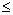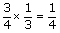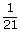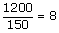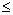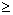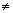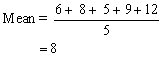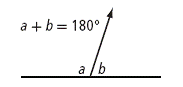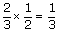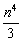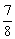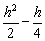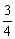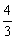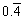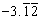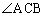| acute angle | An angle that is between 0° and 90°.
|
 |
 |
 |
| angle of rotation (for symmetry) | The minimum size of the angle needed to turn a shape or design onto itself. The angle may be measured in degrees or fractions of a turn.
(See page(s) 17)
|
 |
 |
 |
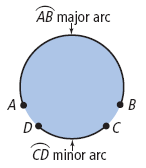
| arc (of a circle) | A portion of the circumference of a circle. A minor arc is less than a semicircle, and a major arc is more than a semicircle.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image001.png','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=png::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image001.png','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 378)
|
 |
 |
 |
| area | The number of square units contained in a two-dimensional region.
|
 |
 |
 |
| assumption | Something taken for granted, as though it were true.
|
 |
 |
 |
| base (of a power) | number used as a factor for repeated multiplication. In 46, the base is 4.
(See page(s) 93)
|
 |
 |
 |
| biased sample | Does not represent the population, and can make survey results inaccurate.
(See page(s) 431)
|
 |
 |
 |
| binomial | An expression with two terms, such as 6y2 + 3 and 2x − 5y.
|
 |
 |
 |
| bisect | Divide into two equal parts.
|
 |
 |
 |
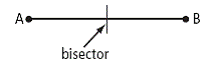
| bisector | A line or line segment that cuts an angle or line segment into two equal parts.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image004.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image004.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| boundary point | The point that separates the values less than from the values greater than a specified value. If it is a possible value, it is shown with a closed circle on a number line. If it is not a possible value, the circle is open. For example, the boundary points for the inequality −4 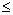 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image006.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>x < 4 are −4 (closed circle) and 4 (open circle). <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image006.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>x < 4 are −4 (closed circle) and 4 (open circle).
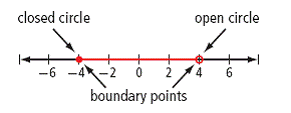 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image008.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image008.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 342)
|
 |
 |
 |
| central angle | An angle formed by two radii of a circle. The vertex of the angle is at the centre of the circle, and the endpoints are on the circle.
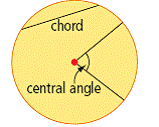 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image010.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image010.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 378)
|
 |
 |
 |
| centre of rotation | The point about which the rotation of an object or design turns.
(See page(s) 16)
|
 |
 |
 |
| chord | A line segment joining two points on the circumference of a circle.
(See page(s) 378)
|
 |
 |
 |
| circumference | The boundary of or distance around a circle. This is a linear measurement. It is often represented by the variable C.
|
 |
 |
 |
| coefficient | See numerical coefficient.
|
 |
 |
 |
| common denominator | | A common multiple of the denominators of a set of fractions. A common denominator for | 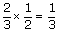 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image012.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image012.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | | is 6 because a common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6. |
|
 |
 |
 |
| common multiple | A common multiple is a number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. For example, common multiples of 3 and 5 include 0, 15, and 30.
|
 |
 |
 |
| composite object | An object made from two or more separate objects.
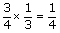 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image014.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image014.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| congruent | Identical in shape and size.
|
 |
 |
 |
| constant | A known value in an equation or an expression. In the equation s = 3n − 2, −2 is a constant.
|
 |
 |
 |
| convenience sample | A group of individuals that is chosen because its members are easy to access.
|
 |
 |
 |
| coordinate grid | A grid made of intersecting vertical and horizontal lines. Also called a Cartesian plane.
|
 |
 |
 |
| coordinate pair(s) | See coordinates.
|
 |
 |
 |
| coordinate(s) | An ordered pair (x, y), is a pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate grid. Coordinates are the values in an ordered pair. The x-coordinate is the distance from the vertical or y-axis. The y-coordinate in the distance from the horizontal or x-axis.
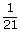 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image016.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image016.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| corresponding angles | Angles that have the same relative position in two geometric figures.
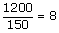 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image018.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image018.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 146)
|
 |
 |
 |
| corresponding sides | Sides that have the same relative position in two geometric figures.
(See page(s) 146)
|
 |
 |
 |
| degree of a polynomial | The degree of the highest degree term in a polynomial. For example, the polynomial 7a2 − 3a has a degree of two.
(See page(s) 176)
|
 |
 |
 |
| degree of a term | The sum of the exponents on the variables in a single term. For example, the degree of 3x3z2 is 5. A variable with no exponent has a degree of one.
(See page(s) 176)
|
 |
 |
 |
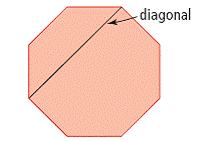
| diagonal | A line joining two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image020.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image020.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| diameter | The distance across a circle through its centre. Represented by the variable d.
|
 |
 |
 |
| distributive property | The rule that states a(b + c) = ab + ac for all real numbers a, b, and c.
|
 |
 |
 |
| enlargement | An increase in the dimensions of an object by a constant factor. The enlargement can be 2-D or 3-D.
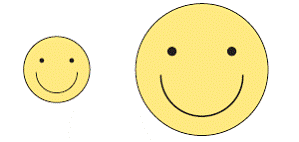 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image022.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image022.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 131)
|
 |
 |
 |
| equation | A statement that two mathematical expressions are equal and have the same value.
|
 |
 |
 |
| equilateral triangle | A triangle with three equal sides.
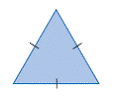 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image024.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image024.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| ethics | Involves judgments of right and wrong behaviour. For example, cheating on a test is wrong, or unethical.
|
 |
 |
 |
| experimental probability | The probability of an event occurring based on experimental results.
|
 |
 |
 |
| exponent | The number of times you multiply the base in a power by itself. For example, in 23, 3 is the exponent, so the base is multiplied by itself three times: 2 × 2 × 2 = 8.
(See page(s) 93)
|
 |
 |
 |
| exponential form | A shorter way of writing repeated multiplication, using a base and an exponent. For example, 5 × 5 × 5 in exponential form is 53.
(See page(s) 93)
|
 |
 |
 |
| extrapolate | To estimate a value beyond a given set of values.
(See page(s) 223)
|
 |
 |
 |
| generalize | To infer a general principle or make a broad statement from known facts.
|
 |
 |
 |
| heptagon | A 2-D shape with seven sides.
|
 |
 |
 |
| hypotenuse | side opposite the right angle in a right triangle.
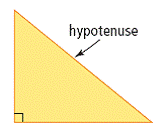 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image026.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image026.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| hypothesis | A proposition put forward to guide an investigation.
|
 |
 |
 |
| inequality | A mathematical statement comparing expressions that may not be equal. These can be written using the symbols less than (<), greater than (>), less than or equal (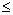 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image006.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>), greater than or equal ( <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image006.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>), greater than or equal (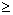 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image029.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>), <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image029.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>),
or not equal (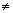 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image031.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>). <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image031.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>).
(See page(s) 341)
|
 |
 |
 |
| inscribed angle | An angle formed by two chords that share a common endpoint. The vertex and endpoints are on the circle.
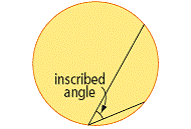 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image033.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image033.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 378)
|
 |
 |
 |
| interior angle | An angle that is formed inside a polygon by two sides meeting at a vertex.
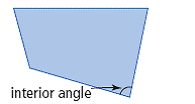 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image035.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image035.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| interpolate | To estimate the value between two given values.
(See page(s) 222)
|
 |
 |
 |
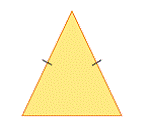
| isosceles triangle | A triangle with exactly two equal sides.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image037.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image037.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| like terms | Terms that have the same variable(s) raised to the exponent(s). For example, 3x − 2x are like terms.
(See page(s) 184)
|
 |
 |
 |
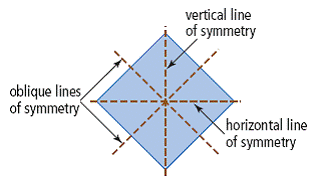
| line of symmetry | A line running through the centre of an object or design such that the halves on each side of the line are mirror images. These lines can be vertical, horizontal, or oblique. A figure may have more than one line of symmetry. Also called a line of reflection.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image039.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image039.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 6)
|
 |
 |
 |
| linear equation | An equation whose graph is a straight line.
|
 |
 |
 |
| linear relation | A relation that appears as a straight line when graphed.
|
 |
 |
 |
| mean | A measure of central tendency calculated by finding the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values in the set. For example, for the set of values 6, 8, 5, 9, and 12,
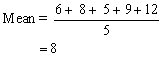 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image041.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image041.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| median | A measure of central tendency determined by the middle number in a set of data after the data have been arranged in order.
For the data 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9, the median is 6.
For the data 1, 3, 7, 7, 9, and 10, the median is 7.
|
 |
 |
 |
| mode | A measure of central tendency determined by the most frequently occurring number in a set of data. There can be more that one mode.
For the data 3, 5, 7, 7, and 9, the mode is 7.
For the data 2, 2, 4, 6, 6, 8, and 11, the modes are 2, and 6.
|
 |
 |
 |
| monomial | | An algebraic expression with one term. For example, 5, 2x, 3s2, −8cd, and | 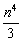 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image043.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image043.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | are all monomials. |
|
 |
 |
 |
| non-perfect square | A rational number that cannot be expressed as the product of two rational factors. For example, you | cannot multiply any rational number by itself and get an answer of 3, 5, 1.5, or | 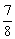 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image045.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>. <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image045.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>. |
The square root of a non-perfect square is a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal.
(See page(s) 77)
|
 |
 |
 |
| numerical coefficient | A number that multiplies the variable. In 3n − 2, the numerical coefficient is 3.
|
 |
 |
 |
| oblique | Slanted, rather than vertical or horizontal.
|
 |
 |
 |
| octagon | A 2-D shape with eight sides.
|
 |
 |
 |
| opposite operation | Operations that “undo” other operations. Sometimes called “inverse operations.” Examples of opposite operations are addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, and squaring and taking the square root.
|
 |
 |
 |
| opposites | Two numbers or expressions with the same numeral, but different signs. For example, +2 and −2, and 3x + 2 and −3x − 2, are opposites.
|
 |
 |
 |
| order of operations | The correct sequence of steps for a calculation: Brackets, Exponents, Divide and Multiply in order from left to right, Add and Subtract in order from left to right.
|
 |
 |
 |
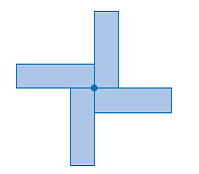
| order of rotation | The number of times a shape or design fits onto itself in one turn. The order of rotation of this figure is 4.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image047.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/image047.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 17)
|
 |
 |
 |
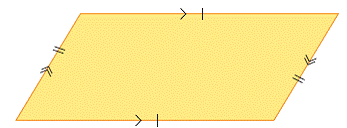
| parallegram | A four-sided figure with opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| pentagon | A 2-D shape with five sides.
|
 |
 |
 |
| perfect square | A number that is the product of two identical factors.
2 × 2 = 4, so 4 is a perfect square
6 × 6 = 36, so 36 is a perfect square
|
 |
 |
 |
| perimeter | The distance around the outside of a two-dimensional shape or figure.
|
 |
 |
 |
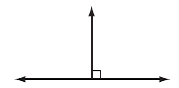
| perpendicular | Describes lines that intersect at right angles (90o).
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| perpendicular bisector | A line that divides a line segment in half and is at right angles to it.
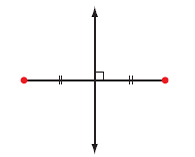 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| plane | A two-dimensional flat surface that extends in all directions.
|
 |
 |
 |
| polygon | A two-dimensional closed figure made of three or more line segments.
(See page(s) 154)
|
 |
 |
 |
| polynomial | An algebraic expression formed by adding or subtracting terms. For example,
| x + 5, 2d − 2.4, 3s2 + 5s − 6, and | 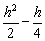 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | are all polynomials. |
(See page(s) 175)
|
 |
 |
 |
| population | All of the individuals that belong to a group being studied.
(See page(s) 423)
|
 |
 |
 |
| power | An expression made up of a base and an exponent. For example, for the power 63, 6 is the base and 3 is the exponent.
(See page(s) 93)
|
 |
 |
 |
| prime factorization | A number written as the product of its prime factors. For example, the prime factorization of 18 is 2 × 3 × 3.
|
 |
 |
 |
| prime factors | Factors that are prime numbers. For example, the prime factors of 10 are 2 and 5.
|
 |
 |
 |
| probability | The likelihood or chance of an event occurring. Probability can be expressed as a ratio, fraction, or percent.
|
 |
 |
 |
| proportion | An equation that says that two ratios or two rates are equal. It can be written
| in fraction form as |  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p5.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p5.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | , or in ratio form as 1 : 4 = 4 : 16. |
|
 |
 |
 |
| Pythagorean relationship | The relationship between the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. The sum of the areas of the squares attached to the legs of the triangle equals the area of the square attached to the hypotenuse.
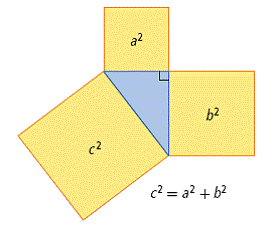 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p6.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p6.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| quadrilateral | A polygon that has four sides.
|
 |
 |
 |
| radius | A line segment joining the centre of a circle to the outside edge. It can also refer to the length of this line segment and may be represented by the variable, r.
|
 |
 |
 |
| random | An event in which every outcome has an equal chance of occurring.
|
 |
 |
 |
| random sample | A sample of individuals chosen randomly from the whole population as a way of representing the whole population. Stratified samples and systematic samples are types of random samples.
|
 |
 |
 |
| ratio | A comparison of two quantities with the same units.
|
 |
 |
 |
| rational number | A number that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, where the divisor is not zero.
| For example, 0.75, | 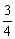 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | , and −2 are rational numbers. |
(See page(s) 47)
|
 |
 |
 |
| reciprocal | The multiplier of a number to give a product of 1. For example,
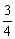 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | is the reciprocal of | 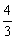 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p24.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p24.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | because | 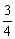 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p23.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | × | 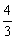 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p24.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p24.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | = 1. |
|
 |
 |
 |
| reduction | A decrease in the dimensions of an object by a constant factor. For example, in the diagram, the second bulb is half as large as the first. A reduction can be 2-D or 3-D.
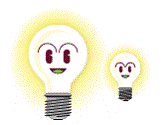 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p9.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p9.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 133)
|
 |
 |
 |
| regular polygon | A polygon with all sides equal and all interior angles equal.
|
 |
 |
 |
| repeating decimal | A decimal number with a digit or group of digits that repeats forever.
| Repeating digits are shown with a bar: | 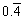 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p10.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p10.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | = 0.444... and | 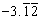 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p11.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p11.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | = −3.121212.... |
|
 |
 |
 |
| right triangle | A triangle containing a 90o angle.
|
 |
 |
 |
| rotation symmetry | Occurs when a shape or design can be turned about its centre of rotation so that it fits onto its outline more than once in a complete turn. The design in the figure fits onto itself 10 times in one turn.
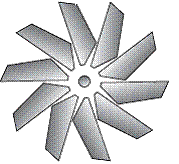 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 16)
|
 |
 |
 |
| sample | Any group of individuals selected from the population.
(See page(s) 423)
|
 |
 |
 |
| scale | A comparison between the actual size of an object and the size of its image. This can be expressed as a ratio, as a fraction, as a percent, in words, or in a diagram. For example, a scale of 1 cm : 50 km on a map means that 1 cm on the map represents 50 km.
(See page(s) 139)
|
 |
 |
 |
| scale diagram | A diagram that is similar to the actual figure or object. It may be smaller than or larger than the actual object, but must be in the same proportions.
(See page(s) 140)
|
 |
 |
 |
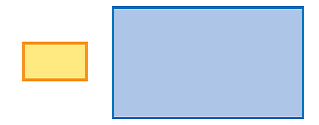
| scale factor | The constant factor by which all dimensions of an object are enlarged or reduced in a scale drawing. The dimensions of this rectangle is multiplied by 3 so the scale factor is 3.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p13.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p13.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 132)
|
 |
 |
 |
| similar figures | Figures that have the same shape, but different size. They have equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding sides.
(See page(s) 147)
|
 |
 |
 |
| simulate | To create a model that reflects a particular situation.
|
 |
 |
 |
| solution (of an inequality) | A value or set of values that result in a true statement. The solution can contain a specific value or many values.
(See page(s) 353)
|
 |
 |
 |
| square root | One of two equal factors of a number. The symbol is R. For example, 9 is the square root of 81 because 9 × 9 is 81.
|
 |
 |
 |
| stratified sample | A sample that is created by dividing the whole population into distinct groups and then choosing the same fraction of members from each group.
|
 |
 |
 |
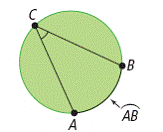
| subtended | | Lying opposite to. For example, in the figure, the arc AB subtends the angle, | 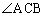 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> . <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p14.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> . |
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p15.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| supplementary angles | Angles that add to 180o.
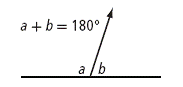 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p16.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p16.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| surface area | The number of square units needed to cover a 3-D object. The sum of the areas of all the faces of an object.
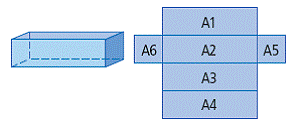 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p17.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p17.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 26)
|
 |
 |
 |
| survey | A question or questions asked of a sample of the population to gather opinions.
|
 |
 |
 |
| symmetry | An object or image has symmetry if it is balanced and can fit onto itself either by reflection or rotation.
(See page(s) 5)
|
 |
 |
 |
| systematic sample | A sample created by choosing individuals at fixed intervals from an ordered list of the whole population.
|
 |
 |
 |
| tangent (of a circle) | A line that touches a circle at exactly one point. The line is perpendicular to the radius at that point. The point where the line touches the circle is called the point of tangency.
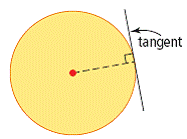 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p18.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p18.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
(See page(s) 394)
|
 |
 |
 |
| term | A number or a variable, or the product of numbers and variables. The expression 5x + 3 has two terms: 5x and 3.
(See page(s) 175)
|
 |
 |
 |
| terminating decimal | A decimal number in which the digits stop. 0.4, 0.86, and 0.25 are terminating decimals.
|
 |
 |
 |
| tessellation | A pattern or arrangement that covers an area or plane without overlapping or leaving gaps. Also called a tiling pattern.
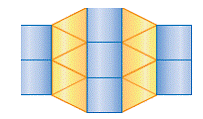 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p19.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p19.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| theoretical probability | The expected probability of an event occurring. The ratio of the number of expected favourable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes for an event.
|
 |
 |
 |
| transformation | A change in a figure that results in a different position or orientation. Examples are translations, reflections, and rotations.
|
 |
 |
 |
| translation | A slide along a straight line.
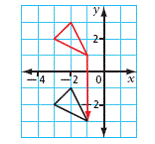 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p20.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p20.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
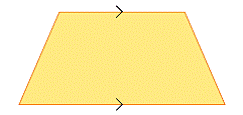
| trapezoid | A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p21.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p21.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| trinomial | A polynomial with three terms. x2 + 3x − 1 is a trinomial.
|
 |
 |
 |
| variable | A letter that represents an unknown number.
|
 |
 |
 |
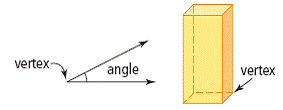
| vertex | The point where two or more edges of a figure or object meet. The plural is vertices.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p22.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0070973407/645442/ml9_glossary_p22.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (4.0K)</a>
|
 |
 |
 |
| volume | The amount of space an object occupies. Measured in cubic units.
|
 |
 |
 |
| voluntary response sample | A sample where the whole population is invited to participate.
|