 |
1 |  | 
The expansion path shows... |
|  | A) | how input prices change as the firm's output level changes. |
|  | B) | how the marginal products change as the firm's output level changes. |
|  | C) | how the profit-maximizing input choices change as the firm's output level changes. |
|  | D) | how the cost-minimizing input choices change as the firm's output level changes. |
|  | E) | how the cost-minimizing input prices change as the firm's output level changes. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
The marginal rate of technical substitution is... |
|  | A) | the rate at which the firm can substitute labor for capital while holding output constant. |
|  | B) | the rate at which the firm can substitute labor for capital while holding total cost constant. |
|  | C) | the slope of the isocost curve. |
|  | D) | both a and c |
|  | E) | both b and c |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
A firm is using 400 units of capital and 200 units of labor to produce 20,000 units of output. Capital costs $80 per unit and labor $20 per unit. The last unit of capital added 100 units of output, while the last unit of labor added 30 units of output. The firm... |
|  | A) | is using the cost-minimizing combination of capital and labor. |
|  | B) | should use more of both inputs in equal proportions. |
|  | C) | should use less of both inputs in equal proportions. |
|  | D) | could produce the same level of output at a lower cost by using less capital and more labor. |
|  | E) | could produce the same level of output at a lower cost by using more capital and less labor. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Suppose that when a firm increases its usage of all inputs by 100%, output increases by less than 100%. The firm's production function exhibits... |
|  | A) | a decreasing marginal rate of technical substitution. |
|  | B) | diminishing marginal returns. |
|  | C) | decreasing returns to scale. |
|  | D) | both b and c |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
The next 7 questions refer to the following: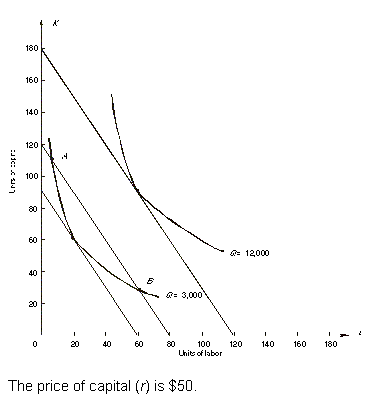 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124370/chap10_5.gif','popWin', 'width=435,height=473,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070601607/124370/chap10_5.gif','popWin', 'width=435,height=473,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
What is the price of labor (w)? |
|  | A) | $25 |
|  | B) | $50 |
|  | C) | $75 |
|  | D) | $100 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
What combination of labor (L) and capital (K) can produce 3,000 units of output at the lowest cost? |
|  | A) | 10K, 110L |
|  | B) | 42K, 52L |
|  | C) | 60K, 20L |
|  | D) | 90K, 60L |
|  | E) | 110K, 10L |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
What is the lowest possible cost of producing 3,000 units of output? |
|  | A) | $6,000 |
|  | B) | $4,500 |
|  | C) | $3,000 |
|  | D) | $1,500 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
Why wouldn't the firm choose to produce 3,000 units of output with the combination at A? |
|  | A) | At A, MRTS > 3/2. |
|  | B) | At A, MPK/r > MPL/w. |
|  | C) | At A, MPL > MPK. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
Why wouldn't the firm choose to produce 3,000 units of output with the combination at B? |
|  | A) | At B, MRTS > 3/2. |
|  | B) | At B, MPK/r < MPL/w. |
|  | C) | At B, MPL < MPK. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
At the optimal combination of inputs for producing 14,000 units of output, what is the marginal rate of technical substitution? |
|  | A) | 0.80 |
|  | B) | 0.67 |
|  | C) | 1.5 |
|  | D) | 2.5 |
|  | E) | impossible to tell from the graph |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
If, at the optimal combination of inputs for producing 14,000 units of output, the marginal product of capital is 60, what is the marginal product of labor? |
|  | A) | 30 |
|  | B) | 50 |
|  | C) | 62.5 |
|  | D) | 90 |
|  | E) | impossible to tell from the graph |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
In the long run... |
|  | A) | a firm is making the optimal input choice when the marginal rate of technical substitution is equal to the input price ratio. |
|  | B) | the expansion path shows how the input marginal products change as the firm's output level changes. |
|  | C) | all inputs are fixed. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both b and c |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
Which of the following are characteristics of a typical isoquant? |
|  | A) | All input combinations on the isoquant will produce the same level of output. |
|  | B) | A change in input prices shifts the isoquant map. |
|  | C) | The marginal rate of technical substitution decreases as labor is substituted for capital. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both a and c |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
The slope of an isoquant is... |
|  | A) | the marginal rate of technical substitution. |
|  | B) | MPK/MPL. |
|  | C) | −ΔK/ΔL. |
|  | D) | both a and c |
|  | E) | all of the above |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
If the price of labor is $4 and the price of capital is $16, what is the marginal rate of technical substitution at the optimal input choice? |
|  | A) | 4.0 |
|  | B) | 2.0 |
|  | C) | 0.5 |
|  | D) | 0.25 |
|  | E) | none of the above |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
Which of the following is (are) characteristics of an isocost curve? |
|  | A) | The slope shows the rate at which the firm can substitute labor for capital while holding total cost constant. |
|  | B) | The slope shows the rate at which the firm can substitute labor for capital in the market. |
|  | C) | If the price of capital is unchanged and the price of labor increases, the intercept of the isocost curve on the horizontal axis will increase. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both a and c |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
If the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital is 1.5, the price of labor is $20, and the price of capital is $10, then the firm... |
|  | A) | can substitute one unit of capital for 1.5 units of labor and keep output unchanged. |
|  | B) | should use more labor and less capital. |
|  | C) | should use more capital and less labor. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both a and c |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
If a firm is producing the level of output at which long-run average cost equals long-run marginal cost, then... |
|  | A) | long-run total cost is at its minimum point. |
|  | B) | long-run marginal cost is at its minimum point. |
|  | C) | long-run average cost is at its minimum point. |
|  | D) | both b and c |
|  | E) | all of the above |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
If a firm is producing the level of output at which short-run average cost equals long-run average cost, then... |
|  | A) | the firm has chosen the profit-maximizing level of output. |
|  | B) | with a fixed amount of capital, short-run average cost is greater than long-run average cost at any other level of output. |
|  | C) | the firm has chosen the cost-minimizing combination of inputs to produce this level of output. |
|  | D) | both b and c |
|  | E) | all of the above |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
Economies of scale exist when... |
|  | A) | fixed cost decreases as output increases. |
|  | B) | long-run average cost decreases as output increases. |
|  | C) | long-run marginal cost is greater than long-run average cost. |
|  | D) | both a and b |
|  | E) | both b and c |
 |

