 |
| 1 |  | 
Microorganisms belonging to the same __________ would be expected to have the most characteristics in common with each other. |
|  | A) | order |
|  | B) | species |
|  | C) | family |
|  | D) | kingdom |
|  | E) | genus |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The Cavalier-Smith's eight kingdom system of classification includes all of the following except: |
|  | A) | fungi |
|  | B) | bacteria |
|  | C) | viruses |
|  | D) | algae |
|  | E) | slime molds |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
To which kingdom do the cyanobacteria belong? |
|  | A) | Fungi |
|  | B) | Eubacteria |
|  | C) | Protista |
|  | D) | Plantae |
|  | E) | Animalia |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A unicellular heterotroph with a nucleus but possess 70S ribosomes and lack golgi apparatuses should be placed in which kingdom |
|  | A) | Fungi |
|  | B) | Eubacteria |
|  | C) | Archezoa |
|  | D) | Chromista |
|  | E) | Animalia |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Which is NOT true of the name Escherichia coli |
|  | A) | Escherichia is the genus to which it belongs |
|  | B) | coli is the strain to which it belongs |
|  | C) | it is a scientific name |
|  | D) | more characteristics have to be met to belong to the coli taxon compared to Escherichia taxon. |
|  | E) | the name is based on binomial nomenclature |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Which kingdom would an organism with the following characteristics most likely belong: true nucleus, non-photosynthetic, non-motile, absorb nutrients, and reproduce by forming spores? |
|  | A) | Fungi |
|  | B) | Eubacteria |
|  | C) | Protista |
|  | D) | Plantae |
|  | E) | Animalia |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
What is being compared during DNA hybridization studies of two bacteria? |
|  | A) | rate of DNA replication |
|  | B) | mechanism of RNA synthesis from DNA |
|  | C) | ratio of nitrogenous base to all other bases |
|  | D) | similarity of base sequences |
|  | E) | nature of the 16S RNA component |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Which pair of microorganisms would you expect to be most closely related? |
|  | A) | yeasts and actinomycetes |
|  | B) | Staphylococcus and Escherichia |
|  | C) | Streptococcus pyogenes and type a and Streptococcus pyogenes type b |
|  | D) | Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae |
|  | E) | Micrococcus and Staphylococcus |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
What was one of the first and most useful microscopic tests for classifying bacteria that is still important today? |
|  | A) | Gram stain |
|  | B) | flagella stains |
|  | C) | simple stain |
|  | D) | negative stain for capsule |
|  | E) | metachromatic granule stain |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Organism A has 65 percent G+C and organism B has 35 percent G+C. Which of the following can be concluded from these data? |
|  | A) | The two organisms are related. |
|  | B) | The two organisms are unrelated. |
|  | C) | The organisms make entirely different enzymes. |
|  | D) | Their nucleic acids will not hybridize. |
|  | E) | Nothing can be concluded from G+C information. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Bacterial strains A and B both have % GC of 51. This would indicate that they |
|  | A) | are closely related. |
|  | B) | are the same species. |
|  | C) | have the same habitat. |
|  | D) | might be closely related. |
|  | E) | would undergo genetic recombination. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are not in the same family. This indicates that which of the following is not sufficient to assign an organism to a taxon? |
|  | A) | Biochemical characteristics |
|  | B) | Amino acid sequencing |
|  | C) | Phage typing |
|  | D) | Serology |
|  | E) | Morphological characteristics |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Amino acid sequencing infers information about |
|  | A) | morphology. |
|  | B) | identification of an organism. |
|  | C) | nucleotide bases making up a gene. |
|  | D) | antigenic composition. |
|  | E) | enzymatic activities. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Biochemical tests are used to determine |
|  | A) | enzymatic activities. |
|  | B) | nucleic acid base composition. |
|  | C) | amino acid sequences. |
|  | D) | staining characteristics. |
|  | E) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which kingdom would an organism with the following characteristics most likely belong: true nucleus, multicellular, photosynthetic, chloroplasts within cytoplasmic matrix? |
|  | A) | Chromista |
|  | B) | Eubacteria |
|  | C) | Protozoa |
|  | D) | Plantae |
|  | E) | Animalia |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Which of the following is the arrangement of organisms into groups or taxa? |
|  | A) | nomenclature |
|  | B) | identification |
|  | C) | systematics |
|  | D) | classification |
|  | E) | phylogeny |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Extensive sequential nucleotide analysis and analysis of rRNA has divided the living world into three domains called |
|  | A) | bacteria, archaea and eucarya. |
|  | B) | procarya, eucarya and animals. |
|  | C) | fungi, plants and animals. |
|  | D) | archaea, eucarya and viruses. |
|  | E) | bacteria, archaea and cyanobacteria. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
A(n) _____ classification system arranges organisms into groups whose members share many characteristics and reflects as much as possible the biological nature of organisms. |
|  | A) | artificial |
|  | B) | natural |
|  | C) | phylogenetic |
|  | D) | molecular |
|  | E) | phrenetic |
|
|
Compare the following entities (I and II). Characterize them according to the following key:
 |
| 19 |  | 
I. The similarity between a pair of species that has a simple matching coefficient of 0.9. II. The similarity between a pair of species that has a simple matching coefficient of 0.6. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | I is less than II. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
I. Degree of similarity of base sequences between species A and B when A has a G+C content of 44. II. Degree of similarity of base sequences between species B and A when B has a G+C content of 44. |
|  | A) | I is greater than II. |
|  | B) | I is less than II. |
|  | C) | I is exactly or approximately equal to II. |
|  | D) | I may stand in more than one of the above relations to II. |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
A _____ is a diagram usually placed on its side with the X-axis graduated in units of similarity. |
|  | A) | similarity matrix |
|  | B) | simple matching coefficient |
|  | C) | dendrogram |
|  | D) | profile number |
|  | E) | Harvard matrix transformation |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
All of the following are examples of morphological features used for classification and identification of procaryotes except |
|  | A) | staining behavior. |
|  | B) | colonial shape and color. |
|  | C) | endospore morphology and location. |
|  | D) | cell shape. |
|  | E) | fermentation products. |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
All of the following are examples of physiological and metabolic characteristics used for classification and identification of procaryotes except |
|  | A) | oxygen relationships. |
|  | B) | staining behavior. |
|  | C) | luminescence. |
|  | D) | cell wall constituents. |
|  | E) | fermentation products. |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
If the figures below represent the hybridization that occurs between two strands of DNA from different organisms, which result shows the greatest degree of similarity between organisms?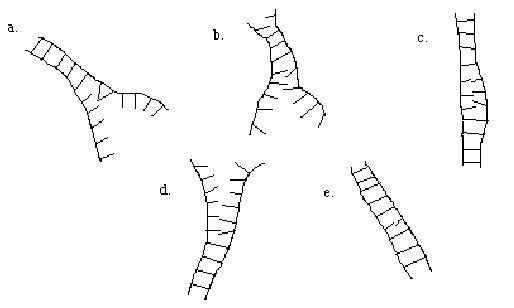 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20554/ch19_num24_quizimage.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072556781/20554/ch19_num24_quizimage.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | See above image. |
|  | B) | See above image. |
|  | C) | See above image. |
|  | D) | See above image. |
|  | E) | See above image. |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
Molecular chronometers is based on the concept that nucleic acid and amino acid sequences - of similar molecules are quite different in two groups of organisms indicating a recent divergence between the groups.
- change over time without destroying their function because changes are neutral.
|
|  | A) | I only is true. |
|  | B) | II only is true. |
|  | C) | Both I and II are true. |
|  | D) | Neither I nor II are true. |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
An oligonucleotide signature sequence is a set of nucleotide sequences that - occur in a large number of phylogenetic groups.
- occur in most or all members of a particular phylogetic group.
|
|  | A) | I only is true. |
|  | B) | II only is true. |
|  | C) | Both I and II are true. |
|  | D) | Neither I nor II are true. |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
Even though the two domains are procaryotic, the Archaea domain differs from the Bacteria domain in that the Archaea - lack muramic acid in their cell walls.
- posses membrane lipids with ether-linked branched aliphatic chains.
|
|  | A) | I only is true. |
|  | B) | II only is true. |
|  | C) | Both I and II are true. |
|  | D) | Neither I nor II are true. |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
The Whittaker five kingdom system of classification divides living organisms into which of the following kingdoms? |
|  | A) | Archaea, Bacteria, Fungi, Plants, Animals |
|  | B) | Monera, Protista, Plants, Animals, Fungi |
|  | C) | Monera, Protista, Archaea, Animals, Fungi |
|  | D) | Monera, Protista, Plants, Animals, Archaea |
|  | E) | Viruses, Protista, Plants, Animals, Fungi |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
The Cavalier-Smith's eight kingdom system of classification includes all of the following except: |
|  | A) | Protozoa |
|  | B) | Eubacteria |
|  | C) | Archezoa |
|  | D) | Chromista |
|  | E) | Virons |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
All of the following are used to characterize procaryotic organisms for the First Edition of Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriologyexcept: |
|  | A) | Gram-staining properties |
|  | B) | presence of endospores |
|  | C) | oxygen relationship |
|  | D) | phylogenetic information |
|  | E) | motility |
|
|

