|
| 1 | The fundamental unit for length is the mile. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 2 | The kilogram is equivalent to a mass of 1000 g. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 3 | Only vectors having the same dimensions may be added. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 4 | The difference between two vectors is obtained by adding one vector to the negative of the other. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 5 | The order in which two or more vectors are added does not affect their resultant. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 6 | Given the x component of one vector and the y component of another vector, it is possible to find the resultant of the two vectors mathematically. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 7 | The graphical methods of vector addition are not as accurate as the mathematical method. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 8 | Vector addition can be performed only for concurrent vectors. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 9 | If a boat travels upstream with a speed of 8 km/h in a current whose speed is 3 km/h, the boat's speed relative to the shore is 5 km/h. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 10 | The x component of the resultant vector is equal to the sum of the x components of the individual vectors. |
 | A) | True |
 | B) | False |
|
| 11 | Which of the following is not a fundamental quantity? |
 | A) | Length |
 | B) | Force |
 | C) | Mass |
 | D) | Time |
|
| 12 | The resultant of 10 and 15 lb acting in opposite directions on an object is |
 | A) | 150 lb |
 | B) | 25 lb |
 | C) | 5 lb |
 | D) | 20 lb |
|
| 13 | Which is a scalar quantity? |
 | A) | Velocity |
 | B) | Force |
 | C) | Speed |
 | D) | Displacement |
|
| 14 | A force of 3 N acts perpendicularly to a force of 4 N. Their resultant has a magnitude of |
 | A) | 12 N |
 | B) | 7 N |
 | C) | 5 N |
 | D) | 1 N |
|
| 15 | Which is a vector quantity? |
 | A) | Volume |
 | B) | Time |
 | C) | Distance |
 | D) | Displacement |
|
| 16 | Given that the units of s, v, a, and t are feet, feet per second, feet per second squared, and seconds, respectively, which of the following equations is dimensionally incorrect? |
 | A) | s = vt + ½at |
 | B) | 2as = vf 2 - v0 2 |
 | C) | v = v0 + at |
 | D) | s = vt |
|
| 17 | A force of 16 N is directed 30o north of east. The y component of the force is |
 | A) | 8 N |
 | B) | 13.8 N |
 | C) | 12 N |
 | D) | 4.8 N |
|
| 18 | A man walks 9 km east and then 12 km north. The magnitude of his resultant displacement is |
 | A) | 21 km |
 | B) | 15 km |
 | C) | 13 km |
 | D) | 3 km |
|
| 19 | The resultant of the forces in Fig. 3-2 is
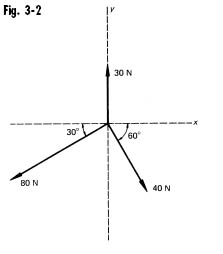 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077158733/294229/fig32.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077158733/294229/fig32.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> |
 | A) | 66.5 N, 222o |
 | B) | 66.5 N, 132o |
 | C) | 66.5 N, 228o |
 | D) | none of these |
|
| 20 | A 20-lb force acts to the left while an 80-lb force acts upward and to the right at an angle of 37o. The magnitude of the resultant force is |
 | A) | 80 lb |
 | B) | 70 lb |
 | C) | 65 lb |
 | D) | 100 lb |
|
| 21 | If two quantities are to be added or subtracted, they must be of the same . |
|
| 22 | Three examples of vector quantities are , , and . |
|
| 23 | A physical quantity that is specified completely by a number and a unit is called a(n) . |
|
| 24 | Every vector can be resolved into two perpendicular vectors called its . |
|
| 25 | A physical quantity that is specified completely by a number, a unit, and a direction is called a(n) . |
|
| 26 | In the method of vector addition, the tail of one vector is connected to the tip of another until all vectors have been represented. |
|
| 27 | The is a single force whose effect is the same as that of a given set of concurrent forces. |
|
| 28 | In the component method, the x component of the resultant vector is equal to the sum of the of each vector. |
|
| 29 | Forces that intersect at a common point or have the same point of application are said to be . |
|
| 30 | The difference between two vectors is obtained by adding one vector to the of the other. |

