 |
| 1 |  | 
Of the following fiscal policies, which one is most expansionary? |
|  | A) | $100 billion tax cut |
|  | B) | $100 billion increase in government spending |
|  | C) | $100 billion increase in both government spending and taxes |
|  | D) | $100 billion decrease in both government spending and taxes |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following diagram.
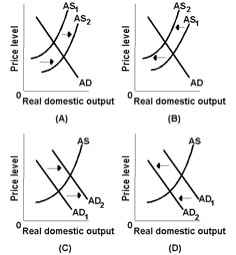 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz11c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz11c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a>
An expansionary fiscal policy is best represented by graph: |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
In 2005, the debt held by the public as a percentage of GDP was about: |
|  | A) | 17% |
|  | B) | 69% |
|  | C) | 31% |
|  | D) | 116% |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The majority of the public debt does not represent a burden on future generations because: |
|  | A) | future generations need pay back only the interest on borrowed funds, not the principal |
|  | B) | the debt can be paid off by selling government land, buildings, and other real assets |
|  | C) | the debt can be paid off by printing new money |
|  | D) | the majority of the debt is owned by the U.S. public and institutions |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Compared to a proportional tax, a progressive tax system: |
|  | A) | increases built-in stability |
|  | B) | reduces built-in stability |
|  | C) | increases the size of the standardized budget deficit |
|  | D) | shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
A strict rule requiring a constantly balanced actual budget would: |
|  | A) | increase the effectiveness of built-in stabilizers |
|  | B) | be impossible with a progressive tax system |
|  | C) | produce a standardized budget surplus when the economy is producing beyond its potential GDP |
|  | D) | produce a standardized budget surplus when the economy is in a recession |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Which of the following exemplifies the crowding-out effect? An increase in government spending: |
|  | A) | is financed by increasing the money supply, reducing interest rates and causing net exports to fall |
|  | B) | is financed by borrowing, raising interest rates and causing private investment to fall |
|  | C) | causes taxes to rise automatically, reducing consumption spending |
|  | D) | causes the price level to rise, reducing net exports |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
A very high level of U.S. public debt to GDP: |
|  | A) | may bankrupt the U.S. |
|  | B) | cannot bankrupt the U.S. because of its ability to tax and to refinance its debt |
|  | C) | is, by itself, evidence of the burden of the debt on future generations |
|  | D) | will offset any attempts at expansionary fiscal policy |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Built-in stabilizers arise from the fact that tax revenues vary directly with GDP. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following diagram.
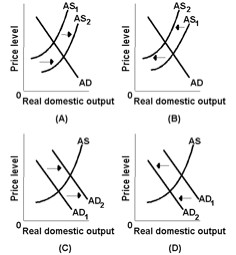 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz11c_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz11c_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. A contractionary fiscal policy is best represented by graph: |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|

