 |
| 1 |  | 
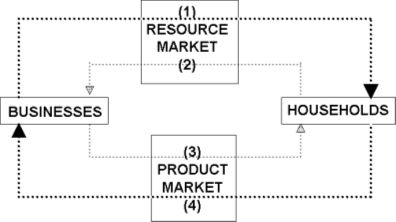
Refer to the following diagram of a circular flow model of the economy:
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883729/ch02_q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883729/ch02_q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a>
In the diagram, consumer expenditures are represented by: |
|  | A) | Flow 1. |
|  | B) | Flow 2. |
|  | C) | Flow 3. |
|  | D) | Flow 4. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
For a market system, which of the following best answers the question, "What goods and services will be produced?" |
|  | A) | Only those goods whose long-term profits are greater than average |
|  | B) | Any good for which consumers are willing to pay a positive price |
|  | C) | Any good whose production is characterized by the least-cost technology |
|  | D) | Any good that returns its producers sufficient revenue to cover its total costs |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The command systems of the Soviet Union and eastern Europe failed in part because: |
|  | A) | previously abundant economic resources became scarce. |
|  | B) | central planners found it increasingly difficult to coordinate the economic decisions of consumers, resource suppliers, and businesses. |
|  | C) | firms manufactured more output than consumers could afford to buy, resulting in a general glut. |
|  | D) | prices were set too low in all markets. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The competitive market system encourages innovation and technological advance, primarily through: |
|  | A) | the government's tax code. |
|  | B) | the process of "dollar voting". |
|  | C) | the guiding function of consumer needs and preferences. |
|  | D) | profitable returns to innovative firms. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Human specialization, or the division of labor: |
|  | A) | reduces output by dehumanizing workers. |
|  | B) | reduces output by discouraging workers from learning a wide variety of tasks. |
|  | C) | increases output by enabling workers to take advantage of differences in their skills. |
|  | D) | increases output by allowing workers to each perform a wide variety of tasks. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Economic profits and losses: |
|  | A) | answer the question "Who will get the output?" |
|  | B) | answer the question "How will the goods and services be produced?" |
|  | C) | help determine which industries survive or fail. |
|  | D) | are the expected outcomes of a decrease in dollar votes and an increase in dollar votes, respectively. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
If a change in consumer preferences results in many more consumers registering their "dollar votes" in favor of peaches, which of the following will most likely follow? |
|  | A) | Profits of peach growers will rise and peach production will rise |
|  | B) | Profits of peach growers will rise and peach production will fall |
|  | C) | Profits of peach growers will fall and peach production will rise |
|  | D) | Profits of peach growers will fall and peach production will fall |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
The market system is characterized by: |
|  | A) | widespread use of government price controls. |
|  | B) | centralized decision-making. |
|  | C) | limited use of capital goods. |
|  | D) | private property rights. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
A firm will earn a positive economic profit if: |
|  | A) | its total sales revenue equals the total cost of labor, capital, raw materials, and entrepreneurship. |
|  | B) | it produces its output utilizing the least-cost production method. |
|  | C) | it is regulated by government. |
|  | D) | its total sales revenue exceeds the sum of all its costs. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
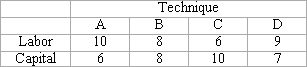
A firm can produce a single unit of output by combining labor and capital in any of the combinations shown in the following table. Labor costs $2 per unit and capital costs $4 per unit.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883729/ch02_q10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883729/ch02_q10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. Which is the most efficient technique for producing the output? |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|

