 |
| 1 |  | 
GDP excludes expenditures for: |
|  | A) | additions to inventories. |
|  | B) | new housing. |
|  | C) | government purchases of military equipment. |
|  | D) | corporate stock. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The "G" term in C + Ig + G + Xn includes all of the following except: |
|  | A) | state government purchases of new computers. |
|  | B) | Social Security checks received by retirees. |
|  | C) | salaries received by members of the military. |
|  | D) | local government expenditures for building new roads. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
The income approach to GDP sums the total income earned by resource suppliers and: |
|  | A) | adds net transfer payments and personal taxes. |
|  | B) | adds net investment and depreciation. |
|  | C) | subtracts net foreign factor income but adds depreciation and taxes on production and imports. |
|  | D) | net transfer payments, depreciation, and net foreign factor income. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Refer to the following data, which shows output and prices for five years of an economy that produces just one product.
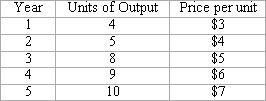 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883752/ch24_q4.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077337727/883752/ch24_q4.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
If Year 3 is the base year, the price index for year 4 is: |
|  | A) | 80. |
|  | B) | 120. |
|  | C) | 20%. |
|  | D) | 1.2. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
The change in real GDP is not an accurate measure of the change in economic welfare because, for example: |
|  | A) | improvements in product quality are overstated. |
|  | B) | expenditures for personal services are excluded. |
|  | C) | the price level changes over time. |
|  | D) | some production creates pollution. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
"The market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year." This best describes: |
|  | A) | net domestic product. |
|  | B) | gross domestic product. |
|  | C) | national income. |
|  | D) | personal income. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
In calculating GDP: |
|  | A) | both exports and imports are added. |
|  | B) | neither exports nor imports are added. |
|  | C) | exports are added and imports are subtracted. |
|  | D) | imports are added and exports are subtracted. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Suppose that last year domestic firms spent $80 billion on final purchases of plant and equipment, of which $15 billion replaced equipment that had worn out during the year. In addition, firms collectively added $10 billion to inventories and new construction totaled $35 billion. In calculating GDP, national income accountants would add gross investment of: |
|  | A) | $95 billion. |
|  | B) | $100 billion. |
|  | C) | $110 billion. |
|  | D) | $125 billion. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Suppose nominal GDP in the base year was $380 billion. Five years later, nominal GDP was $480 and the GDP price index was 120. Over those five years, real GDP: |
|  | A) | increased by $20 billion. |
|  | B) | increased by $96 billion. |
|  | C) | increased by $80 billion. |
|  | D) | did not change. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Disposable income consists of: |
|  | A) | personal income plus personal taxes. |
|  | B) | net domestic product minus personal taxes. |
|  | C) | GDP corrected for inflation. |
|  | D) | consumption plus saving. |
|
|

