 |
| 1 |  | 
The valence shell electrons are? |
|  | A) | The inner most shell of electrons. |
|  | B) | The outer most shell of electrons. |
|  | C) | Only those involved in a bond to another atom. |
|  | D) | Only those NOT involved in a bond to another atom. |
|  | E) | All electrons around the atom. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which atom has the following ground state configuration?
[Ne]3s23p4 |
|  | A) | Oxygen. |
|  | B) | Silicon. |
|  | C) | Phosphorus. |
|  | D) | Sulfur. |
|  | E) | Chlorine. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following statements about Ionic bonds is false? |
|  | A) | Ionic bonds are produced when cations and anions are held together by strong electrostatic (or coulombic) forces. |
|  | B) | Cations are formed from atoms with low ionization energies. |
|  | C) | Anions are formed from atoms with high electron affinities. |
|  | D) | Ionic bonds are common in organic compounds. |
|  | E) | Ionic bonds are common in inorganic compounds. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Covalent bonds differ from Ionic bonds by... |
|  | A) | Sharing electrons equally between atoms. |
|  | B) | Gaining electrons from the other atom. |
|  | C) | Losing electrons to the other atom. |
|  | D) | There is no difference between the two. |
|  | E) | Occurs between metals and non-metals. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
The octet rule represents... |
|  | A) | Stable electronic configurations for second row elements. |
|  | B) | A common trend in the electronic configuration of the noble gasses. |
|  | C) | A limit on the number of bonds that can be formed, i.e. only four bonds. |
|  | D) | A and B. |
|  | E) | A and C. |
|  | F) | B and C. |
|  | G) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Multiple bonds (i.e. double or triple) are? |
|  | A) | Uncommon in organic molecules. |
|  | B) | Are not possible in the Lewis concepts of bonding. |
|  | C) | Still satisfy the octet rule. |
|  | D) | Can only occur between carbon atoms. |
|  | E) | Can be Ionic bonds. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
The best definition of Polar Covalent Bonds is? |
|  | A) | A bond involving atoms with formal charges. |
|  | B) | A bond involving atoms with different electronegativities. |
|  | C) | A bond involving atoms of different sizes. |
|  | D) | A bond involving atoms with different numbers of electrons. |
|  | E) | A bond involving atoms with multiple bonds. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
What is the formal charge on the N atom in nitromethane, CH3NO2? |
|  | A) | +1 |
|  | B) | 0 |
|  | C) | -1 |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which of the following is the best Lewis structure for HCO3- |
|  | A) | 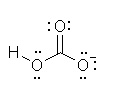 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (13.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (13.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 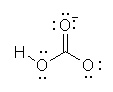 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 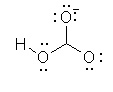 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 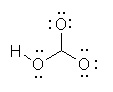 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_9d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
The following are examples of?
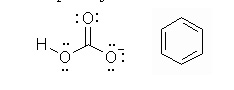 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Condensed structural formula. |
|  | B) | Molecular formula. |
|  | C) | Bond-line formula. |
|  | D) | Complete chemical formula. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Structural isomers are? |
|  | A) | Compounds with different types of atoms. |
|  | B) | Compounds with the same types of atoms but different numbers of those atoms. |
|  | C) | Compounds with the same types and numbers of atoms bonded in a different arrangement. |
|  | D) | Compounds with the same types and numbers of atoms bonded in the same arrangement. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Which of the following is not a resonance structure of
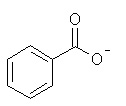 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 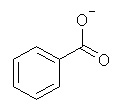 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 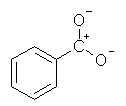 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 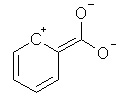 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 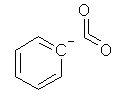 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_12d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
According to the VSEPR model the carbon atoms in bromobutane have what shape?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_13.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_13.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Tetrahedral. |
|  | B) | Pyramidal. |
|  | C) | Bent. |
|  | D) | Linear. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
The molecule with the largest dipole moment is? |
|  | A) | 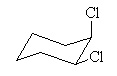 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 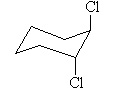 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 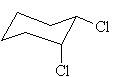 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | D) |  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_14d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which of the following reactions shows the correct use of "curly arrows"? |
|  | A) | 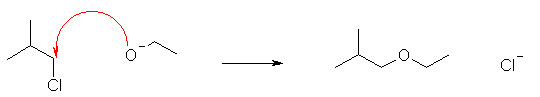 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15a.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 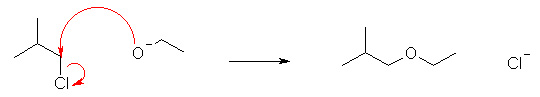 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15b.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 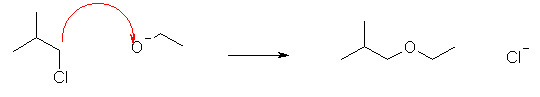 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15c.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 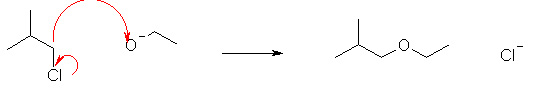 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0070667160/211137/1_15d.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
There are a number of definitions for acids
and bases. Match the following definitions to the correct theory.
| Theory | Definition | | A. Arrhenius | I - donates or accepts protons | | B. Bronsted-Lowry | II - donates or accepts a lone pair of electrons | | C. Lewis | III - donates a proton or a hydroxide |
|
|  | A) | A-I, B-II, C-III |
|  | B) | A-I, B-III, C-II |
|  | C) | A-II, B-III, C-I |
|  | D) | A-II, B-I, C-III |
|  | E) | A-III, B-I, C-II |
|  | F) | A-III, B-II, C-I |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
The correct equation for the Ka for an acid is? |
|  | A) | Ka = [HA][A-] / [H+] |
|  | B) | Ka = [HA] [H+] / [A-] |
|  | C) | Ka = [A-] / [HA][H+] |
|  | D) | Ka = [H+] / [HA][A-] |
|  | E) | Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA] |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
The pKa of an acid is more commonly used to compare the strength of acids where stronger acids have a lower pKa. It is related to the Ka by: pKa = -logKa. Rank the following compounds in order of their decreasing pKa for the hydrogen in bold.
|
|  | A) | A > B > C |
|  | B) | A > C > B |
|  | C) | B > A > C |
|  | D) | B > C > A |
|  | E) | C > A > B |
|  | F) | C > B > A |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
In the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids, an acid will lose a proton (H+) and leave behind the conjugate base of the acid. The conjugate base of a strong acid is? |
|  | A) | A strong base. |
|  | B) | Neutral. |
|  | C) | A weak base. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
There are a number of structural features which effect the pKa of an acid. These are? |
|  | A) | Electronegativity. |
|  | B) | The strength of the bond to the acidic hydrogen atom. |
|  | C) | Inductive effects. |
|  | D) | Resonance delocalization. |
|  | E) | A and B. |
|  | F) | A and C. |
|  | G) | B and D. |
|  | H) | All of the above. |
|
|

