 |  Behavioral Statistics in Action, 3/e Mark W. Vernoy,
Palomar College
Diana J. Kyle,
Fullerton College
Correlation
Glossary
| Coefficient of determination | is the effect size. It is the part of the variance of one variable that can be explained or attributed to the variance of a related variable. Coefficient of determination = r2
|  |  |  | | Correlation | is a relationship between two variables whereby a change in one variable is associated with a congruent change in the other.
|  |  |  | | Correlation coefficient | is a measure that indicates the relationship between two variables. The Pearson product moment correlation coefficient symbol is r and the range is -1.00 to +1.00. The sign of the coefficient indicates the direction of the relationship and the number indicates the size of the relationship.
A positive correlation represents the situation where both variables vary in the same direction and a negative correlation indicates a situation where the variables vary in opposite directions. A correlation coefficient near +1.00 or -1.00 is a large correlation, whereas a correlation close to 0 is small. 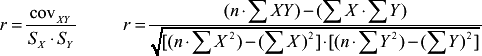 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/gloss8_1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/gloss8_1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
|  |  |  | | Covariance | is basically a number that represents the degree to which two different variables change together. 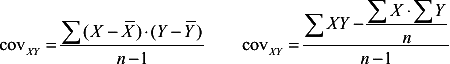 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/gloss8_2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0767422759/35691/gloss8_2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
|  |  |  | | Critical value | refers to a numerical value, according to the value of the degrees of freedom that is used as a decision point. In statistical analyses, critical values are based on the probability of a certain outcome occurring merely by chance. When the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value, it is said to be statistically significant.
df = n - 2
|  |  |  | | Scatterplots | are a type of graph in which two sets of data are displayed, one along the abscissa and the other along the ordinate. The points are plotted where corresponding X and Y values intersect and show the direction and degree of correlation between two variables.
|
|



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education

 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education