 |
| 1 |  | 
The effectiveness of an expansionary fiscal policy will be reduced if: |
|  | A) | borrowing increases interest rates and crowds out private investment. |
|  | B) | the dollar depreciates because of an increased outflow of currency. |
|  | C) | the price level falls. |
|  | D) | stock prices rise. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Built-in stabilizers: |
|  | A) | automatically increase the size of deficits when the economy experiences demand-pull inflation. |
|  | B) | avoid the problems associated with the administrative lag of discretionary fiscal policy. |
|  | C) | automatically produce a cyclically balanced budget. |
|  | D) | tend to offset the impact of discretionary fiscal policy. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Answer the question on the basis of the following diagrams.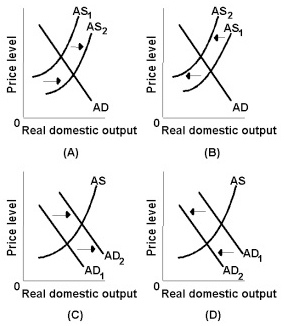 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch13_q3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (41.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch13_q3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (41.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagrams. A contractionary fiscal policy is best represented by graph: |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A very high level of U.S. public debt to GDP: |
|  | A) | may bankrupt the United States. |
|  | B) | cannot bankrupt the United States because of its ability to refinance the debt and its ability to tax. |
|  | C) | is, by itself, evidence of the burden of the debt on future generations. |
|  | D) | will offset any attempts at expansionary fiscal policy. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Which of the following exemplifies the crowding-out effect? An increase in government spending: |
|  | A) | is financed by increasing the money supply, reducing interest rates, and causing net exports to fall. |
|  | B) | is financed by borrowing, raising interest rates, and causing investment to fall. |
|  | C) | causes taxes to rise automatically, reducing consumption spending. |
|  | D) | causes the price level to rise, reducing net exports. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Of the following groups, the largest proportion of the public debt is held by: |
|  | A) | foreign individuals and institutions. |
|  | B) | U.S. government agencies, including the Federal Reserve. |
|  | C) | state and local governments. |
|  | D) | U.S. individuals, banks, and other financial institutions. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Answer the question using the following graph: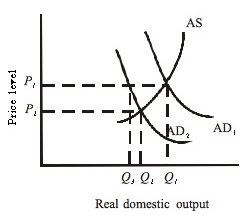 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch13_q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073511455/991476/ch13_q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a>
Refer to the graph. If AD1 represents the current level of expenditures and Q2 is the full-employment level of GDP, the economy is: |
|  | A) | in a recession and expansionary fiscal policy is in order. |
|  | B) | in a recession and contractionary fiscal policy is in order. |
|  | C) | experiencing demand-pull inflation and expansionary fiscal policy is in order. |
|  | D) | experiencing demand-pull inflation and contractionary fiscal policy is in order. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Use the following table to answer the next question:
- Treasury bills, notes, and bonds
- Federal Reserve Notes
- State and local government bonds
- Corporate bonds
- Corporate stock certificates
- U.S. savings bonds
Refer to the table. The public debt consists of item(s): |
|  | A) | 1 and 6 only |
|  | B) | 1, 2, and 6 only |
|  | C) | 1, 2, 3, and 6 only |
|  | D) | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
All else equal, the economic burden of a deficit (an increase in the public debt) will be higher the: |
|  | A) | greater the increase in the interest rate. |
|  | B) | greater the increase in public investment. |
|  | C) | smaller the crowding-out effect. |
|  | D) | greater the increase in the money supply. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
An economy currently is experiencing a negative GDP gap of $500 billion, or 3 percent of its GDP. An appropriate fiscal policy would be: |
|  | A) | a decrease in taxes. |
|  | B) | a decrease in government spending. |
|  | C) | an equal decrease in taxes and government spending. |
|  | D) | an increase in interest rates. |
|
|

