 |
1 |  | 
In the picture below, if you watch a star from 10 PM until 4 AM, it will
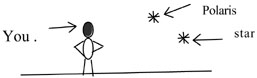 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | move in a clockwise circle about Polaris. |
|  | B) | move in a counterclockwise circle about Polaris. |
|  | C) | move in a clockwise ellipse about Polaris. |
|  | D) | move in a counterclockwise ellipse about Polaris. |
|  | E) | not move. |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
In order to account for the looping paths that planets appear to have in the night sky, Ptolemy said that planets must move in small circles about a point that travels |
|  | A) | in a large circle about the earth. |
|  | B) | in a large circle about the sun. |
|  | C) | in a large ellipse about the earth. |
|  | D) | in a large ellipse about the sun. |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
Occam’s Razor says that if two theories predict the same physical phenomenon, |
|  | A) | the most complicated one almost always turns out to be the correct one. |
|  | B) | the simplest one almost always turns out to be the correct one. |
|  | C) | any theory is as good as any other. |
|  | D) | more theories are needed. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
The planet Venus is sometimes called the Morning Star or the Evening Star. This is because it only appears in the sky at sunrise or at sunset. Why is this? |
|  | A) | The sun only illuminates Venus in the morning and the evening. |
|  | B) | Venus is fairly dim because it is far away from the earth and we only notice it at these times. |
|  | C) | Venus orbits closer to the sun than we do so that, when we look at it, we always have to look toward the sun. |
|  | D) | None of these. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
Below is a sketch (not to scale, of course) of the sun and a planet. The planet’s elliptical orbit has been exaggerated. At which point does the planet travel fastest in its orbit?
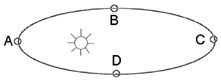 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg02.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg02.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
Below is a sketch of a planet with two artificial satellites in orbit around it. Which satellite has a shorter orbital period?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg03.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg03.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | A has a shorter period. |
|  | B) | B has a shorter period. |
|  | C) | A and B both have the same period. |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
If the earth’s orbit was farther from the sun than it is now, |
|  | A) | our year would be longer. |
|  | B) | our year would be shorter. |
|  | C) | our day would be longer. |
|  | D) | our day would be shorter. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
How is a spinning water balloon like the earth? |
|  | A) | Both show the effects of tides. |
|  | B) | Both tend to flatten down on the top and bottom, and bulge out along the sides due to the rotation. |
|  | C) | Both have comparable densities. |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
In the picture below, which point or points on the earth are at low tide?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg04.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509791/169244/dcqCh01fg04.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 1 only |
|  | B) | 3 only |
|  | C) | 1 and 3 |
|  | D) | 2 and 4 |
|  | E) | 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
The reason the moon does not crash into the earth is that the |
|  | A) | earth’s gravitational field is weak at the moon. |
|  | B) | gravitational pull of other planets keeps the moon up. |
|  | C) | moon’s velocity is just right to keep it in orbit. |
|  | D) | the natural state of motion of an object is to travel in a circle. |
 |

