 |
1 |  | 
An analytical guide or tool for making decisions in situations involving interdependence is known as... |
|  | A) | a payoff table. |
|  | B) | strategic entry deterrence. |
|  | C) | game theory. |
|  | D) | a decision node. |
|  | E) | limit pricing. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
Situations in which competing firms must make their individual decisions without knowing the decisions of their rivals are known as... |
|  | A) | sequential decisions. |
|  | B) | simultaneous decision games. |
|  | C) | dominated strategies. |
|  | D) | strategic deterrence. |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
When both players have dominant strategies and play them, the result is: |
|  | A) | dominant strategy equilibrium |
|  | B) | Nash equilibrium |
|  | C) | strategic stability |
|  | D) | successive elimination of dominated strategies |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Nash decisions are likely to be chosen because... |
|  | A) | Nash decisions are strategically stable. |
|  | B) | they represent a set of actions for which all managers are choosing their best actions given the actions chosen by their rivals. |
|  | C) | both players have dominant strategies and play them. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both a and c |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
The next four questions refer to the following: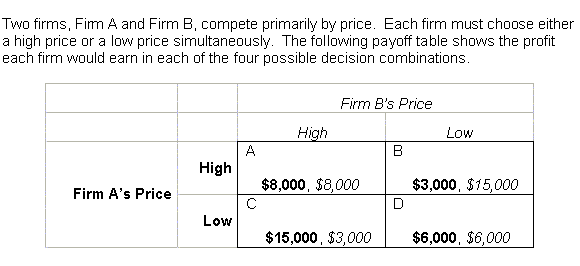 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_05.gif','popWin', 'width=630,height=336,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_05.gif','popWin', 'width=630,height=336,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
What is Firm A's dominant strategy? |
|  | A) | Price high. |
|  | B) | Price low. |
|  | C) | Firm A does not have a dominant strategy. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
What is Firm B's dominant strategy? |
|  | A) | Price high. |
|  | B) | Price low. |
|  | C) | Firm B does not have a dominant strategy. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
What do you predict will be the outcome of this simultaneous decision? |
|  | A) | Image Here |
|  | B) | Image Here |
|  | C) | Image Here |
|  | D) | Image Here |
|  | E) | Impossible to tell from the information given in the table. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Is this decision a prisoners' dilemma? |
|  | A) | Yes, since when both firms choose their dominant strategies they each are worse off than if they could cooperate. |
|  | B) | Yes, since when both firms choose their dominant strategies they each are better off then if they could cooperate. |
|  | C) | No, since when both firms choose their dominant strategies they each are worse off than if they could cooperate. |
|  | D) | No, since the likely outcome is strategically stable. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
The next seven questions refer to the following payoff table.
What dominant strategies exist in the original payoff table above? |
|  | A) | Firm A Medium |
|  | B) | Firm B High |
|  | C) | Firm B Medium |
|  | D) | Firm A Low |
|  | E) | There are no dominant strategies. |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
Using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies, which strategies, if any, are eliminated after the first round? |
|  | A) | Firm A High |
|  | B) | Firm B Low |
|  | C) | both a and b |
|  | D) | No strategies are eliminated after the first round. |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
After the first round of elimination, are there any more dominated strategies to eliminate? If so, which one(s)? |
|  | A) | Firm A low |
|  | B) | Firm B High |
|  | C) | Firm B Medium |
|  | D) | both b and c |
|  | E) | Neither firm has dominated strategies after the first round. |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
After the first round of elimination, are there any dominant strategies? If so, which one(s)? |
|  | A) | Firm A High |
|  | B) | Firm A High |
|  | C) | Firm B Medium |
|  | D) | both a and c |
|  | E) | Neither firm has a dominant strategy after the first round. |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
Which cell in the payoff table represents the likely outcome of this advertising game? |
|  | A) | Cell A (Low, Low) |
|  | B) | Cell C (Low, High) |
|  | C) | Cell I (High, High) |
|  | D) | Cell E (Medium, Medium) |
|  | E) | Cell H (High, Medium) |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
Is the likely outcome a Nash equilibrium? |
|  | A) | Yes, since the outcome represents the mutually best pair of decisions. |
|  | B) | No, since the outcome represents the mutually best pair of decisions. |
|  | C) | Yes, since this situation is a prisoners' dilemma. |
|  | D) | No, since the outcome does not represent the mutually best pair of decisions. |
|  | E) | Unable to tell from the information given. |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
Is the likely outcome strategically stable? |
|  | A) | Yes, since both firms applied their dominant strategies. |
|  | B) | No, since this situation represents a prisoners' dilemma. |
|  | C) | Yes, since neither firm can, by itself, make a different decision and reach a higher level of profit. |
|  | D) | No, since both firms can, unilaterally, make a different decision and reach a higher level of profit. |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
In every prisoners' dilemma situation, cooperation is... |
|  | A) | impossible. |
|  | B) | possible. |
|  | C) | reduces the payoff to all players. |
|  | D) | both a and c. |
|  | E) | both b and c. |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
In an oligopoly market, cooperation is achieved when... |
|  | A) | each firm in the market decides not to cheat. |
|  | B) | a majority of firms in the market decides not to cheat. |
|  | C) | an explicit agreement not to cheat is reached by at least two firms in the market. |
|  | D) | a pricing agreement is reached in which one firm in the market sets a price that the other firms match. |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
Price matching... |
|  | A) | must be reversible to be credible. |
|  | B) | must be irreversible to be credible. |
|  | C) | is not a strategic commitment. |
|  | D) | both a and c |
|  | E) | both b and c |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
In a repeated decision for which the present value of the benefits of cheating are greater than the present value of the costs of cheating, |
|  | A) | deciding to cooperate is a value-maximizing decision. |
|  | B) | deciding to cheat is a value-maximizing decision. |
|  | C) | deciding to cheat is never a value-maximizing decision. |
|  | D) | both a and c |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
Which of the following conditions make it LESS likely that a cartel will succeed? |
|  | A) | a small number of cartel members. |
|  | B) | the lack of an explicit agreement among cartel members. |
|  | C) | similar cost structures among cartel members. |
|  | D) | differentiated cost structures among cartel members. |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
21 |  | 
The next three questions refer to the following: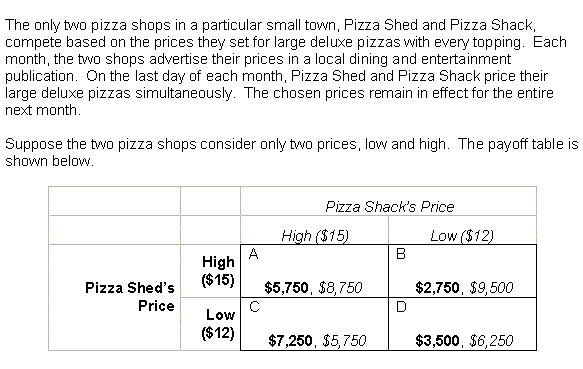 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_21.gif','popWin', 'width=633,height=439,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_21.gif','popWin', 'width=633,height=439,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
Does this decision represent a prisoners' dilemma? |
|  | A) | Yes, since only one firm has a dominant strategy. |
|  | B) | Yes, since both firms have a dominant strategy. |
|  | C) | No, since both firms have a dominant strategy. |
|  | D) | No, since there is no incentive to cheat. |
 |
 |
22 |  | 
Which cell(s) represent cheating in the pricing decision? |
|  | A) | Pizza Shed cheats in Cell C |
|  | B) | Pizza Shed cheats in Cell D |
|  | C) | Pizza Shack cheats in Cell B |
|  | D) | both a and c |
|  | E) | both b and c |
 |
 |
23 |  | 
If Pizza Shed and Pizza Shack make their pricing decisions just one time, |
|  | A) | no punishment is possible for cheating. |
|  | B) | dominant strategy equilibrium occurs. |
|  | C) | Nash equilibrium occurs. |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
24 |  | 
The next two questions refer to the following: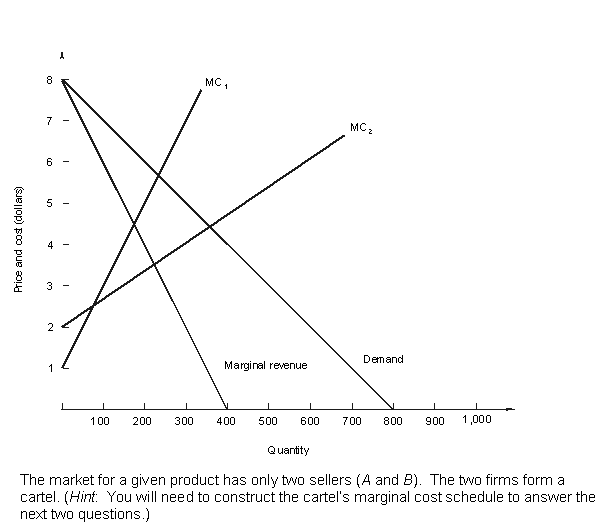 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_24.gif','popWin', 'width=649,height=594,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124374/chap13_24.gif','popWin', 'width=649,height=594,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Which price and level of output maximize the cartel's profit? |
|  | A) | $30; 2,500 |
|  | B) | $55; 2,500 |
|  | C) | $50; 3,000 |
|  | D) | $40; 2,000 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
25 |  | 
How should the total cartel output be allocated between the two firms? |
|  | A) | 1,500 to Firm A; 1,000 to Firm B |
|  | B) | 1,500 to Firm A; 1,500 to Firm B |
|  | C) | 1,000 to Firm A; 1,500 to Firm B |
|  | D) | 1,000 to Firm A; 1,000 to Firm B |
|  | E) | 500 to Firm A; 1,500 to Firm B |
 |

