 |
| 1 |  | 
Answer the next question using the following data. All amounts are in billions of dollars.
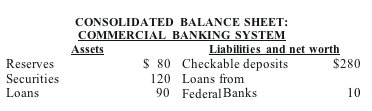 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz14a_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz14a_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
Suppose the reserve requirement is 20%. Further suppose the Federal Reserve Banks buy $5 billion in securities from the public, who deposits this amount into their checking accounts. As a result of these transactions, the supply of money will: |
|  | A) | be unaffected, but the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $25 billion |
|  | B) | directly increase by $5 billion and the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $20 billion |
|  | C) | directly increase by $25 billion and the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will increase by $125 billion |
|  | D) | directly decrease by $5 billion and the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will be unaffected |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
If the current interest rate is below the equilibrium rate: |
|  | A) | the money supply exceeds the quantity of money demanded |
|  | B) | the money supply will increase and the interest rate will rise |
|  | C) | the money supply will decrease and the interest rate will rise |
|  | D) | the interest rate will rise and the quantity of money demanded will decrease |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
An increase in the required reserve ratio will reduce both excess reserves and the size of the monetary multiplier. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A decrease in the money supply will: |
|  | A) | raise interest rates, reducing investment and GDP |
|  | B) | raise interest rates, increasing investment and lowering GDP |
|  | C) | reduce interest rates, increasing investment and GDP |
|  | D) | reduce interest rates, reducing investment and GDP |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Fed purchases of bonds from the public will: |
|  | A) | raise interest rates and increase aggregate demand |
|  | B) | lower interest rates and increase aggregate demand |
|  | C) | lower interest rates and decrease aggregate demand |
|  | D) | raise interest rates and decrease aggregate demand |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Morton Bank goes to the Fed to borrow funds. The interest rate charged by the Fed is known as the: |
|  | A) | prime rate |
|  | B) | Federal funds rate |
|  | C) | bond rate |
|  | D) | discount rate |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
If the Fed buys bonds from the public: |
|  | A) | both the price of bonds and the interest rate received by bond holders will increase |
|  | B) | both the price of bonds and the interest rate received by bond holders will decrease |
|  | C) | the price of bonds will decrease and the interest rate received by bond holders will increase |
|  | D) | the price of bonds will increase and the interest rate received by bond holders will decrease |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
By targeting the Federal funds rate, the Fed: |
|  | A) | can generally push the prime rate in the opposite direction |
|  | B) | can generally push the prime rate in the same direction |
|  | C) | has little control over other interest rates |
|  | D) | can generally push investment in the same direction |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Suppose the interest rate is 10% and a particular bond is priced at $1000. If the interest rate falls to 8%, which of the following represents a possible price for the bond? |
|  | A) | $1000 |
|  | B) | $800 |
|  | C) | $920 |
|  | D) | $1080 |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Refer to the following:
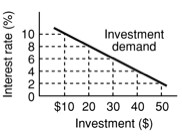 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz14a_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073273082/384258/quiz14a_10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (8.0K)</a>
Suppose the interest rate is currently 6% and the Fed determines that investment of $40 is required to reach full employment GDP. To target this outcome, the Fed might: |
|  | A) | sell bonds to the public |
|  | B) | lower the discount rate |
|  | C) | raise the reserve requirement |
|  | D) | announce a restrictive monetary policy |
|
|

