 |
1 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image190.gif','popWin', 'width=250,height=275,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image190.gif','popWin', 'width=250,height=275,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
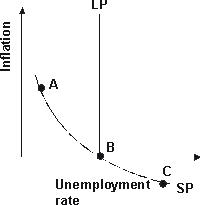
Refer to the graph above. At points A, B, and C, expected inflation is: |
|  | A) | greater than actual inflation. |
|  | B) | equal to actual inflation. |
|  | C) | less than actual inflation. |
|  | D) | zero. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image191.gif','popWin', 'width=305,height=290,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/olc/dl/107057/Image191.gif','popWin', 'width=305,height=290,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
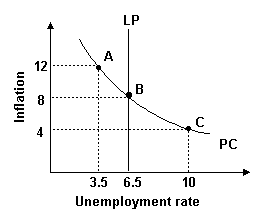
Refer to the graph above. Suppose an economy begins at point B but then adopts an expansionary monetary policy. In the short run, this policy would most likely: |
|  | A) | reduce inflation to 4 percent and raise unemployment to 10 percent. |
|  | B) | reduce inflation to 4 percent and reduce unemployment to 3.5 percent. |
|  | C) | raise inflation to 12 percent and raise unemployment to 10 percent. |
|  | D) | raise inflation to 12 percent and reduce unemployment to 3.5 percent. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
If lenders and borrowers correctly anticipate inflation, then inflation will hurt: |
|  | A) | lenders. |
|  | B) | borrowers. |
|  | C) | both lenders and borrowers. |
|  | D) | neither lenders nor borrowers. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Suppose inflation in 2001, 2002, and 2003 was 7 percent, 8 percent, and 9 percent respectively. If people use this information and all other available information about the state of the economy and expect inflation to be 3 percent as a result, then their expectations are best described as: |
|  | A) | adaptive. |
|  | B) | rational. |
|  | C) | extrapolative. |
|  | D) | perfect. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
The quantity theory of money implies that: |
|  | A) | the price level varies in response to changes in the quantity of money. |
|  | B) | the quantity of output produced in an economy varies in response to changes in the price level. |
|  | C) | the velocity of money varies in response to the quantity of output produced in an economy. |
|  | D) | the price level varies in response to changes in the velocity of money. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
According to institutional theories of inflation: |
|  | A) | the economy is made up of perfectly competitive markets. |
|  | B) | expected inflation always equals actual inflation. |
|  | C) | social forces and explicit contracts play a large role in price determination in the short run. |
|  | D) | there is no link between money supply and inflation. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
According to the quantity theory of money: |
|  | A) | changes in PQ cause changes in MV. |
|  | B) | changes in MV cause changes in PQ. |
|  | C) | changes in PQ can cause changes in MV and vice versa. |
|  | D) | PQ and MV are unrelated. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
If expectations are adaptive, then they will depend on: |
|  | A) | the forecasts of economic models. |
|  | B) | what has happened in the past. |
|  | C) | what is happening in the current economic environment. |
|  | D) | the continuation of past trends. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
According to the insider/outsider model, those workers first to be hired during a recovery tend to be: |
|  | A) | insiders. |
|  | B) | outsiders. |
|  | C) | union members. |
|  | D) | owners. |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
Institutional theories of inflation argue that the unemployment costs of fighting inflation: |
|  | A) | are borne primarily by outsiders because insiders have greater job security. |
|  | B) | are borne primarily by insiders because outsiders have greater job security. |
|  | C) | are negligible. |
|  | D) | are evenly distributed among workers. |
 |