 |
| 1 |  | 
The tissue surrounding an entire muscle is known as |
|  | A) | epimysium. |
|  | B) | perimysium. |
|  | C) | endomysium. |
|  | D) | superficial mysium. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The tissue that surrounds a muscle cell (myofiber) is known as |
|  | A) | epimysium |
|  | B) | perimysium |
|  | C) | endomysium |
|  | D) | superficial mysium |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Muscle fibers are bundled into groups known as
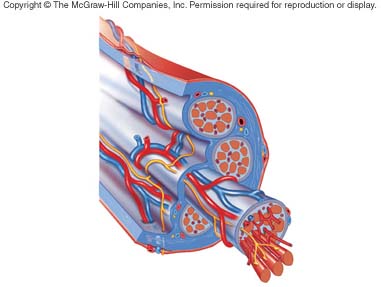 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234423/mc_ch09_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234423/mc_ch09_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | myotendrils |
|  | B) | endomysium |
|  | C) | myosin |
|  | D) | fascicles |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Bundles of muscle fibers (fascicles) are wrapped by a tissue known as
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234423/mc_ch09_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234423/mc_ch09_fig01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (31.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | epimysium |
|  | B) | perimysium |
|  | C) | endomysium |
|  | D) | superficial mysium |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
A connective tissue on the surface of muscles (that extends onto the tendon and bone) is known as |
|  | A) | fascia |
|  | B) | perimysium |
|  | C) | endomysium |
|  | D) | connective to muscle tissue |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
One of the characteristics of muscle tissue is that is has conductivity. Which of the following best describes this characteristic? |
|  | A) | Muscles contract when stimulated. |
|  | B) | Muscles have local electrical charges that are capable of moving along the muscle fiber. |
|  | C) | Muscles only pull; they cannot push. |
|  | D) | Muscles can stretch when needed. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
One of the characteristics of muscle tissue is that is has extensibility. Which of the following best describes this characteristic? |
|  | A) | Muscles contract when stimulated. |
|  | B) | Muscles have local electrical charges that move along the muscle fiber. |
|  | C) | Muscles only pull; they cannot push. |
|  | D) | Muscles can stretch when needed. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
One of the characteristics of muscle tissue is that is has excitability. Which of the following best describes this characteristic? |
|  | A) | Muscles contract when stimulated. |
|  | B) | Muscles have local electrical charges that move along the muscle fiber. |
|  | C) | Muscles only pull; they cannot push. |
|  | D) | Muscles can stretch when needed. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which of the following groups are considered to be parts of the series-elastic components of muscle? |
|  | A) | actin and myosin |
|  | B) | ligaments and tendons |
|  | C) | thick and thin filaments |
|  | D) | endomysium, perimysium, epimysium, fascia, and tendons |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Which of the following best describes the function of the series-elastic component of muscle? |
|  | A) | These components help the muscle contract. |
|  | B) | The components help maintain muscle tone. |
|  | C) | These are not excitable or contractile, but are extensible and elastic. |
|  | D) | These assist the thick and thin filaments to contract. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
What part of a muscle is the muscle fiber? |
|  | A) | actin and myosin component |
|  | B) | series-elastic component |
|  | C) | muscle cell itself |
|  | D) | nuclei and the mitochondria |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The outer membrane of the muscle fiber is known as the |
|  | A) | cell surface membrane. |
|  | B) | sarcolemma. |
|  | C) | sarcoplasm. |
|  | D) | sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
The cytoplasm within the muscle fiber is known as the |
|  | A) | myoglobin component. |
|  | B) | sarcolemma. |
|  | C) | sarcoplasm. |
|  | D) | sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
The cytoplasm within the muscle fiber contains a molecule to distribute oxygen within the cell. This molecule is known as |
|  | A) | myoglobin |
|  | B) | sarcolemma |
|  | C) | hemoglobin. |
|  | D) | sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
The molecule within the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber that supplies quick energy for contraction is |
|  | A) | fructose. |
|  | B) | glycogen. |
|  | C) | sucrose. |
|  | D) | ADP. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The myofilaments within the muscle fiber are composed of three integral items. Which of the following lists the components correctly? |
|  | A) | myosin, actin, and elastic (titin) filament. |
|  | B) | thick, thin, and straight filaments |
|  | C) | A, H, and B filaments |
|  | D) | sarcoplasm and sarcolemma components |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Thick filaments within the myofibril are composed of |
|  | A) | actin |
|  | B) | myosin |
|  | C) | titin |
|  | D) | sarconin |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Thin filaments within the myofibril are composed primarily of |
|  | A) | actin |
|  | B) | myosin |
|  | C) | titin |
|  | D) | sarconin |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
The elastic filaments within a myofibril are composed of molecules known as |
|  | A) | tropomyosin. |
|  | B) | titin. |
|  | C) | troponin. |
|  | D) | ADP |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
The elastic filaments within a myofibril are attached to and wound around, which of the following? |
|  | A) | myosin |
|  | B) | troponin |
|  | C) | actin |
|  | D) | sarcolemma |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
In the myofibril, ATP is used for which of the following? |
|  | A) | muscle tone |
|  | B) | muscle contraction |
|  | C) | muscle relaxation |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
Which of the following tissues has the greatest ability to repair itself? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | all have about the same ability |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
Of the following muscles types, which one has long, cylindrical-shaped cells? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | all are about the same |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
Of the following muscle types, which one has only one nucleus? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
Of the following muscle types, which one does NOT have striations? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
Of the following muscle types, which one is usually voluntary? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
Objects that move through organs that are surrounded by smooth muscle are often moved by means of |
|  | A) | neuron stimulated control. |
|  | B) | peristalsis. |
|  | C) | wave summation movement. |
|  | D) | treppe patterns. |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
Of the following muscle types, which one is found in the middle layer of the aorta? |
|  | A) | skeletal muscle |
|  | B) | cardiac muscle |
|  | C) | smooth muscle |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
The "all-or-none" concept of skeletal muscle contraction means that |
|  | A) | all muscles contract completely and not partially. |
|  | B) | muscle fascicles contract completely. |
|  | C) | muscle fibers contract completely. |
|  | D) | all of the actin and myosin molecules contract. |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
Which of the following best describes the use of muscle tone in the body? |
|  | A) | It keeps heart muscle activated and functional. |
|  | B) | It keeps smooth muscles in a ready state. |
|  | C) | It prevents fatigue. |
|  | D) | It keeps our backs straight and our heads up. |
|
|
 |
| 31 |  | 
Action potential frequency is best described as: |
|  | A) | The strength of the muscle contractions. |
|  | B) | The size of the muscle contracting. |
|  | C) | The speed of muscle contractions |
|  | D) | The number of action potentials produced per unit of time. |
|
|
 |
| 32 |  | 
Triads in skeletal muscle consist of which of the following? |
|  | A) | sarcoplasm, sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions |
|  | B) | sarcoplasmic reticulum, terminal cisterna, sarcoplasm |
|  | C) | two terminal cisternae and a T-tubule. |
|  | D) | two T-tubules and one terminal cisterna |
|
|
 |
| 33 |  | 
When acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft, what happens to the choline? |
|  | A) | It is destroyed. |
|  | B) | It is made into new acetylcholinesterase. |
|  | C) | It is reabsorbed at the presynaptic terminal and combined with more acetic acid to make acetylcholine. |
|  | D) | It is taken up at the postsynaptic terminal. |
|
|
 |
| 34 |  | 
The recovery stroke in muscle contraction involves which of the following? |
|  | A) | movement of the myosin molecule while the cross-bridge is attached |
|  | B) | return of the myosin head to its original position after the cross bridge releases |
|  | C) | actin slides on myosin |
|  | D) | myosin slides on actin |
|
|
 |
| 35 |  | 
Which of the following is one of the primary functions of muscle tissue? |
|  | A) | regeneration of mass |
|  | B) | heat production |
|  | C) | growth |
|  | D) | the ability to last forever |
|
|
 |
| 36 |  | 
The ability of a muscle to be stimulated is called |
|  | A) | contractility |
|  | B) | elasticity |
|  | C) | extensibility |
|  | D) | excitability |
|
|
 |
| 37 |  | 
Which of the following muscles is involuntary and is the most widely found throughout the body? |
|  | A) | skeletal |
|  | B) | smooth |
|  | C) | cardiac |
|  | D) | somatic |
|
|
 |
| 38 |  | 
Which of the following types of muscles contain intercalated discs and branching fibers? |
|  | A) | skeletal |
|  | B) | smooth |
|  | C) | cardiac |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 39 |  | 
Which of the following muscle types contains peripherally located, multiple nuclei in its cells? |
|  | A) | skeletal |
|  | B) | cardiac |
|  | C) | smooth |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 40 |  | 
The striations in striated muscle correspond with actual molecular structures. Which of the following is the Z line? |
|  | A) | a band where only actin molecules are found |
|  | B) | a band where only myosin molecules are found |
|  | C) | an attachment point for actin molecules |
|  | D) | an attachment point for myosin molecules |
|
|
 |
| 41 |  | 
The striations in striated muscle correspond with actual molecular structures. Which of the following is the I band? |
|  | A) | a band where only actin molecules are found |
|  | B) | a band where only myosin molecules are found |
|  | C) | an attachment point for actin molecules |
|  | D) | an attachment point for myosin molecules |
|
|
 |
| 42 |  | 
The striations in striated muscle correspond with actual molecular structures. Which of the following is the H band? |
|  | A) | a band where only actin molecules are found |
|  | B) | a band where only myosin molecules are found |
|  | C) | an attachment point for actin molecules |
|  | D) | an attachment point for myosin molecules |
|
|
 |
| 43 |  | 
Which of the following is the A band within a myofibril? |
|  | A) | actin myofilaments in profile |
|  | B) | myosin myofilaments in profile |
|  | C) | Z disks in profile |
|  | D) | gaps between the actin and myosin myofilaments |
|
|
 |
| 44 |  | 
Which of the following is the unit in a myofibril from Z line to Z line? |
|  | A) | sarcomere |
|  | B) | sarcolemma |
|  | C) | somatic motor fibers |
|  | D) | thick and thin filaments uniting |
|
|
 |
| 45 |  | 
Which of the following best describes a muscle motor unit? |
|  | A) | a section of myofibrils from Z lines to Z lines |
|  | B) | one nerve fiber and all the muscle fibers innervated by that nerve |
|  | C) | all of the nerves that unite to make a whole muscle contract |
|  | D) | all of the fascicles innervated by several neurons |
|
|
 |
| 46 |  | 
On the surface of the sarcolemma, the voltage may shift up and down rapidly. This change in electrical potential caused by shifts in ions across the membrane is known as a(n) |
|  | A) | action potential |
|  | B) | myosin potential |
|  | C) | energy of dissipation |
|  | D) | all-or-none potential energy |
|
|
 |
| 47 |  | 
During an action potential, calcium is released into the sarcoplasm, near the actin and myosin molecules. Which of the following is the best explanation of what the calcium does? |
|  | A) | The calcium binds to the actin and myosin and makes them work together. |
|  | B) | The calcium breaks apart ATP to ADP and P. |
|  | C) | The calcium removes the tropomyosin block. |
|  | D) | The calcium causes the release of acetylcholine. |
|
|
 |
| 48 |  | 
When the myosin head (of the thick filament) flexes into a bend, while releasing ADP and inorganic phosphate, pulling the thin filament along with it, this is called the |
|  | A) | action reaction |
|  | B) | power stroke |
|  | C) | recovery stroke |
|  | D) | muscle tone |
|
|
 |
| 49 |  | 
When the thick and the thin filaments pull together, which of the following is TRUE? |
|  | A) | The Z to Z line unit moves apart. |
|  | B) | The myofibril doubles in size. |
|  | C) | The muscle loses tone. |
|  | D) | The sarcomere gets shorter. |
|
|
 |
| 50 |  | 
The tissues of cardiac muscle have unique structures known as |
|  | A) | circular muscle fibers |
|  | B) | abundant elastic fibers |
|  | C) | intercalated discs |
|  | D) | pacemaker cells |
|
|
 |
| 51 |  | 
Intercalated discs are capable of doing which of the following? |
|  | A) | allow for re-growth of damaged muscle cells |
|  | B) | pass the resting potential to other cardiac cells |
|  | C) | pass electrical stimulation to other cardiac cells |
|  | D) | allow for cardiac tissue to expand and contract properly |
|
|
 |
| 52 |  | 
Which of the following is unique about cardiac muscle tissue? |
|  | A) | The cells have large mitochondria. |
|  | B) | The cells are large and wide. |
|  | C) | There are very few nuclei within the cells. |
|  | D) | There is no neuron innervation. |
|
|
 |
| 53 |  | 
Which of the following is TRUE of cardiac tissue? |
|  | A) | It contains only small amounts of myoglobin and glycogen. |
|  | B) | It has few nerve endings within the tissue. |
|  | C) | The fibers are not arranged in bundles. |
|  | D) | It has abundant glycogen and myoglobin and is aerobic |
|
|
 |
| 54 |  | 
Which of the following proteins attaches Z discs to myosin myofilaments? |
|  | A) | nebulin |
|  | B) | titin |
|  | C) | actin |
|  | D) | both A and C |
|
|
 |
| 55 |  | 
The functional connection between a nerve fiber and a muscle fiber is called a(an) |
|  | A) | T tubule. |
|  | B) | I band. |
|  | C) | synapse. |
|  | D) | troponin-myosin component. |
|
|
 |
| 56 |  | 
When the neuron stimulates a muscle fiber, what molecule diffuses across the gap between them? |
|  | A) | calcium |
|  | B) | acetylcholine |
|  | C) | sodium |
|  | D) | sodium and potassium |
|
|
 |
| 57 |  | 
Once a signal molecule has left the neuron and binds to a receptor molecule on the surface of the muscle fiber, a sodium channel opens, allowing entry of sodium into the muscle fiber. Which substance is then released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum? |
|  | A) | calcium |
|  | B) | acetylcholine |
|  | C) | sodium |
|  | D) | sodium and potassium |
|
|
 |
| 58 |  | 
Muscle fibers and neurons are called electrically excitable cells because |
|  | A) | their membranes respond to electricity |
|  | B) | their plasma membranes exhibit voltage changes in response to stimulation |
|  | C) | their surfaces respond to the release of acetylcholine |
|  | D) | they have junctional folds in the membranes that can trap electrical charges |
|
|
 |
| 59 |  | 
Movement of which of the following proteins causes exposure of the active sites on the actin molecule? |
|  | A) | troponin |
|  | B) | tropomyosin |
|  | C) | myosin |
|  | D) | acetylcholine |
|
|
 |
| 60 |  | 
What type of molecule is acetylcholine? |
|  | A) | It is a protein. |
|  | B) | It is a neurotransmitter. |
|  | C) | It is an activator molecule. |
|  | D) | It is a polarized molecule. |
|
|
 |
| 61 |  | 
Binding of acetylcholine with its receptor on muscle cells causes |
|  | A) | opening of a ligand-gated sodium channel |
|  | B) | a gap in the cell membrane for calcium diffusion |
|  | C) | vesicle release of sodium ions |
|  | D) | opening of a ligand-gated calcium channel |
|
|
 |
| 62 |  | 
What kind of molecule is ACh? |
|  | A) | nucleic acid |
|  | B) | protein |
|  | C) | carbohydrate |
|  | D) | lipid |
|
|
 |
| 63 |  | 
In the muscle fiber, what is the function of acetylcholinesterase? |
|  | A) | It closes the neuromuscular junction to stop a muscle contraction. |
|  | B) | It acts as a receptor for acetylcholine. |
|  | C) | It deactivates acetylcholine. |
|  | D) | It stimulates the synaptic knob into functioning. |
|
|
 |
| 64 |  | 
What is the voltage of the resting potential of the sarcolemma? |
|  | A) | 70 mv |
|  | B) | -70 mv |
|  | C) | -45 mv |
|  | D) | -15 mv |
|
|
 |
| 65 |  | 
Which of the following is a molecule that binds to a receptor? |
|  | A) | acetylcholine |
|  | B) | tropomyosin |
|  | C) | acetylcholinesterase |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 66 |  | 
Which of the following assures quick removal of neurotransmitter at the junction between a nerve and a muscle? |
|  | A) | acetylcholine |
|  | B) | dopamine |
|  | C) | acetylcholinesterase |
|  | D) | PABA |
|
|
 |
| 67 |  | 
A buildup of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft without breakdown may cause which of the following? |
|  | A) | spastic paralysis |
|  | B) | treppe |
|  | C) | myasthenia gravis |
|  | D) | flaccid paralysis |
|
|
 |
| 68 |  | 
In a muscle twitch, which of the following represents the time between application of a stimulus and the beginning of contraction? |
|  | A) | treppe |
|  | B) | tetany |
|  | C) | lag |
|  | D) | relaxation |
|
|
 |
| 69 |  | 
Which of the following determines the height of the peaks in multiple motor unit summation? |
|  | A) | the speed of stimuli |
|  | B) | the amount of tension produced by the number of motor units responding |
|  | C) | the strength of each stimulus |
|  | D) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 70 |  | 
Which of the following would represent incomplete tetanus? |
|  | A) | multiple contractions with no relaxation |
|  | B) | multiple contractions with slight relaxation |
|  | C) | multiple contractions followed by a long rest period |
|  | D) | a long rest period before contractions start |
|
|
 |
| 71 |  | 
Which of the following explains why treppe takes place in muscle contractions? |
|  | A) | decreased calcium levels around the myofibrils |
|  | B) | increased sodium around the myofibrils |
|  | C) | increased calcium levels around the myofibrils |
|  | D) | decreased potassium around the myofibrils |
|
|
 |
| 72 |  | 
Which of the following is true of an isometric muscle contraction? |
|  | A) | The length of the muscle increases during the contraction. |
|  | B) | responsible for rapid movements of the extremities |
|  | C) | divided into concentric and eccentric |
|  | D) | The amount of tension increases during the contraction. |
|
|
 |
| 73 |  | 
Eccentric muscle contractions occur when |
|  | A) | a person slowly lowers a heavy weight |
|  | B) | the length of the muscle does not change |
|  | C) | a person rapidly raises a lighter weight |
|  | D) | the length of the muscle decreases |
|
|
 |
| 74 |  | 
All of the following are true of muscle tone except |
|  | A) | exists for long periods of time |
|  | B) | depends on multiple motor units contracting in phase with each other |
|  | C) | helps maintain the head upright |
|  | D) | Tension in the whole muscle remains constant. |
|
|
 |
| 75 |  | 
Smooth body movements result from |
|  | A) | large numbers of motor units in complete tetanus throughout the contraction. |
|  | B) | small numbers of motor units firing in a "single twitch" fashion simultaneously. |
|  | C) | isometric contractions only. |
|  | D) | both incomplete and complete titanic contractions of motor units contracting out of phase with each other. |
|
|
 |
| 76 |  | 
Active tension in a muscle is defined as |
|  | A) | the tension applied to load when the muscle is stretched but not stimulated. |
|  | B) | the tension applied to a load when myofilaments within sarcomeres minimally overlap. |
|  | C) | the tension applied to a load when the muscle contracts. |
|  | D) | muscle contraction produced wholly from complete tetanus. |
|
|
 |
| 77 |  | 
The sum of active and passive tension is called |
|  | A) | concentric tension. |
|  | B) | total tension. |
|  | C) | sarcomere tension. |
|  | D) | treppe. |
|
|
 |
| 78 |  | 
Which of the following types of muscle fatigue represents depletion of ATP? |
|  | A) | psychological |
|  | B) | synaptic |
|  | C) | muscular |
|  | D) | physiological |
|
|
 |
| 79 |  | 
Which of the following types of fatigue is caused by the release of more acetylcholine than can be produced to replace it? |
|  | A) | muscular |
|  | B) | psychological |
|  | C) | synaptic |
|  | D) | physiological |
|
|
 |
| 80 |  | 
Muscle soreness can be produced by which of the following? |
|  | A) | muscular fatigue |
|  | B) | enzymes in the extracellular fluid commonly found within muscle |
|  | C) | collagen in the extracellular fluid |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 81 |  | 
Which of the following represents extreme muscular fatigue when the muscle is incapable of either contracting or relaxing? |
|  | A) | physiological contracture |
|  | B) | physiological contraction |
|  | C) | psychological fatigue |
|  | D) | synaptic fatigue |
|
|
 |
| 82 |  | 
Which of the following energy storages source is most commonly used during the first 10 seconds of exercise? |
|  | A) | ATP |
|  | B) | creatine phosphate |
|  | C) | lactic acid |
|  | D) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 83 |  | 
During anaerobic respiration, what is the net amount of ATP produced? |
|  | A) | 4 ATP |
|  | B) | 6 ATP |
|  | C) | 20 ATP |
|  | D) | 2 ATP |
|
|
 |
| 84 |  | 
Which of the following represents the amount of oxygen that is necessary for the body to recover from anaerobic respiration? |
|  | A) | creatine phosphate utilization period |
|  | B) | oxygen overload |
|  | C) | oxygen debt |
|  | D) | aerobic respiration |
|
|
 |
| 85 |  | 
All of the following are characteristics of slow-twitch fibers except |
|  | A) | slow contraction. |
|  | B) | large diameter. |
|  | C) | good blood supply. |
|  | D) | many mitochondria. |
|
|
 |
| 86 |  | 
All of the following are true about fast-twitch fibers except |
|  | A) | high amount of myoglobin |
|  | B) | rapid contraction |
|  | C) | break down ATP rapidly |
|  | D) | fewer mitochondria than slow-twitch fibers |
|
|
 |
| 87 |  | 
Which of the following is true about distribution of fast and slow-twitch fibers in the body? |
|  | A) | Fast-twitch fibers are primarily found in long distance runners. |
|  | B) | Slow-twitch fibers are usually more resistant to fatigue. |
|  | C) | There is a clear separation of slow- and fast-twitch fibers in individual muscles. |
|  | D) | Training does not influence the balance of fast- and slow-twitch fibers. |
|
|
 |
| 88 |  | 
A person with an arm immobilized in a cast for 6 weeks will |
|  | A) | develop muscular hypertrophy. |
|  | B) | decrease the number of muscle fibers. |
|  | C) | develop muscular atrophy. |
|  | D) | Both B and C. |
|
|
 |
| 89 |  | 
Which of the following effects of exercise elevate the body temperature? |
|  | A) | elevated metabolism from the oxygen debt |
|  | B) | vasodilation of blood vessels in the skin |
|  | C) | skeletal muscle contractions |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 90 |  | 
Unitary smooth muscle is found in which of the following locations in the body? |
|  | A) | digestive tract |
|  | B) | reproductive tract |
|  | C) | urinary tract |
|  | D) | all of the above |
|
|
 |
| 91 |  | 
Which of the following is true about smooth muscle? |
|  | A) | The resting membrane potential is less negative than in skeletal muscle. |
|  | B) | It responds in an "all or none" fashion. |
|  | C) | It does not respond to hormones. |
|  | D) | It has a faster speed of contraction than skeletal muscle. |
|
|
 |
| 92 |  | 
Which of the following are the most common neurotransmitters in smooth muscle? |
|  | A) | dopamine and epinephrine |
|  | B) | acetylcholine and epinephrine |
|  | C) | acetylcholine and norepinephrine |
|  | D) | acetylcholine and dopamine |
|
|
 |
| 93 |  | 
All of the following are properties of cardiac muscle cells except |
|  | A) | intercalated discs |
|  | B) | involuntary |
|  | C) | branching fibers |
|  | D) | shorter in duration of contraction than skeletal muscles. |
|
|
 |
| 94 |  | 
Which of the following is not an effect of aging on skeletal muscle? |
|  | A) | increased time for muscle to respond to stimuli |
|  | B) | increased myoglobin |
|  | C) | increased recovery time |
|  | D) | loss of muscle fibers |
|
|
 |
| 95 |  | 
Which of the following exercises slows the loss of muscle fibers in older people? |
|  | A) | jogging |
|  | B) | aerobic dancing |
|  | C) | weight training |
|  | D) | swimming |
|
|
 |
| 96 |  | 
Which of the following is true about skeletal muscle fibers in aging people? |
|  | A) | The number of fibers decreases. |
|  | B) | There is a decreased density of capillaries that supply muscle cells. |
|  | C) | The number of motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscle decreases. |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
|
|

