 |
1 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image153.gif','popWin', 'width=309,height=307,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image153.gif','popWin', 'width=309,height=307,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a>
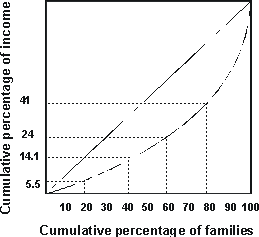
According to the Lorenz curve shown, the middle quintile of families earn: |
|  | A) | 14.1 percent of the income. |
|  | B) | 24 percent of the income. |
|  | C) | 9.9 percent of the income. |
|  | D) | 38.1 percent of the income. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image152.gif','popWin', 'width=383,height=310,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image152.gif','popWin', 'width=383,height=310,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
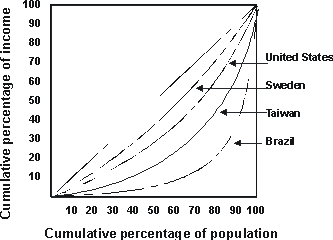
Which of the following statements can be made based on the above Lorenz curve? |
|  | A) | Income is more equally distributed in Sweden than it is in Brazil. |
|  | B) | Income is more equally distributed in Brazil than it is in the United States. |
|  | C) | Income is more equally distributed in Taiwan than it is in Sweden. |
|  | D) | Income is more equally distributed in the United States than it is in Sweden. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Other things equal, tax cuts favoring the poor and increases in funding for government programs favoring the poor would be expected to: |
|  | A) | increase income inequality, causing the Lorenz curve to bow in toward the diagonal line. |
|  | B) | decrease income inequality, causing the Lorenz curve to bow in toward the diagonal line. |
|  | C) | increase income inequality, causing the Lorenz curve to bow out away from the diagonal line. |
|  | D) | decrease income inequality, causing the Lorenz curve to bow out away from the diagonal line. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
The share distribution of income: |
|  | A) | is an absolute measure of income. |
|  | B) | is a relative measure of income. |
|  | C) | takes into account changes in the standard of living. |
|  | D) | has elements of absolute and relative measures. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
In the United States and most other developed countries, the largest class is the: |
|  | A) | lower class, defined as all those living in poverty. |
|  | B) | lower class, defined as the poorest third of the population. |
|  | C) | middle class. |
|  | D) | upper class. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
The way poverty is defined in United States makes this measure: |
|  | A) | is an absolute measure. |
|  | B) | is a relative measure. |
|  | C) | both a relative and absolute measure. |
|  | D) | an unfair measure. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image154.gif','popWin', 'width=331,height=310,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image154.gif','popWin', 'width=331,height=310,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a>
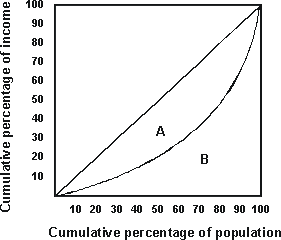
Refer to the graph above. If the area of region A is 0.17 and the area of region B is 0.33, then the Gini coefficient is: |
|  | A) | 0.0561. |
|  | B) | 0.34. |
|  | C) | 0.515. |
|  | D) | 1.94. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Since there is a tradeoff between equality and efficiency: |
|  | A) | redistribution of income improves economic equality without reducing economic efficiency. |
|  | B) | income is distributed equally in an efficient economy. |
|  | C) | the optimal level of redistribution involves a value judgment. |
|  | D) | the optimal level of redistribution is zero. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
A primary purpose of the 1996 Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act was to: |
|  | A) | reduce the negative incentive effects of welfare. |
|  | B) | replace all cash assistance programs with non-cash assistance, like food stamps. |
|  | C) | allow individuals to remain on welfare for a longer time period. |
|  | D) | guarantee that no one receives assistance unless they are working. |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
When most people talk about believing in equality of income, they mean they believe in equality of __________. |
|  | A) | effort |
|  | B) | opportunity |
|  | C) | skills and talents |
|  | D) | wealth |
 |