 |
| 1 |  | 
Which planets have bigger densities? |
|  | A) | The inner planets |
|  | B) | The outer planets |
|  | C) | The densities of the inner and outer planets are about the same |
|  | D) | The densities of the inner and outer planets are too varied and do not have a pattern |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
How many planets in our solar system have rings? |
|  | A) | 1 |
|  | B) | 2 |
|  | C) | 3 |
|  | D) | 4 |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
If a comet were to fall into a solar system with two suns, which way would the tail point? |
|  | A) | The tail would point behind the comet as it falls in toward the center of the solar system. |
|  | B) | The tail would point halfway between the two suns. |
|  | C) | Two tails would form, one pointing toward one sun and the other pointing toward the second sun. |
|  | D) | Two tails would form, one pointing away from one sun and the other pointing away from the second sun. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A "shooting star" is a |
|  | A) | star that collides with another star and gets bumped out of position. |
|  | B) | comet. |
|  | C) | small piece of matter that falls into the earth's atmosphere. |
|  | D) | star that explodes. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
The planet Mercury is difficult to see in the sky because |
|  | A) | it is so small that it doesn't show up very well. |
|  | B) | the sun's light tends to obscure it. |
|  | C) | it is always behind the sun when we look at it. |
|  | D) | it doesn't reflect sunlight very well. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Venus is unique among the planets in that |
|  | A) | it rotates backwards. |
|  | B) | it revolves backwards. |
|  | C) | it is closest to the sun. |
|  | D) | you can only see it in the sky in the morning and the evening. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Which statement is true about Mars? |
|  | A) | It has two moons that are similar to the earth's moon. |
|  | B) | It is about the same size as the earth. |
|  | C) | It has a day that is about the same as the earth's. |
|  | D) | It has a year that is about the same as the earth's. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Asteroids |
|  | A) | are only found in the Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. |
|  | B) | present no danger to the earth or the other planets. |
|  | C) | are all very small. |
|  | D) | are sometimes the size of a moon. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Galileo used a telescope to see four big moons around which planet? |
|  | A) | Mars |
|  | B) | Jupiter |
|  | C) | Saturn |
|  | D) | Pluto |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Assuming that they don't collide with one another, how do the particles that make up the rings of Saturn move? |
|  | A) | They are stationary in space. |
|  | B) | They move in circles. |
|  | C) | They move in ellipses. |
|  | D) | The rings of Saturn are solid and not made of particles. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
How many planets (excluding the earth) were discovered by observers on the earth without the aid of a telescope? |
|  | A) | 4 |
|  | B) | 5 |
|  | C) | 6 |
|  | D) | 7 |
|  | E) | 8 |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Below is a sketch (not to scale, of course) of the sun, the earth, and the moon. Which position of the moon makes it possible to have a solar eclipse?
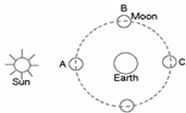 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|  | E) | It is impossible to have a solar eclipse in any of these arrangements. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Below is a sketch (not to scale, of course) of the sun, the earth, and the moon. For which position of the moon would it be possible for people on Earth to view a full moon?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|  | E) | It is impossible to view a full moon in any of these arrangements. |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
What kind of eclipse is it possible to have when the alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth is as follows:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_14.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077263960/649643/Question17_14.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Solar |
|  | B) | Lunar |
|  | C) | Both solar and lunar |
|  | D) | Neither solar nor lunar |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which statement about the moon is TRUE? |
|  | A) | When the moon goes through its phases, the dark part that we can't see is caused by the shadow of the earth. |
|  | B) | The moon is very, very tiny compared to the earth. |
|  | C) | The moon revolves at the same rate that it rotates. |
|  | D) | The craters displayed on the moon's surface were caused by a fairly recent event. |
|
|

