derives the weights assigned to specific tax return attributes from historical IRS audit adjustment data from the National Research Program. The DIF system then uses these (undisclosed) weights to score each tax return based on the tax return’s characteristics. Returns with higher DIF scores are then reviewed to determine if an audit is the best course of action. |
| Direct conversion | when a taxpayer receives noncash property as a replacement for property damaged or destroyed in an involuntary conversion rather than a cash payment. |
| Direct write-off method | required method for deducting bad debts for tax purposes. Under this method, businesses deduct bad debt only when the debt becomes wholly or partially worthless. |
| Disability insurance | sometimes called sick pay or wage replacement insurance. It pays the insured for wages lost due to injury or disability. |
| Discharge of indebtedness | debt forgiveness. |
| Discount factor | the factor based on the taxpayer’s rate of return that is used to determine the present value of future cash inflows (e.g., tax savings) and outflows (taxes paid). |
| Disproportionate distributions | partnership distributions that change the partners’ relative ownership of hot assets. |
| Disqualifying disposition | the sale of stock acquired using incentive stock options prior to satisfying certain holding period requirements. Failing to satisfy the holding period requirements converts the options into nonqualified stock options. |
| Disregarded entities | unincorporated entities with one owner that are treated as flow-through entities for U.S. income tax purposes. |
| Distributable net income (DNI) | the maximum amount of the distribution deduction by fiduciaries and the maximum aggregate amount of gross income reportable by beneficiaries. |
| Distribution deduction | deduction by fiduciaries for distributions of income to beneficiaries that operates to eliminate the potential for double taxation of fiduciary income. |
| Dividend | a distribution to shareholders of money or property from the corporation’s earnings and profits. |
| Dividends received deduction | a corporate deduction for part or all of a dividend received from other taxable, domestic corporations. |
| Document perfection program | a program under which all tax returns are checked for mathematical and tax calculation errors. |
| Domestic production activities deduction (DPAD) | a deduction for businesses that manufacture goods in the United States. |
| Donee | person receiving a gift. |
| Donor | person making a gift. |
| Double taxation | the tax burden when an entity’s income is subject to two levels of tax. Income of C corporations is subject to double taxation. The first level of tax is at the corporate level and the second level of tax on corporate income occurs at the shareholder level. Income of flow-through entities is generally not subject to double taxation. |
| DRD modified taxable income | taxable income for purposes of applying the taxable income limitation for the dividends received deduction. Computed as the dividend receiving corporation’s taxable income before deducting the dividends received deduction, any net operating loss deduction, the domestic production activities deduction, and capital loss carrybacks. |
| Dwelling unit | property that provides a place suitable for people to occupy (live and sleep). |
| Dynamic forecasting | the process of forecasting tax revenues that incorporates into the forecast how taxpayers may alter their activities in response to a tax law change. |
| Earmarked tax | a tax assessed for a specific purpose (e.g., for education). |
| Earned income | compensation and other forms of income received for providing goods or services in the ordinary course of business. |
| Earned income credit | a refundable credit designed to help offset the effect of employment taxes on compensation paid to low income taxpayers and to encourage lower income taxpayers to seek employment. |
| Earnings and profits | a measure of a corporation’s earnings that is similar to its economic earnings. Corporate dividends are taxable to shareholders to the extent they come from earnings and profits. |
| Economic nexus | the concept that businesses without a physical presence in the state may establish income tax nexus in the state through an economic presence there. |
| Economic performance test | the third requirement that must be met for an accrual method taxpayer to deduct an expense currently. The specific event that satisfies the economic performance test varies based on the type of expense. |
| Economic substance doctrine | doctrine that requires transactions to meaningfully change a taxpayer’s economic position and to have a substantial purpose (apart from a federal income tax purpose) in order for a taxpayer to obtain tax benefits. |
| Economy | one of the criteria used to evaluate tax systems. Economy means a tax system should minimize its compliance and administration costs. |
| Educational assistance benefit | a nontaxable fringe benefit that allows an employer to provide a certain amount of education benefits on an annual basis. |
| Effective tax rate | the taxpayer’s average rate of taxation on each dollar of total income (taxable and nontaxable income). Specifically, 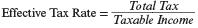 |
| Effectively connected income | net income that results from the conduct of a U.S. trade or business by a nonresident. |
| Employee | a person who is hired to provide services to a company on a regular basis in exchange for compensation and who does not provide these services as part of an independent business. |
| Employment taxes | taxes consisting of the Old Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) tax, commonly called the Social Security tax, and the Medical Health Insurance (MHI) tax known as the Medicare tax. |
| Enacted tax rate | the statutory tax rate that will apply in the current or a future period. |
| Entity approach | a theory of taxing partnerships that treats partnerships as entities separate from partners. |
| Equity | one of the criteria used to evaluate a tax system. A tax system is considered fair or equitable if the tax is based on the taxpayer’s ability to pay; taxpayers with a greater ability to pay tax, pay more tax. |
| Escrow account (mortgage-related) | a holding account with a taxpayer’s mortgage lender. The taxpayer makes mortgage payments to the lender that include payment for the interest and principal and payments for property taxes. The lender maintains the payments for property taxes in the escrow account and uses the funds in the account to pay the property taxes when the taxes are due. |
| Estate | fiduciary legal entity that comes into existence upon a person’s death and is empowered by the probate court to gather and transfer the decedent’s real and personal property. |
| Estimated tax payments | quarterly tax payments that a taxpayer makes to the government if the tax withholding is insufficient to meet the taxpayer’s tax liability. |
| Excess net passive income | net passive investment income × passive investment income in excess of 25% of the S corporation’s gross receipts divided by its passive investment income. |
| Excess net passive income tax | a tax levied on an S corporation that has accumulated earnings and profits from years in which it operated as a C corporation if the corporation reports excess net passive income. |
| Exchanged basis | the basis of an asset received in a nontaxable exchange. An exchanged basis is generally the basis of the asset given up in a nontaxable exchange. |
| Excise taxes | taxes levied on the retail sale of particular products. They differ from other taxes in that the tax base for an excise tax typically depends on the quantity purchased, rather than a monetary amount. |
| Excluded income | or |
| exclusions | realized income that is exempted from income taxation. |
| Ex-dividend date | the relevant date for determining who receives a dividend from a stock. Anyone purchasing stock before this date will receive current dividends. Otherwise, the purchaser must wait until subsequent dividends are declared before receiving them. |
| Executor | the person who takes responsibility for collecting the assets of the decedent, paying the decedent’s debts, and distributing the remaining assets to the rightful heirs. |
| Exemption | a fixed income tax deduction a taxpayer may claim for each person who qualifies as a dependent of the taxpayer. This includes the taxpayer (and spouse on a joint return) who does not qualify as a dependent of another. |
| Exemption equivalent | the amount of cumulative taxable transfers a taxpayer can make without exceeding the unified credit. |
| Exercise date | the date employees use their stock options to acquire employer stock at a discounted price. |
| Exercise price | the price at which holders of stock options may purchase stock in the corporation issuing the option. |
| Explicit tax | a tax directly imposed by a government. |
| Face value | a specified final amount paid to the owner of a coupon bond on the date of maturity. The face value is also known as the maturity value. |
| Facts and circumstances test | a test used to make subjective determination such as whether the amount of salary paid to an employee is reasonable. The test requires the taxpayer and the IRS to consider all the relevant facts and circumstances surrounding the situation in order to make a decision. The relevant facts and circumstance are situation specific. |
| Family limited partnership | a partnership designed to save estate taxes by dividing a family business into various ownership interests representing control of operations and future income and appreciation of the assets. |
| Favorable book-tax difference | a book-tax difference that requires a subtraction from book income in determining taxable income. |
| Federal/state adjustments | amounts added to or subtracted from federal taxable income when firms compute taxable income for a particular state. |
| Federal short-term interest rate | the quarterly interest rate used to determine the interest charged for tax underpayments (federal short-term rate plus 3 percent). |
| FICA taxes | FICA (Federal Insurance Contribution Act) taxes are a term used to denote both the Social Security and Medicare taxes upon earned income. For self-employed taxpayers, the terms “FICA tax” and “self-employment tax” are synonymous. |
| Fiduciary | a person or legal entity that takes possession of property for the benefit of beneficiaries. |
| Fiduciary duty | a requirement that a fiduciary act in an objective and impartial manner and not favor one beneficiary over another. |
| Field examination | the least common audit. The IRS conducts these audits at the taxpayer’s place of business or the location where the taxpayer’s books, records, and source documents are maintained. Field examinations are generally the broadest in scope and most complex of the three audit types. They can last many months to multiple years and generally are limited to business returns and the most complex individual returns. |
| FIFO | see first-in first-out (FIFO) method. |
| Filing status | filing status places taxpayers into one of five categories (married filing jointly, married filing separately, qualifying widow or widower, head of household, and single) by marital status and family situation as of the end of the year. Filing status determines whether a taxpayer must file a tax return, appropriate tax rate schedules, standard deduction amounts, and several deduction and credit limitation thresholds. |
| Final regulations | regulations that have been issued in final form, and thus, until revoked, they represent the Treasury’s interpretation of the Code. |
| Financial reporting income | see book or financial reporting income. |
| First-in first-out (FIFO) method | an accounting method that values the cost of assets sold under the assumption that the assets are sold in the order purchased (i.e., first purchased, first sold). |
| Fiscal year | a year that ends on the last day of a month other than December. |
| Fixed and determinable, annual or periodic income | U.S. source passive income earned by a nonresident. |
| Flat tax | a tax in which a single tax rate is applied throughout the tax base. |
| Flexible spending account | a plan that allows employees to contribute before-tax dollars that may be used for unreimbursed medical expenses or dependent care. |
| Flipping | a term used to describe the real estate investment practice of acquiring a home, repairing or remodeling the home, and then immediately, or soon thereafter, selling it (presumably at a profit). |
| Floor limitation | a minimum amount that an expenditure (or credit or other adjustment to taxable income) must meet before any amount is allowed. |
| Flow-through entities | legal entities like partnerships, limited liability companies, and S corporations that do not pay income tax. Income and losses from flow-through entities are allocated to their owners. |
| For the convenience of the employer benefits | nontaxable benefits employers provide to employees and employee spouses or dependents in the form of meals or lodging if provided on the employer’s premises and are provided for a purpose that is helpful or convenient for the employer. |
| Foreign joint venture | a 50 percent or less owned foreign entity. |
| Foreign personal holding company income | a category of foreign source passive income that includes interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and gains from sale of assets. |
| Foreign subsidiary | a more than 50 percent owned foreign corporation. |
| Foreign tax credit | a credit for income taxes paid to a foreign jurisdiction. |
| Foreign tax credit limitation | the limit put on the use of creditable foreign taxes for the current year. |
| Form 1065 | the form partnerships file annually with the IRS to report partnership ordinary income (loss) and separately stated items for the year. |
| Form 1120S | the form S corporations file annually with the IRS to report S corporation ordinary income (loss) and separately stated items for the year. |
| Form 7004 | the form C corporations, partnerships, and S corporations file to receive an automatic extension to file their annual tax return. |
| Form W-2 | used to report wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from them. The form is also used to report FICA taxes to the Social Security Administration. |
| Form W-4 | a form used by a taxpayer to supply her employer with the information necessary to determine the amount of tax to withhold from each paycheck. |
| Forward triangular merger | an acquisition in which the acquired (target) corporation merges into an acquisition subsidiary of the acquiring corporation, after which the acquired corporation becomes part of the acquisition subsidiary of the acquiring corporation. |
| Fringe benefits | noncash benefit provided to an employee as a form of compensation. As a general rule, fringe benefits are taxable. However, certain fringe benefits are excluded from gross income. |
| FTC basket | a category of income that requires a separate FTC limitation computation. |
| Full-inclusion method | the method for accounting for advance payments for goods that requires that businesses immediately recognize advance payments as taxable income. |
| Full-month convention | a convention that allows owners of intangibles to deduct an entire month’s amortization in the month of purchase and month of disposition. |
| Functional currency | the currency of the primary economic environment in which an entity operates (that is the currency of the jurisdiction in which an entity primarily generates and expends cash). |
| Future interest | the right to receive property in the future. |
| GAAP capital accounts | partners’ capital accounts maintained using generally accepted accounting principals. |
| General category income | foreign source income that is not considered passive category income for foreign tax credit purposes (generally income from an active trade or business). |
| General partnership | a partnership with partners who all have unlimited liability with respect to the liabilities of the entity. |
| Generation-skipping tax (GST) | supplemental transfer tax designed to prevent the avoidance of estate and gift taxes through transfers that skip a generation of recipients. |
| Gift | a transfer of property where no consideration (or inadequate consideration) is paid for the property. |
| Golsen rule | the rule that states that the U.S. Tax Court will abide by the circuit court’s rulings that has appellate jurisdiction for a case. |
| Goodwill | the value of a business in excess of the fair market value of identifiable assets. |
| Graded vesting | a qualified plan rule that requires an increasing percentage of plan benefits to vest with each additional year of employment. |
| Graduated taxes | taxes in which the tax base is divided into a series of monetary amounts, or brackets, where each successive bracket is taxed at a different (gradually higher or gradually lower) percentage rate. |
| Grant date (stock options) | the date on which employees receive stock options to acquire employer stock at a specified price. |
| Grantor | person creating a trust. |
| Gross estate | property owned by the decedent at death and certain property transfers taking effect at death. |
| Gross income | realized income reduced for any excluded or deferred income. |
| Gross receipts (for purposes of net passive investment income tax calculation) | the total amount of revenues (including passive investment income) received or accrued under the corporation’s accounting method, not reduced by returns, allowances, cost of goods sold, or deductions. Gross receipts include net capital gains from the sales or exchanges of capital assets and gains from the sales or exchanges of stock or securities (losses do not offset gains). |
| Group-term life insurance | term life insurance provided by an employer to a group of employees. |
| Guaranteed payments | payments made to partners or LLC members that are guaranteed because they are not contingent on partnership profits or losses. They are economically similar to shareholder salary payments. |
| Half-year convention | a depreciation convention that allows owners of tangible personal property to take one-half of a year’s worth of depreciation in the year of purchase and in the year of disposition regardless of when the asset was actually placed in service or sold. |
| Head of household | one of five primary filing statuses. A taxpayer may file as head of household if s/he is unmarried as of the end of the year and pays more than half of the cost to maintain a household for a qualifying person who lives with the taxpayer for more than half of the year; or, s/he pays more than half the costs to maintain a household for a parent who qualifies as the taxpayer’s dependent. |
| Heirs | persons who inherit property from the deceased. |
| Hobby | a revenue-generating activity that is motivated by personal motives rather than profit objectives. |
| Home-equity indebtedness | debt (except for acquisition indebtedness) secured by the taxpayer’s qualified residence to the extent it does not exceed the fair market value of the residence over the acquisition indebtedness. Interest paid on up to $100,000 of home-equity indebtedness is allowed as an itemized deduction. |
| Home office deduction | deductions relating to the use of an office in the home. When the taxpayer qualifies, expenses are allocated between personal use and business use of the home. |
| Horizontal equity | one of the dimensions of equity. Horizontal equity is achieved if taxpayers in similar situations pay the same tax. |
| Hot assets | unrealized receivables or inventory items defined in §751(a) that give rise to ordinary gains and losses. The exact definition of hot assets depends on whether it is in reference to dispositions of a partnership interest or distributions. |
| Hybrid entity | an entity for which an election is available to choose the entity’s tax status for U.S. tax purposes. |
| Impermissible accounting method | an accounting method prohibited by tax laws. |
| Implicit tax | indirect taxes that result from a tax advantage the government grants to certain transactions to satisfy social, economic, or other objectives. They are defined as the reduced before-tax return that a tax-favored asset produces because of its tax-advantaged status. |
| Imputed income | income from an economic benefit the taxpayer receives indirectly rather than directly. The amount of the income is based on comparable alternatives. |
| Inbound transaction | a transaction conducted by a foreign person that is subject to U.S. taxation. |
| Incentive stock option | a type of stock option that allows employees to defer the bargain element for regular tax purposes until the stock acquired from option exercises is sold. The bargain element is taxed at capital gains rates provided the stock is retained long enough to satisfy certain holding period requirements. Employers cannot deduct the bargain element as compensation expense. |
| Income effect | one of the two basic responses that a taxpayer may have when taxes increase. The income effect predicts that when taxpayers are taxed more (e.g., tax rate increases from 25 to 28 percent), they will work harder to generate the same after-tax dollars. |
| Income tax | a tax in which the tax base is income. Income taxes are imposed by the federal government and by most states. |
| Independent contractor | a person who provides services to another entity, usually under terms specified in a contract. The independent contractor has more control over how and when to do the work than does an employee. |
| Indirect conversion | the receipt of money or other property as a replacement for property that was destroyed or damaged in an involuntary conversion. |
| Individual retirement account (IRA) | a tax-advantaged account in which individuals who have earned income can save for retirement. |
| Information matching program | a program that compares the taxpayer’s tax return to information submitted to the IRS from other taxpayers (e.g., banks, employers, mutual funds, brokerage companies, mortgage companies). Information matched includes items such as wages (e.g., Form W-2 submitted by employers), interest income (e.g., Form 1099-INT submitted by banks), dividend income (e.g., Form 1099-DIV submitted by brokerage companies), and so forth. |
| Inheritance | a transfer of property when the owner is deceased (the transfer is made by the decedent’s estate). |
| Initial public offering | the first sale of stock by a company to the public. |
| Inside tax basis | the tax basis of an entity’s assets and liabilities. |
| Installment sale | a sale for which the taxpayer receives payment in more than one period. |
| Institutional shareholder | an entity with large amounts to invest in corporate stock, such as investment companies, mutual funds, brokerages, insurance companies, pension funds, investment banks, and endowment funds. |
| Intangible assets | assets that do not have physical characteristics. Examples include goodwill, covenants not to compete, organizational expenditures, and research and experimentation expenses. |
| Internal Revenue Code of 1986 | the codified tax laws of the United States. Although the Code is frequently revised, there have only been three different codes since the Code was created in 1939 (i.e., the IRC of 1939, IRC of 1954, and IRC of 1986). |
| Interpretative regulations | the most common regulation; they represent the Treasury’s interpretation of the Code and are issued under the Treasury’s general authority to interpret the Code. |
| Interstate commerce | business conducted between parties in two or more states. |
| Intervivos transfers | gifts made by a donor during his or her lifetime. |
| Inventory items | (for sale of partnership interest purposes) classic inventory defined as property held for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business, but also assets that are not capital assets or §1231 assets, which would produce ordinary income if sold by the entity. There are actually two definitions of inventory items in §751. §751(a) inventory items are defined in §751(d) to include all inventory items. The §751(b) definition includes only substantially appreciated inventory. |
| Investment activities | a profit-seeking activity that is intermittent or occasional in frequency including the production or collection of income or the management, conservation, or maintenance of property held for the production of income. |
| Investment expenses | expenses such as safe deposit rental fees, attorney fees, and accounting fees that are necessary to produce portfolio income. Investment expenses are allowed for individuals as miscellaneous itemized deductions subject to the 2 percent of AGI floor limitation. |
| Investment income | income received from portfolio type investments. Portfolio income includes capital gains and losses, interest, dividend, annuity, and royalty income not derived in the ordinary course of a trade or business. When computing the deductibility of investment interest expense, however, capital gains and dividends subject to the preferential tax rate are not treated as investment income unless the taxpayer elects to have this income taxed at ordinary tax rates. |
| Investment interest expense | interest paid on borrowings or loans that are used to fund portfolio investments. Individuals are allowed an itemized deduction for qualified investment interest paid during the year. |
| Involuntary conversion | a direct or indirect conversion of property through natural disaster, government condemnation, or accident that allows a taxpayer to defer realized gain if certain requirements are met. |
| IRS allocation method | allocates expenses associated with rental use of the home between rental use and personal use. The percentage of total expenses allocated to rental use is the ratio of the number of rental use days for the property to the total days the property was used during the year. |
| Itemized deductions | certain types of expenditures that Congress allows taxpayers to deduct as from AGI deductions. |
| Joint tenancy with the right of survivorship | title to property that provides the co-owners with equal rights to it and that automatically transfers to the survivor at the death of a co-owner. |
| Kiddie tax | a tax imposed at the parent’s marginal rate on a child’s unearned income. |
| Last will and testament | the document that directs the transfer of ownership of the decedent’s assets to the heirs. |
| Late filing penalty | a penalty assessed if a taxpayer does not file a tax return by the required date (the original due date plus extension). |
| Least aggregate deferral | an approach to determine a partnership’s required year-end if a majority of the partners don’t have the same year-end and if the principal partners don’t have the same year-end. As the name implies, this approach minimizes the combined tax deferral of the partners. |
| Legislative grace | the concept that taxpayers receive certain tax benefits only because Congress writes laws that allow taxpayers to receive the tax benefits. |
| Legislative regulations | the rarest type of regulation, issued when Congress specifically directs the Treasury Department to create regulations to address an issue in an area of law. In these instances, the Treasury is actually writing the law instead of interpreting the Code. Because legislative regulations actually represent tax law instead of an interpretation of tax law, legislative regulations have more authoritative weight than interpretative and procedural regulations. |
| Life estate | the right to possess property and/or collect income from property for the duration of someone’s life. |
| Life insurance trust | a trust funded with an irrevocable transfer of a life insurance policy and that gives the trustee the power to redesignate beneficiaries. |
| LIFO | last-in, first-out method; an accounting method that values the cost of assets sold under the assumption that assets are sold in the reverse order in which they are purchased (i.e., last purchased, first sold). |
| LIFO recapture amount | the excess of a C corporation’s inventory basis under the FIFO method in excess of the inventory basis under the LIFO method in its final tax year as a C corporation before it becomes an S corporation. |
| LIFO recapture tax | a tax levied on a C corporation that elects to be taxed as an S corporation when it is using the LIFO method for accounting for inventories. |
| Like-kind exchange | a nontaxable (or partially taxable) trade or exchange of assets that are similar or related in use. |
| Limited liability company (LLC) | a type of flow-through entity for federal income tax purposes. By state law, the owners of the LLC have limited liability with respect to the entity’s debts or liabilities. Limited liability companies are taxed as partnerships for federal income tax purposes. |
| Limited partnership | a partnership with at least one general partner with unlimited liability for the entity’s debts and at least one limited partner with liability limited to the limited partner’s investment in the partnership. |
| Liquidating distributions | a distribution that terminates an owner’s interest in the entity. |
| Liquidation value | the amount a partner would receive if the partnership were to sell all its assets, pay its debts, and distribute its remaining assets to the partners in exchange for their partnership interests. |
| Listed property | business assets that are often used for personal purposes. Depreciation on listed property is limited to the business use portion of the asset. |
| Local tax | taxes imposed by local governments (cities, counties, school districts, etc.). |
| Long-term capital gain property | property that would generate long-term capital gain if it were sold. This includes capital assets held for more than a year. |
| Long-term capital gains or losses | gains or losses from the sale of capital assets held for more than 12 months. |
| Luxury automobile | an automobile on which the amount of annual depreciation expense is limited because the cost of the automobile exceeds a certain threshold. The definition excludes vehicles with gross vehicle weight exceeding 6,000 pounds. |
| M adjustments | see Schedule M adjustments. |
| Majority interest taxable year | the common tax year of a group of partners who jointly hold greater than 50% of the profits and capital interests in the partnership. |
| Marginal tax rate | the tax rate that applies to the next additional increment of a taxpayer’s taxable income (or to deductions). Specifically,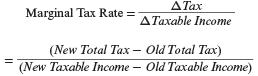 where “old” refers to the current tax and “new” refers to the revised tax after incorporating the additional income (or deductions) in question. |
| Marital deduction | the deduction for transfers of qualified property to a spouse. |
| Market discount | the difference between the amount paid for a bond in a market purchase rather than at original issuance when the amount paid is less than the maturity value of the bond. |
| Market premium | the difference between the amount paid for a bond in a market purchase rather than at original issuance when the amount paid is greater than the maturity value of the bond. |
| Marriage benefit | the tax savings married couples receive by filing a joint return relative to the tax they would have paid had they each filed as single taxpayers. This typically occurs when one spouse is either not working or earns significantly less than the other spouse. |
| Marriage penalty | the extra tax cost a married couple pays by filing a joint return relative to what they would have paid had they each filed as single taxpayers. This typically occurs when both spouses earn approximately the same amount of income. |
| Married filing jointly | one of five primary filing statuses. A taxpayer may file jointly if s/he is legally married as of the end of the year (or one spouse died during the year and the surviving spouse did not remarry) and both spouses agree to jointly file. Married couples filing joint returns combine their income and deductions and share joint and several liability for the resulting tax. |
| Married filing separately | one of five primary filing statuses. When married couples file separately, each spouse reports the income he or she received during the year and the deductions he or she paid on a tax return separate from the other spouse. |
| Maturity | the amount of time to the expiration date, or maturity date, of a debt instrument. The maturity of a debt instrument is generally the life of the instrument at which a payment of the face value is due or the instrument terminates. |
| Maturity value | the amount paid to a bondholder when the bond matures and the bondholder redeems the bond for cash. |
| Medicare Contribution Tax | For years after 2012, a new tax that equals 3.8% of the lesser of (a) net investment income or (b) the excess of modified adjusted gross income over $250,000 for married joint filers and surviving spouses, $125,000 for married separate filers, and $200,000 for other taxpayers. |
| Medicare tax | the Medical Health Insurance (MHI) tax. This tax helps pay medical costs for qualifying individuals. The Medicare tax rate for employees is 1.45% on salary or wages up to $200,000 ($125,000 for married filing separate; $250,000 of combined salary or wages for married filing joint) and is 2.35% on salary or wages in excess of $200,000 ($125,000 for married filing separate; $250,000 of combined salary or wages for married filing joint). For employers, the Medicare tax rate is 1.45% of employee salary or wages, regardless of the amount of salary or wages. Self-employed taxpayers pay both the employee and employer Medicare tax. |
| Merger | the acquisition by one (acquiring) corporation of the assets and liabilities of another (target) corporation. No new entity is created in the transaction. |
| Mid-month convention | a convention that allows owners of real property to take one-half of a month’s depreciation during the month when the property was placed in service and in the month it was disposed of. |
| Mid-quarter convention | a depreciation convention for tangible personal property that allows for one-half of a quarter’s worth of depreciation in the quarter of purchase and in the quarter of disposition. This convention must be used when more than 40% of tangible personal property is placed into service in the fourth quarter of the tax year. |
| Minimum tax credit | credit available in certain situations for the alternative minimum tax paid. The credit can be used only when the regular tax exceeds the tentative minimum tax. |
| Miscellaneous itemized deductions | deductions representing the sum of certain itemized deductions, such as unreimbursed employee business expenses, investment expenses, and tax preparation fees, that are subject to a special floor limitation. |
| Mixed-motive expenditures | activities that involve a mixture of business and personal objectives. |
| Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) | the current tax depreciation system for tangible personal and real property. Depreciation under MACRS is calculated by finding the depreciation method, the recovery period, and the applicable convention. |
| Municipal bond | the common name for state and local government debt. |
| Mutual fund | a diversified portfolio of securities owned and managed by a regulated investment company. |
| Negative basis adjustment | (for special basis adjustment purposes) the sum of the recognized loss and the amount of the basis increase made by an owner receiving the distribution. |
| Net capital gain | the net gain resulting when taxpayers combine net long-term capital gains with net short-term capital losses. |
| Net earnings from self-employment | the amount of earnings subject to self-employment income taxes. The amount is 92.35% of the net income from a taxpayer’s Schedule C (for self-employed taxpayers). |
| Net investment income | gross investment income reduced by deductible investment expenses. |
| Net long-term capital gain | the net gain resulting when taxpayers combine long-term capital gains and losses for the year. |
| Net long-term capital loss | the net loss resulting when taxpayers combine long-term capital gains and losses for the year. |
| Net operating loss (NOL) | the excess of allowable deductions over gross income. |
| Net operating loss carryback | the amount of a current year net operating loss that is carried back to offset income in a prior year. |
| Net operating loss carryover | the amount of a current year net operating loss that is carried forward for up to 20 years to offset taxable income in those years. |
| Net passive investment income | passive investment income less any expenses connected with producing it. |
| Net short-term capital gain | the net gain resulting when taxpayers combine short-term capital gains and losses for the year. |
| Net short-term capital loss | the net loss resulting when taxpayers combine short-term capital gains and losses for the year. |
| Net unearned income | unearned income in excess of a specified threshold amount of a child under the age of 19 or under the age of 24 if a full-time student. |
| Net unrealized built-in gain | the net gain (if any) an S corporation that was formerly a C corporation would recognize if it sold each asset at its fair market value. It is measured on the first day of the corporation’s first year as an S corporation. |
| Nexus | the connection between a business and a tax jurisdiction sufficient to subject the business to the tax jurisdiction’s tax system. Also, the connection that is required to exist between a jurisdiction and a potential taxpayer such that the jurisdiction asserts the right to impose a tax. |
| No-additional-cost services | a nontaxable fringe benefit that provides employer services to employees with little cost to the employer (e.g., airline tickets or phone service). |
| Nonacquiescence | issued after the IRS loses a trial-level or circuit court case when the IRS has decided to continue to litigate this issue. |
| Nonbusiness income | all income except for business income—generally investment income and rental income. |
| Nondeductible terminable interests | transfers of property interests to a spouse that do not qualify for a marital deduction, because the interest of the spouse terminates when some event occurs or after a specified amount of time and the property is then transferred to another person. |
| Nondomiciliary business | a business operating in a state other than its commercial domicile. |
| Nonperformance based compensation | compensation paid to an employee that does not depend on the employee’s performance or the corporation’s performance or success. It usually is straight salary. |
| Nonqualified deferred compensation | compensation provided for under a nonqualified plan allowing employees to defer compensation to a future period. |
| Nonqualified stock option | a type of stock option requiring employees to treat the bargain element from options exercised as ordinary income in the tax year options are exercised. Correspondingly, employers may deduct the bargain element as compensation expense in the tax year options are exercised. |
| Nonrecaptured net §1231 losses | a net §1231 loss that is deducted as an ordinary loss in one year and has not caused subsequent §1231 gain to be taxed as ordinary income. |
| Nonrecognition provisions | tax laws that allow tax payers to permanently exclude income from taxation or to defer recognizing realized income until a subsequent period. |
| Nonrecognition transaction | a transaction where at least a portion of the realized gain or loss is not currently recognized. |
| Nonrecourse debt | debt for which no partner bears any economic risk of loss. Mortgages on real property are a common form of nonrecourse debt. |
| Nonrefundable credits | tax credits that reduce a taxpayer’s gross tax liability but are limited to the amount of gross tax liability. Any credit not used in the current year is lost. |
| Nonresident alien | an individual who does not meet the criteria to be treated as a resident for U.S. tax purposes. |
| Nonservice partner | a partner who receives a partnership interest in exchange for property rather than services. |
| Nontaxable fringe benefit | an employer provided benefit that may be excluded from an employee’s income. |
| Not definitely related deductions | deductions that are not associated with a specific item or items of gross income in computing the foreign tax credit limitation. |
| Office examination | the second most common audit. As the name suggests, the IRS conducts these audits at the local IRS office. These audits are typically broader in scope and more complex than correspondence examinations. Small businesses, taxpayers operating sole proprietorships, and middle- to high-income individual taxpayers are more likely, if audited, to have office examinations. |
| Operating distributions | payments to the owners from an entity that represent a distribution of entity profits. Distributions generally fall into the category of operating distributions when the owners continue their interests in the entity after the distribution. |
| Operating income | the annual income from a trade or business or rental activity. |
| Operating loss | the annual loss from a trade or business or rental activity. |
| Option exercise | the use of a stock option to acquire employer stock at a specified price. |
| Ordinary asset | an asset created or used in a tax payer’s trade or business (e.g., accounts receivable or inventory) that generates ordinary income (or loss) on disposition. |
| Ordinary business income (loss) | a partnership’s or S corporation’s remaining income or loss after separately stated items are removed. It is also referred to as nonseparately stated income (loss). |
| Ordinary income property | property that if sold would generate income taxed at ordinary rates. |
| Ordinary and necessary | an expense that is normal or appropriate and that is helpful or conducive to the business activity. |
| Organization costs | costs associated with legally forming a partnership (such as attorneys’ and accountants’ fees). |
| Organizational expenditures | expenses that are (1) connected directly with the creation of a corporation or partnership, (2) chargeable to a capital account, and (3) generally amortized over 180 months (limited immediate expensing may be available). |
| Original issue discount | a type of bond issued for less than the maturity or face value of the bond. |
| Outbound transaction | a transaction conducted outside the United States by a U.S. person that is subject to U.S. taxation. |
| Outside tax basis | an investor’s tax basis in the stock of a corporation or the interest in a partnership or LLC. |
| PAL | an acronym for “passive activity loss.” Losses allocated to partners who are not material participants in the partnership are passive activity losses. |
| Parent-subsidiary controlled group | a form of controlled group consisting of one corporation that owns at least 80% of the voting power or stock value of another corporation on the last day of the year. |
| Partial liquidation | a distribution made by a corporation to shareholders that results from a contraction of the corporation’s activities. |
| Partnership agreement | an agreement among the partners in a partnership stipulating the partners’ rights and responsibilities in the partnership. |
| Partnership interest | an intangible asset reflecting the economic rights a partner has with respect to a partnership including the right to receive assets in liquidation of the partnership called a capital interest and the right to be allocated profits and losses called a profits interest. |
| Passive activity | an activity in which the taxpayer does not materially participate. |
| Passive activity income or loss | income or loss from an activity in which the taxpayer does not materially participate. |
| Passive activity loss rules | tax rules designed to limit taxpayers’ ability to deduct losses from activities in which they don’t materially participate against income from other sources. |
| Passive category income | foreign source personal holding company income such as interest, dividends, rents, royalties, annuities, and gains from sale of certain assets that is combined in computing the FTC limitation. |
| Passive investment income (PII) | royalties, rents, dividends, interest (including tax exempt interest), annuities, and gains from the sales or exchanges of stock or securities. |
| Passive investments | direct or indirect investments (other than through a C corporation) in a trade or business or rental activity in which the taxpayer does not materially participate. |
| Payment liability | liabilities of accrual method businesses for which economic performance occurs when the business actually pays the liability for, among others: worker’s compensation; tort; breach of contract or violation of law; rebates and refunds; awards, prizes, and jackpots; insurance, warranties, and service contracts provided to the business; and taxes. |
| Percentage depletion | a method of recovering the cost of a natural resource that allows a taxpayer to recover or expense an amount based on a statutorily determined percentage. |
| Permanent book-tax differences | items of income or deductions for either book purposes or for tax purposes during the year but not both. Permanent differences do not reverse over time so over the long run the total amount of income or deduction for the item is different for book and tax purposes. |
| Permanent establishment | generally, a fixed place of business through which an enterprise carries out its business. Examples include a place of management, a branch, an office, and a factory. |
| Permissible accounting method | accounting method allowed under the tax law. Permissible accounting methods are adopted the first time a taxpayer uses the method on a tax return. |
| Person | an individual, trust, estate, partnership, association, company, or corporation. |
| Personal exemption | a fixed deduction allowed for an individual taxpayer, and spouse if filing a joint tax return. |
| Personal expenses | expenses incurred for personal motives. Personal expenses are not deductible for tax purposes. |
| Personal holding companies | closely held corporations generating primarily investment income. |
| Personal holding company tax | penalty tax on the undistributed income of a personal holding company. |
| Personal property | all tangible property other than real property. |
| Personal property tax | a tax on the fair market value of all types of tangible and intangible property, except real property. |
| Phase-outs | limitations that gradually eliminate deductions, credits, or other adjustments to taxable income typically done ratably over a phase-out range (based on AGI or related income measure). |
| Point | one percent of the principal amount of a loan. A home buyer might pay points to compensate the lender for services or for a lower interest rate. |
| Portfolio investments | investments producing dividends, interest, royalties, annuities, or capital gains. |
| Positive basis adjustment | (for special basis adjustment purposes) the sum of the gain recognized by the owners receiving distributed property and the amount of any required basis reduction. |
| Post-termination transition period (PTTP) | the period that begins on the day after the last day of a corporation’s last taxable year as an S corporation and generally ends on the later of (a) one year after the last S corporation day, or (b) the due date for filing the return for the last year as an S corporation (including extensions). |
| Preferential tax rate | tax rates lower than the tax rate applied to ordinary income. |
| Preferentially taxed income | income taxed at a preferential rate such as long-term capital gains and qualified dividends. |
| Present interest | right to presently enjoy property or receive income from the property. |
| Present value | the concept that $1 today is worth more than $1 in the future. For example, assuming an investor can earn a 5% after-tax return, $1 invested today should be worth $1.05 in one year. Hence, $1 today is equivalent to $1.05 in one year. |
| Primary authority | official sources of the tax law generated by the legislative branch (i.e., statutory authority issued by Congress), judicial branch (i.e., rulings by the U.S. District Court, U.S. Tax Court, U.S. Court of Federal Claims, U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals, or U.S. Supreme Court), or executive/administrative branch (i.e., Treasury or IRS pronouncements). |
| Principal partner | a partner having a 5% interest or more in partnership capital or profits. |
| Principal residence | the main place of residence for a taxpayer during the taxable year. |
| Private activity bond | a bond issued by a municipality but proceeds of which are used to fund privately owned activity. |
| Private letter rulings | IRS pronouncements issued in response to a taxpayer request for a ruling on specific issues for the taxpayer. They are common for proposed transactions with potentially large tax implications. For the requesting taxpayer, a private letter ruling has very high authority. For all other taxpayers, private letter rulings have little authoritative weight. |
| Private nonoperating foundations | privately sponsored foundations that disburse funds to other charities. |
| Private operating foundations | privately sponsored foundations that actually fund and conduct charitable activities. |
| Probate | the process in the probate court of gathering property possessed by or titled in the name of a decedent at the time of death, paying the debts of the decedent and transferring the ownership of any remaining property to the decedent’s heirs. |
| Probate estate | property possessed by or titled in the name of a decedent at the time of death. |
| Procedural regulations | regulations that explain Treasury Department procedures as they relate to administering the Code. |
| Production of income | a for-profit activity that doesn’t rise to the level of a trade or business. |
| Profits interest | an interest in a partnership giving a partner the right to share in future profits but not the right to share in the current value of a partnership’s assets. Profits interests are generally not taxable in the year they are received. |
| Progressive tax rate structure | a tax rate structure that imposes an increasing marginal tax rate as the tax base increases. As the tax base increases, both the marginal tax rate and the taxes paid increase. |
| Proportional tax rate structure | also known as a flat tax, this tax rate structure imposes a constant tax rate throughout the tax base. As the tax base increases, the taxes paid increase proportionally. |
| Proposed regulations | regulations issued in proposed form; they do not carry the same authoritative weight as temporary or final regulations. All regulations are issued in proposed form first to allow public comment on them. |
| Public Law 86-272 | federal law passed by Congress that provides additional protection for sellers of tangible personal property against income tax nexus. |
| Publicly state traded corporations | corporations whose stock is publicly traded on a stock exchange. |
| Qualified debt | (for mortgage interest expense deduction purposes) the amount of debt on which qualified residence interest is paid. This includes debt up to $1,000,000 of acquisition indebtedness and up to $100,000 of home-equity indebtedness. |
| Qualified dividends | paid by domestic or certain qualified foreign corporations that are eligible for lower capital gains rates. |
| Qualified educational expenses | consist of tuition and related costs for enrolling the taxpayer, spouse, or a dependent at a postsecondary institution of higher education. |
| Qualified educational loans | loans whose proceeds are used to pay qualified education expenses. |
| Qualified employee discount | a nontaxable fringe benefit that provides employer goods at a discount (but not below the employer’s cost) and services to employees at up to a 20% discount. |
| Qualified moving expense reimbursement | a nontaxable fringe benefit that allows employers to pay moving-related expenses on behalf of employees. |
| Qualified nonrecourse financing | nonrecourse debt secured by real property from a commercial lender unrelated to the borrower. |
| Qualified production activities income (QPAI) | the net income from selling or leasing property that was manufactured in the United States. |
| Qualified replacement property | property acquired to replace property damaged or destroyed in an involuntary conversion. It must be of a similar or related use to the original property even if the replacement property is real property (rental real estate for rental real estate). |
| Qualified residence | the taxpayer’s principal residence and one other residence. |
| Qualified residence interest | interest paid on acquisition indebtedness and on home-equity indebtedness that is secured by a qualified residence. |
| Qualified retirement accounts | plans meeting certain requirements that allow compensation placed in the account to be tax deferred until the taxpayer withdraws money from the account. |
| Qualified retirement plans | employer-sponsored retirement plans that meet government-imposed funding and anti-discrimination requirements. |
| Qualified small business stock | stock received at original issue from a corporation with a gross tax basis in its assets both before and after the issuance of no more than $50,000,000 and with 80% of the value of its assets used in the active conduct of certain qualified trades or businesses. |
| Qualified terminable interest property (QTIP) | an exception to the general prohibition against claiming a marital deduction for a transfer of a terminable interest where the surviving spouse is entitled to all of the income from the property payable at least annually and no person has the power to appoint any part of the property to anyone other than the surviving spouse until the death of the surviving spouse. |
| Qualified transportation fringe benefit | a nontaxable fringe benefit provided by employers in the form of mass transit passes, parking, or vanpool benefits. |
| Qualified tuition plans (529 plans) | a state-sponsored program designed to help parents finance education expenses by generating tax-free income. 529 plans are administered by certain investment companies and are subject to contribution requirements and investment guidelines. |
| Qualifying child | an individual who qualifies as a dependent of a taxpayer by meeting a relationship, age, residence, and support test with respect to the taxpayer. |
| Qualifying relative | an individual who meets a relationship, support, and gross income test may qualify to be a dependent of another taxpayer. |
| Qualifying widow or widower | one of five primary filing statuses. Applies for up to two years after the year in which the taxpayer’s spouse dies (the tax payer files married filing jointly in the year of the spouse’s death) as long as the taxpayer remains unmarried and maintains a household for a dependent child. |
| Question of fact | a research question that hinges upon the facts and circumstances of the taxpayer’s transaction. |
| Question of law | a research question that hinges upon the interpretation of the law, such as interpreting a particular phrase in a code section. |
| Real property | land and structures permanently attached to land. |
| Real property tax | a tax on the fair market value of land and structures permanently attached to land. |
| Realization | gain or loss that results from an exchange of property rights in a transaction. |
| Realization principle | the proposition that income only exists when there is a transaction with another party resulting in a measurable change in property rights. |
| Realized gain or loss | the difference between the amount realized and the adjusted basis of an asset sold or otherwise disposed of. |
| Realized income | income generated in a transaction with a second party in which there is a measurable change in property rights between parties. |
| Reasonable in amount | an expenditure is reasonable when the amount paid is not extravagant nor exorbitant. |
| Recapture | the recharacterization of income from capital gain to ordinary income. |
| Recognition | gain or loss included in the computation of taxable income. |
| Recognized gain or loss | the gain or loss included in gross income on a taxpayer’s tax return. This is usually the realized gain or loss unless a nonrecognition provision applies. |
| Recourse debt | debt held by a partnership for which at least one partner has economic risk of loss. |
| Recovery period | a length of time prescribed by statute in which business property is depreciated or amortized. |
| Recurring item | an election under economic performance to currently deduct an accrued liability if the liability is expected to persist in the future and is either not material or a current deduction better matches revenue. |
| Refinance | when a taxpayer pays off a current loan with the proceeds of a second loan. |
| Refundable credits | credits that are not limited to the amount of the gross tax liability. If the credit exceeds the gross tax liability, the taxpayer receives a refund for the excess credit. |
| Regressive tax rate structure | a tax rate structure that imposes a decreasing marginal tax rate as the tax base increases. As the tax base increases, the taxes paid increase, but the marginal tax rate decreases. |
| Regulations | the Treasury Department’s official interpretation of the Internal Revenue Code. Regulations are the highest authority issued by the IRS. |
| Related-party transaction | financial activities among family members, among owners and their businesses, or among businesses owned by the same owners. |
| Remainder | the right to ownership of a property that transfers to a new owner, the remainderman, following a temporary interest. |
| Remainderman | the person entitled to a remainder interest. |
| Reorganization | a tax-deferred transaction (acquisition, disposition, recapitalization, or change of name or place of incorporation) that meets one of the seven statutory definitions found in §368(a)(1). |
| Research and experimentation costs | expenses for research including costs of research laboratories (salaries, materials, and other related expenses). Taxpayers can elect to amortize research and development costs over not less than 60 months from the time benefits are first derived from the research. |
| Residence-based jurisdiction | taxation of income based on the taxpayer’s residence. |
| Resident alien | an individual who is not a U.S. citizen but is treated as a resident for U.S. tax purposes. |
| Restricted stock | stock employees receive as compensation that may only be sold after the passage of time or after certain performance targets are achieved. Because employees are not entitled to immediately sell the restricted stock they receive, the value of the stock is generally not taxable to employees or deductible by employers until the selling restrictions lapse. |
| Return of capital | the portion of proceeds from a sale (or distribution) representing a return of the original cost of the underlying property. |
| Revenue procedures | second in administrative authoritative weight after regulations. Revenue procedures are much more detailed than regulations and explain in greater detail IRS practice and procedures in administering the tax law. Revenue procedures have the same authoritative weight as revenue rulings. |
| Revenue rulings | second in administrative authoritative weight after regulations. Revenue rulings address the specific application of the Code and regulations to a specific factual situation. Revenue rulings have the same authoritative weight as revenue procedures. |
| Reverse hybrid entity | a “check-the-box” entity owned by multiple persons for which corporation status is elected. |
| Reverse triangular merger | an acquisition in which an acquisition subsidiary of the acquiring corporation merges into the acquired (target) corporation, after which the acquired corporation becomes a subsidiary of the acquiring corporation. |
| Reversion | terms by which ownership of property returns to the original owner following a temporary interest. |
| Rollover | a transfer of funds from a qualified retirement plan to another qualified retirement plan, from a qualified retirement plan to a Roth or traditional IRA, or from a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA. |
| Roth 401(k) | a type of defined contribution plan that allows employees to contribute on an after-tax basis and receive distributions tax free. |
| Roth IRA | an individually managed retirement plan permitting individuals to contribute on an after-tax basis and receive distributions tax free. |
| Royalties | payments taxpayers receive for allowing others to use their tangible or intangible property. |
| S corporation | a corporation under state law that has elected to be taxed under the rules provided in subchapter S of the Internal Revenue Code. Under subchapter S, an S corporation is taxed as a flow-through entity. |
| Safe-harbor provision | provision of the tax law that reduces or eliminates a taxpayer’s liability under the law if the taxpayer meets certain requirements. |
| Sales tax | a tax imposed on the retail sales of goods (plus certain services). Retailers are responsible for collecting and remitting the tax; typically sales tax is collected at the point of sale. |
| Same-day sale | a phrase used to describe a situation where a taxpayer exercises stock options and then immediately sells the stock received through the option exercise. |
| Schedule C | a schedule on which a taxpayer reports the income and deductions for a sole-proprietorship. |
| Schedule K | a schedule filed with a partnership’s annual tax return listing its ordinary income (loss) and its separately stated items. |
| Schedule M adjustments | book-tax differences that corporations report on the Schedule M-1 or M-3 of Form 1120 as adjustments to book income to reconcile to taxable income. |
| Schedule M-1 | a schedule on Form 1120 that reconciles book income to taxable income before special deductions. Book-tax differences are reported in a general way. |
| Schedule M-3 | a schedule on Form 1120 that reconciles book income to taxable income for corporations with total assets of $10 million or more. The schedule M-3 includes much more detail than the Schedule M-1, including identifying whether each book-tax difference is a temporary difference or a permanent book-tax difference. |
| Secondary authority | unofficial tax authorities that interpret and explain the primary authorities, such as tax research services, tax articles, newsletters, and textbooks. Secondary authorities may be very helpful in understanding a tax issue, but they hold little weight in a tax dispute (hence, the term unofficial tax authorities). |
| Secured loan | a loan for which property is used as collateral for the loan. If the loan goes into default, the lender is only allowed to take possession of the property securing the loan. |
| Security | a financial instrument including an equity interest in business organizations and creditor interests such as savings accounts, notes, and bonds. |
| Self-employment taxes | Social Security and Medicare taxes paid by the self-employed on a taxpayer’s net earnings from self-employment. For self-employed taxpayers, the terms “self-employment tax” and “FICA tax” are synonymous. |
| SEP IRA | a simplified employee pension that can be administered through an individual retirement account. |
| Separate tax return | a state tax return methodology requiring that each related entity with nexus files a separate tax return. |
| Separately stated items | income, expenses, gains, losses, credits, and other items that are excluded from a partnership’s or S corporation’s operating income (loss) and disclosed to partners in a partnership or shareholders of an S corporation separately because their tax effects may be different for each partner or shareholder. |
| Serial gift | transfer tax strategy that uses the annual exclusion to convert a potentially large taxable transfer into a tax-exempt transfer by dividing it into multiple intervivos gifts spread over several periods or donees. |
| Service partner | partners who receive their partnership interest by contributing services rather than cash or property. |
| Settlement statement | a statement that details the monies paid out and received by the buyer and seller in a real estate transaction. |
| Short-term capital gains or losses | gains or losses from the sale of capital assets held for one year or less. |
| Simple trust | a trust that must distribute all accounting income currently and cannot make charitable contributions. |
| Sin taxes | taxes imposed on the purchase of goods (e.g., alcohol, tobacco products, etc.) that are considered socially less desirable. |
| Single | one of five primary statuses available. A taxpayer files as single if s/he is unmarried as of the end of the year and does not qualify for any of the other filing statuses. A taxpayer is considered single if s/he is unmarried or legally separated from his or her spouse under a divorce or separate maintenance decree. |
| Single member LLC | a limited liability company with only one member. Single member LLCs with individual owners are taxed as sole proprietorships and as disregarded entities otherwise. |
| Social Security Tax | the Old Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) tax. The tax is intended to provide basic pension coverage for the retired and disabled. Employees pay Social Security tax at a rate of 6.2% (4.2% in 2011 and 2012) on the wage base (employers also pay 6.2%). Self-employed taxpayers are subject to a Social Security tax at a rate of 12.4% (10.4% in 2011 and 2012) on their net earnings from self-employment. The base on which Social Security taxes are paid is limited to an annually determined amount of wages and/or net earnings from self-employment. |
| Sole proprietorship | a business entity that is not legally separate from the individual owner of the business. The income of a sole proprietorship is taxed and paid directly by the owner. |
| Solicitation | selling activities or activities ancillary to selling that are protected under Public Law 86-272. |
| Source-based jurisdiction | taxation of income based on where the income is earned. |
| Special allocations | allocations of income, gain, expense, or loss, etc., that are allocated to the owners of an entity in a manner out of proportion with the owners’ interests in the entity. Special allocations can be made by entities treated as partnerships for federal income tax purposes. |
| Special basis adjustment | an optional (sometimes mandatory) election to adjust the entity asset bases as a result of an owner’s disposition of an interest in the entity or of distributions from the entity to its owners. |
| Specific identification method | an elective method for determining the cost of an asset sold. Under this method, the taxpayer specifically chooses the assets that are to be sold. |
| Split-gift election | election that allows spouses to treat all gifts made in a year as if each spouse made one-half of each gift. |
| Spot rate | the foreign currency exchange rate on a specific day. |
| Standard deduction | a fixed deduction offered in lieu of itemized deductions. The amount of the standard deduction depends on the taxpayer’s filing status. |
| Spousal IRA | an IRA account for the spouse with the lesser amount of earned income. Contributions in this account belong to this spouse no matter where the funds for the contribution came from. |
| Stare decisis | a doctrine meaning that a court will rule consistently with (a) its previous rulings (i.e., unless, due to evolving interpretations of the tax law over time, it decides to overturn an earlier decision) and (b) the rulings of higher courts with appellate jurisdiction (i.e., the courts its cases are appealed to). |
| Start-up costs | expenses that would be classified as business expenses except that the expenses are incurred before the business begins. These costs are generally capitalized and amortized over 180 months, but limited immediate expensing may be available. |
| State tax | a tax imposed by one of the 50 U.S. states. |
| Statements on Standards for Tax Services (SSTS) | standards of practice for tax professionals issued by the AICPA. Currently, there are seven SSTS that describe the tax professional standards when recommending a tax return position, answering questions on a tax return, preparing a tax return using data supplied by a client, using estimates on a tax return, taking a tax return position inconsistent with a previous year’s tax return, discovering a tax return error, and giving tax advice to taxpayers. |
| Static forecasting | the process of forecasting tax revenues based on the existing state of transactions while ignoring how taxpayers may alter their activities in response to a tax law change. |
| Statute of limitations | defines the period in which the taxpayer can file an amended tax return or the IRS can assess a tax deficiency for a specific tax year. For both amended tax returns filed by a taxpayer and proposed tax assessments by the IRS, the statute of limitations generally ends three years from the later of (1) the date the tax return was actually filed or (2) the tax return’s original due date. |
| Step-transaction doctrine | judicial doctrine that allows the IRS to collapse a series of related transactions into one transaction to determine the tax consequences of the transaction. |
| Stock dividend | a dividend made by a corporation of its own stock. |
| Stock-for-stock acquisition | an exchange of solely voting stock by the acquiring corporation in exchange for stock of the target corporation, after which the acquiring corporation controls (owns 80-percent-or-more of ) the target corporation. Often referred to as a “Type B reorganization.” |
| Stock redemption | a property distribution made to shareholders in return for some or all of their stock in the distributing corporation that is not in partial or complete liquidation of the corporation. |
| Stock split | a stock redemption in which a corporation exchanges a ratio of shares of stock (e.g., 2 for 1) for each share held by the shareholder. |
| Strike price | see exercise price. |
| Structural tax rate | the tax rate computed by dividing a company’s income tax provision adjusted for nonrecurring permanent differences by its pretax income from continuing operations. |
| Student loans | loans where the proceeds are used for qualified educational expenses, but do not include home-equity loans. |
| Subchapter K | the portion of the Internal Revenue Code dealing with partnerships tax law. |
| Subchapter S | the portion of the Internal Revenue Code containing tax rules for S corporations and their shareholders. |
| Subpart F income | income earned by a controlled foreign corporation that is not eligible for deferral from U.S. taxation. |
| Substance-over-form doctrine | judicial doctrine that allows the IRS to consider the transaction’s substance regardless of its form and, where appropriate, reclassify the transaction according to its substance. |
| Substantial authority | the standard used to determine whether a tax practitioner may recommend and a taxpayer may take a tax return position without being subject to IRS penalty under IRC §6694 and IRC §6662, respectively. A good CPA evaluates whether supporting authority is substantial or not based upon the supporting and opposing authorities’ weight and relevance. Substantial authority suggests that the probability that the taxpayer’s position is sustained upon audit or litigation is in the 35 to 40 percent range or above. |
| Substantial basis reduction | negative basis adjustment of more than $250,000 resulting from a distribution from an entity taxed as a partnership to its owners. |
| Substantial built-in loss | exists when a partnership’s adjusted basis in its property exceeds the property’s fair market value by more than $250,000 when a transfer of an interest occurs. |
| Substantially appreciated inventory | (for partnership disproportionate distributions purposes) inventory with a fair market value that exceeds its basis by more than 120%. |
| Substituted basis | the transfer of the tax basis of stock or other property given up in an exchange to stock or other property received in return. |
| Substitution effect | one of the two basic responses that a taxpayer may have when taxes increase. The substitution effect predicts that, when taxpayers are taxed more, rather than work more, they will substitute nontaxable activities (e.g., leisure pursuits) for taxable ones because the marginal value of taxable activities has decreased. |
| Sufficiency | a standard for evaluating a good tax system. Sufficiency is defined as assessing the aggregate size of the tax revenues that must be generated and ensuring that the tax system provides these revenues. |
| Syndication costs | costs partnerships incur to promote the sale of partnership interests to the public. Syndication expenses must be capitalized and are not amortizable. |
| Tacks | the adding on of the transferor’s holding period of property to the transferee in a tax-deferred exchange. |
| Tax | a payment required by a government that is unrelated to any specific benefit or service received from the government. |
| Tax accounting balance sheet | a balance sheet that records a company’s assets and liabilities at their tax bases instead of their financial accounting bases. |
| Tax avoidance | the legal act of arranging one’s transactions or affairs to reduce taxes paid. |
| Tax base | the item that is being taxed (e.g., purchase price of a good, taxable income, etc.). |
| Tax basis | the amount of a taxpayer’s unrecovered cost of or investment in an asset. |
| Tax benefit rule | holds that a refund of an amount deducted in a previous period is only included in income to the extent that the deduction reduced taxable income. |
| Tax bracket | a range of taxable income taxed at a specified rate. |
| Tax capital accounts | partners’ capital accounts initially determined using the tax basis of contributed property and maintained using tax accounting income and expense recognition principles. |
| Tax carryforwards | tax deductions or credits that cannot be used on the current year tax return and that can be carried forward to reduce taxable income or taxes payable in a future year. |
| Tax contingency reserve | a company’s reserve for taxes it has not paid, but it may pay in the future, for uncertain tax positions taken on the current and prior year income tax returns. |
| Tax Court allocation method | allocates expenses associated with rental use of the home between to rental use and personal use. Property taxes and mortgage interest are allocated to rental use of the home based on the ratio of the number of rental use days to the total days in the year. All other expenses are allocated to rental use based on the ratio of the number of rental use days to total days the property was used during the year. |
| Tax credits | items that directly reduce a taxpayer’s tax liability. |
| Tax evasion | the willful attempt to defraud the government (i.e., by not paying taxes legally owed). Tax evasion falls outside the confines of legal tax avoidance. |
| Tax haven | generally, a country offering very favorable tax laws for foreign businesses and individuals. |
| Tax rate | the level of taxes imposed on the tax base, usually expressed as a percentage. |
| Tax rate schedule | a schedule of progressive tax rates and the income ranges to which the rates apply that a taxpayer may use to compute her gross tax liability. |
| Tax shelter | an investment or other arrangement designed to produce tax benefits without any expectation of economic profits. |
| Tax tables | IRS-provided tables that specify the federal income tax liability for individuals with taxable income within a specific range. The tables differ by filing status and reflect tax rates that increase with taxable income. |
| Tax treaties | agreements negotiated between countries that describe the tax treatment of entities subject to tax in both countries (e.g., U.S. citizens earning investment income in Spain). The U.S. president has the authority to enter into a tax treaty with another country after receiving the Senate’s advice. |
| Tax year | a fixed period in which a business reports income and deductions generally referred to as an accounting period. |
| Taxable estate | adjusted gross estate reduced by the marital deduction and the charitable deduction. |
| Taxable fringe benefit | a noncash fringe benefit provided by employers to an employee that is included in taxable income (e.g., auto allowance or group-term life over $50,000). |
| Taxable gifts | the amount left after adjusting current gifts for gift splitting, annual exclusions, the marital deduction, and the charitable deduction. |
| Taxable income | the tax base for the individual income tax. |
| Taxable temporary differences | book-tax differences that will result in taxable amounts in future years when the related deferred tax liability is settled. |
| Technical advice memorandum | ruling issued by the IRS national office, requested by an IRS agent, and generally for a completed transaction. |
| Temporary book-tax differences | book-tax differences that reverse over time such that, over the long-term, corporations recognize the same amount of income or deductions for the items on their financial statements as they recognize on their tax returns. |
| Temporary regulations | regulations issued with a limited life (three years for regulations issued after November 20, 1988). During their life, temporary regulations carry the same authoritative weight as final regulations. |
| Tenancy by the entirety | ownership by husband and wife similar to joint tenancy with right of survivorship. |
| Tenancy in common | ownership in which owners hold divided rights to property and have the ability to transfer these rights during their life or upon their death. |
| Tentative minimum tax | the tax on the AMT tax base under the alternative minimum tax system. |
| Term insurance | a form of life insurance without an investment or savings feature. |
| Terminable interest | a right to property that terminates at a specified time or upon the occurrence of a specified event, such as a life estate. |
| Testamentary transfers | transfers that take place upon the death of the donor. |
| Third-party intermediaries | people or organizations that facilitate the transfer of property between taxpayers in a like-kind exchange. Typically, the intermediary receives the cash from selling the property received from the taxpayer and uses it to acquire like-kind property identified by the taxpayer. |
| Throwback rule | the rule that sales into a state without nexus are included with sales from the state the property was shipped from. |
| Topical tax service | a tax service arranged by subject (i.e., topic). For each topic, topical services identify tax issues that relate to each topic, and then explain and cite authorities relevant to the issue (code sections, regulations, court cases, revenue rulings, etc.). |
| Trade or business | a profit-motivated activity characterized by a sustained, continuous, high level of individual involvement or effort. |
| Trade show rule | a rule that permits businesses to have physical presence at conventions and trade shows for up to two weeks a year without creating nexus. |
| Traditional 401(k) | a popular type of defined contribution plan with before-tax employee and employer contributions and taxable distributions. |
| Traditional IRA | an individually managed retirement account with deductible contributions and taxable distributions. |
| Transfer taxes | taxes on the transfer of wealth from one taxpayer to another. The estate and gift taxes are two examples of transfer taxes. |
| Travel expenses | expenditures incurred while “away from home overnight,” including the cost of transportation, meals, lodging, and incidental expenses. |
| Treasury bond | a debt instrument issued by the U.S. Treasury at face value, at a discount, or at a premium, with a set interest rate and maturity date that pays interest semiannually. Treasury bonds have terms of 30 years. |
| Treasury note | a debt instrument issued by the U.S. Treasury at face value, at a discount, or at a premium, with a set interest rate and maturity date that pays interest semiannually. Treasury notes have terms of 2, 5, or 10 years. |
| Triple i agreement | a 10-year agreement filed with the IRS in which the taxpayer agrees to notify the IRS that he or she has acquired a prohibited interest after waiving the family attribution rules in a complete redemption. |
| Trust | fiduciary entity created to hold and administer the property for other persons according to the terms of a trust instrument. |
| Trustee | the person responsible for administering a trust. |
| Uncertain tax positions | a tax return position for which a corporation does not have a high degree of certainty as to its tax consequences. |
| Underpayment penalty | the penalty that applies when taxpayers fail to adequately prepay their tax liability. The underpayment penalty is determined by multiplying the federal short-term interest rate plus three percentage points by the amount of tax underpayment per quarter. |
| Unearned income | income from property that accrues as time passes without effort on the part of the owner of the property. |
| Unemployment tax | the tax that pays for temporary unemployment benefits for individuals terminated from their jobs without cause. |
| Unfavorable book-tax difference | any book-tax difference that requires an add back to book income in computing taxable income. This type of adjustment is unfavorable because it increases taxable income relative to book income. |
| Unified credit | amount of credit based on the exemption equivalent designed to prevent transfer taxation of smaller cumulative transfers. |
| Uniform cost capitalization rules (UNICAP rules) | specify that inventories must be accounted for using full absorption rules to allocate the indirect costs of productive activities to inventory. |
| Unitary tax return | a state tax return methodology requiring the activities of a group of related entities to be reported on a single tax return. The criteria for determining whether a group of entities must file a unitary tax return are functional integration, centralization of management, and economies of scale. |
| Unrealized receivables | any rights to receive payment for (1) goods delivered, or to be delivered, or (2) services rendered, or to be rendered. Unrealized receivables also include other assets to the extent that they would produce ordinary income if sold for their fair market value. |
| Unrecaptured §1250 gain | a gain from the sale of real estate held by a noncorporate taxpayer for more than one year in a trade or business or as rental property attributable to tax depreciation deducted at ordinary tax rates. This gain is taxable at a maximum 25% capital gains rate. |
| Unrecognized tax benefit | a reserve for tax benefits related to a tax position for which the corporation does not have a high degree of certainty as to its sustainability on audit or in a court of law. |
| U.S. Circuit Courts of Appeal | the first level of appeals courts after the trial-level courts. There are 13 U.S. Circuit Courts of Appeal; one for the Federal Circuit and 12 assigned to hear cases that originated from a specific circuit (e.g., the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals only hears cases originating within the 11th Circuit). |
| U.S. Constitution | the founding law of the United States, ratified in 1789. |
| U.S. Court of Federal Claims | one of the three trial-level courts. It is a national court that only hears monetary claims against the federal government. |
| U.S. District Court | one of three trial-level courts. It is the only court that allows a jury trial. There is at least one district court in each state. |
| U.S. savings bonds | debt instruments issued by the U.S. Treasury at face value or at a discount, with a set maturity date. Interest earned from U.S. bonds is paid either at maturity or when the bonds are converted to cash before maturity. |
| U.S. Supreme Court | the highest court in the United States. The Supreme Court hears only a few tax cases a year with great significance to a broad cross-section of taxpayers or cases litigating issues in which there has been disagreement among the circuit courts. For most tax cases, the Supreme Court refuses to hear the case (i.e., the writ of certiorari is denied) and, thus, litigation ends with the circuit court decision. |
| U.S. Tax Court | a national court that only hears tax cases and where the judges are tax experts. The U.S. Tax Court is the only court that allows tax cases to be heard before the taxpayer pays the disputed liability and the only court with a small claims division (hearing claims involving disputed liabilities of $50,000 or less). |
| Use tax | a tax imposed on the retail price of goods owned, possessed, or consumed within a state that were not purchased within the state. |
| Valuation allowance | the portion of a deferred tax asset for which management determines it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized on a future tax return. |
| Value-added tax | a tax imposed on the producer of goods (and services) on the value of goods (services) added at each stage of production. Value-added taxes are common in Europe. |
| Vertical equity | one of the dimensions of equity. Vertical equity is achieved when taxpayers with greater ability to pay tax, pay more tax relative to taxpayers with a lesser ability to pay tax. |
| Vest | to become legally entitled to receive a particular benefit without risk of forfeiture; to gain ownership. |
| Vesting date | the date on which the taxpayer becomes legally entitled to receive a particular benefit without risk of forfeiture. |
| Vesting period | period of employment over which employees earn the right to own and exercise stock options. |
| Wash sale | the sale of an investment if that same investment (or substantially identical investment) is purchased within 30 days before or after the sale date. Losses on wash sales are deferred. |
| Wherewithal to pay | the ability or resources to pay taxes due from a particular transaction. |
| Whole life insurance | a form of life insurance with an investment or savings component. |
| Willing-buyer, willing-seller rule | the guideline for determining fair market value as “the price at which such property would change hands between a willing buyer and a willing seller, neither being under any compulsion to buy or to sell, and both have reasonable knowledge of the relevant facts.” |
| Withholdings | taxes collected and remitted to the government by an employer from an employee’s wages. |
| Working condition fringe benefit | a nontaxable fringe benefit provided by employers that would be deductible as an ordinary and necessary business expense if paid by an employee (e.g., reimbursement for professional dues). |
| Writ of certiorari | a document filed to request the U.S. Supreme Court to hear a case. |
| Zero coupon bond | a type of bond issued at a discount that pays interest only at maturity. |