In the next set of questions we are concerned with the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis. The light reactions are to be considered reaction group I. The enzymatic reactions are to be considered group II. Categorize the next set of questions according to the following keys.
 |
1 |  | 
Oxidation |
|  | A) | a reaction of I but not II. |
|  | B) | a reaction of II but not I. |
|  | C) | a reaction of both I and II. |
|  | D) | not a reaction of either I or II but necessary if either I or II or both are to occur. |
|  | E) | not a reaction of either I or II but occurs as a result of I or II or both. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
Photophosphorylation |
|  | A) | a reaction of I but not II. |
|  | B) | a reaction of II but not I. |
|  | C) | a reaction of both I and II. |
|  | D) | not a reaction of either I or II but necessary if either I or II or both are to occur. |
|  | E) | not a reaction of either I or II but occurs as a result of I or II or both. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Production of photons |
|  | A) | a reaction of I but not II. |
|  | B) | a reaction of II but not I. |
|  | C) | a reaction of both I and II. |
|  | D) | not a reaction of either I or II but necessary if either I or II or both are to occur. |
|  | E) | not a reaction of either I or II but occurs as a result of I or II or both. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
Production of a carbohydrate |
|  | A) | a reaction of I but not II. |
|  | B) | a reaction of II but not I. |
|  | C) | a reaction of both I and II. |
|  | D) | not a reaction of either I or II but necessary if either I or II or both are to occur. |
|  | E) | not a reaction of either I or II but occurs as a result of I or II or both. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
Production of O2 |
|  | A) | a reaction of I but not II. |
|  | B) | a reaction of II but not I. |
|  | C) | a reaction of both I and II. |
|  | D) | not a reaction of either I or II but necessary if either I or II or both are to occur. |
|  | E) | not a reaction of either I or II but occurs as a result of I or II or both. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
If you could label the oxygen in CO2 and provide this CO2 to a plant, where would you expect to find this labeled oxygen after the plant had undergone photosynthesis? |
|  | A) | in the water used |
|  | B) | in the NADPH |
|  | C) | in the carbohydrate produced |
|  | D) | in the oxygen given off by the plant |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
Which one of the following is a product of both cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation? |
|  | A) | NADPH |
|  | B) | O2 |
|  | C) | H2O |
|  | D) | ATP |
|  | E) | Carbohydrate |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
In noncyclic photophosphorylation, the ultimate acceptor of electrons that have been produced from the splitting of water is |
|  | A) | oxygen. |
|  | B) | NADP+. |
|  | C) | chlorophyll a. |
|  | D) | carbon dioxide. |
|  | E) | chlorophyll b. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
All of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis except |
|  | A) | ATP. |
|  | B) | oxygen. |
|  | C) | NADPH. |
|  | D) | glucose. |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
In oxygenic photosynthesis, water is split in order to provide the |
|  | A) | O2 needed for the dark reactions. |
|  | B) | electrons needed to reduce NADH. |
|  | C) | electrons needed for cyclic photophosphorylation. |
|  | D) | electrons needed to reduce P680. |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
The end products of noncyclic photophosphorylation are |
|  | A) | O2, ATP, and NADPH. |
|  | B) | carbon dioxide, PGAL, and H2. |
|  | C) | water, ADP, and NADP+. |
|  | D) | PGAL, ADP, and ribulose. |
|  | E) | carbon dioxide, ATP, and water. |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
Carbon dioxide is reduced in |
|  | A) | cyclic photophosphorylation. |
|  | B) | noncyclic photophosphorylation. |
|  | C) | the Calvin cycle. |
|  | D) | the light reactions. |
|  | E) | both light and dark reactions. |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
Which of the following is/are the products of the light reactions of photosynthesis? |
|  | A) | ATP only |
|  | B) | NADPH only |
|  | C) | O2 only |
|  | D) | ATP and O2 only |
|  | E) | ATP, NADPH, and O2 |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
All of the following produce oxygen as a product of photosynthesis except |
|  | A) | cyanobacteria. |
|  | B) | oak trees. |
|  | C) | purple sulfur bacteria. |
|  | D) | algae. |
|  | E) | phytoplankton. |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
The chlorophyll molecules used by eucaryotes and cyanobacteria absorb radiant energy in the _____ portion(s) of the visible spectrum. |
|  | A) | red |
|  | B) | green |
|  | C) | blue |
|  | D) | green and ultraviolet |
|  | E) | red and blue |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
The bacteriochlorophylls used by the anoxygenic bacteria have absorbance maxima located in the _____ portion(s) of the spectrum. |
|  | A) | infrared |
|  | B) | green |
|  | C) | blue |
|  | D) | ultraviolet |
|  | E) | green and ultraviolet |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
Which of the following is an example of a polymer? |
|  | A) | nucleotide |
|  | B) | amino acid |
|  | C) | monosaccharide |
|  | D) | polysaccharide |
|  | E) | fatty acid |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
Radioisotopes are frequently used in the study of cells. Assume a culture of E. coli is grown in a culture medium containing radioactive sulphur. At the end of 48 hours you would expect to find the radioactive label located in |
|  | A) | enzymes. |
|  | B) | DNA. |
|  | C) | RNA. |
|  | D) | phospholipids. |
|  | E) | all of the above. |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
Radioisotopes are frequently used in the study of cells. Assume a culture of E. coli is grown in a culture medium containing radioactive phosphorous. At the end of 48 hours you would expect to find the radioactive label located in |
|  | A) | enzymes. |
|  | B) | DNA. |
|  | C) | RNA. |
|  | D) | phospholipids. |
|  | E) | all of the above. |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
Which of the following is an example of an amphibolic pathway?
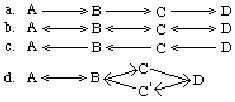 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072320419/20545/ch10_num20_image.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072320419/20545/ch10_num20_image.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | See above image. |
|  | B) | See above image. |
|  | C) | See above image. |
|  | D) | See above image. |
|  | E) | None of the above, there is no such thing as an amphibolic pathway. |
 |
For the following set of questions use the following key to express the truth of statements I and II.



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education