|
| 1 | The total capacitance of two capacitors connected in series is less than that of either capacitor alone. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 2 | The capacitance is dependent on the potential difference placed across its plates. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 3 | If a conductor has a capacitance of one farad, a transfer of one coulomb of charge to the conductor will increase its potential by one volt. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 4 | The capacitance of a given capacitor will be higher if the separation of the plates is reduced without changing the dielectric. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 5 | Insertion of a dielectric between the plates of a capacitor decreases the voltage across it and hence reduces the capacitance. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 6 | If the charge on a capacitor is doubled, the potential energy will be quadrupled. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 7 | For capacitors connected in parallel, the voltage across each capacitor is the same as that across the source. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 8 | The amount of charge that can be placed on a conductor does not depend on |
 | A) | the dielectric strength |
 | B) | its capacitance |
 | C) | its potential |
 | D) | its size or shape |
|
| 9 | The capacitance of a capacitor increases with a decrease in |
 | A) | dielectric constant |
 | B) | permittivity |
 | C) | plate area |
 | D) | plate separation |
|
| 10 | Which of the following is not a representation of the potential energy of a conductor? |
 | A) | ½QV² |
 | B) | Q²/(2 C) |
 | C) | ½QV |
 | D) | ½CV² |
|
| 11 | Which of the following is true for capacitors in series? |
 | A) | The total capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitances. |
 | B) | The total charge is the sum of the charges on each capacitor. |
 | C) | The total voltage is the sum of the voltages across each capacitor. |
 | D) | The available charge is shared between two or more capacitors. |
|
| 12 | The plates of a 2-pF capacitor have an extra of 20 cm2. If air is the dielectric, the plate separation must be approximately |
 | A) | 0.885 mm |
 | B) | 8.85 mm |
 | C) | 88.5 mm |
 | D) | 885 mm |
|
| 13 | What potential difference is required to store 24 µC of charge on a 6-µF capacitor? |
 | A) | 4 V |
 | B) | 0.25 V |
 | C) | 40 V |
 | D) | 144 V |
|
| 14 | The voltage across the 3-µF capacitor in Fig. 26-3 is
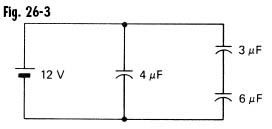 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077158733/294252/fig263.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077158733/294252/fig263.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> |
 | A) | 4 V |
 | B) | 6 V |
 | C) | 8 V |
 | D) | 12 V |
|
| 15 | A certain capacitor has a capacitance of 12 µF when the dielectric is air. The capacitor is charged to 400 V and disconnected from the power source. If a dielectric
(K = 4.0) is inserted, the new voltage will be |
 | A) | 100 V |
 | B) | 400 V |
 | C) | 800 V |
 | D) | 1600 V |
|
| 16 | An 8-µF capacitor is connected to a potential difference of 12 V. The potential energy is |
 | A) | 4.8 X 10-4 J |
 | B) | 5.76 X 10-4 J |
 | C) | 576 J |
 | D) | 480 J |
|
| 17 | The capacitance of a given capacitor will be directly proportional to the of the plates and inversely proportional to . |
|
| 18 | The for a given material is that electric field intensity for which the material ceases to be an insulator and becomes a conductor. |
|
| 19 | Three advantages for the use of dielectrics with capacitors are , , and . |
|
| 20 | Three different physical ratios that can be used to calculate the dielectric constant are , , and . |
|
| 21 | The dielectric constant may also be referred to as the relative of a material. |
|
| 22 | The total capacitance of a number of capacitors connected in series is (less than, greater than, or the same as) the capacitance of any capacitor taken individually. |
|
| 23 | The for a material is the ratio of the capacitance with that material between the plates to the capacitance for a vacuum between the plates. |
|
| 24 | For a given capacitor of known charge Q, voltage V, and capacitance C, list three expressions for calculating its potential energy: , ,and . |
|
| 25 | A group of capacitors connected directly to the same source of potential difference so that the available charge is shared are said to be connected in . |

