 |
| 1 |  | 
Which of the following factors is most likely established based on the results of prior years' audit examinations? |
|  | A) | Expected population deviation rate. |
|  | B) | Population size. |
|  | C) | Risk of overreliance. |
|  | D) | Tolerable rate of deviation. |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
If the risk of overreliance is 5%, the tolerable rate of deviation is 8%, and the expected population deviation rate is 1%, the necessary sample size is: |
|  | A) | 28 |
|  | B) | 36 |
|  | C) | 48 |
|  | D) | 58 |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following combination of factors would yield the largest sample size (ROO = Risk of overreliance, TRD = Tolerable rate of deviation, EPDR = Expected population deviation rate)? |
|  | A) | ROO = 5%, TRD = 2%, EPDR = 0% |
|  | B) | ROO = 10%, TRD = 2%, EPDR = 0% |
|  | C) | ROO = 5%, TRD = 6%, EPDR = 0% |
|  | D) | ROO = 10%, TRD = 6%, EPDR = 0% |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
If the auditor cannot locate a sample item, he or she should: |
|  | A) | Replace the item in the sample with another item. |
|  | B) | Classify the missing item as a deviation. |
|  | C) | Reselect the entire sample and begin examining sample items. |
|  | D) | Issue a qualified opinion on the client's financial statements. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
If the sample rate of deviation is 6.2%, the upper limit rate of deviation is 8%, the tolerable rate of deviation is 7%, and the risk of overreliance is 5%, which of the following statements is not true? |
|  | A) | The auditor is unable to rely on internal control is planned. |
|  | B) | There is a 95% chance that the true deviation rate is less than or equal to 8%. |
|  | C) | The allowance for sampling risk is 1%. |
|  | D) | There is a 5% chance that the true deviation rate is greater than 8%. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
If the auditor examined 60 items and found 6 deviations, which of the following is not true (assuming a risk of overreliance of 5%)? |
|  | A) | The sample rate of deviation is 10%. |
|  | B) | The upper limit rate of deviation is 18.8%. |
|  | C) | The allowance for sampling risk is 8.8%. |
|  | D) | All of the above statements are true. |
|
|
 |
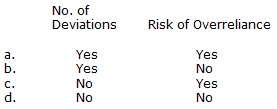
| 7 |  | 
Which of the following has a direct relationship with the upper limit rate of deviation?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077862341/1014840/Ch_Mod_F_q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0077862341/1014840/Ch_Mod_F_q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | a. |
|  | B) | b. |
|  | C) | c. |
|  | D) | d. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
A method of sampling used when deviations from controls are critical yet are expected to occur at a relatively low rate is referred to as: |
|  | A) | Attributes sampling. |
|  | B) | Discovery sampling. |
|  | C) | Statistical sampling. |
|  | D) | Variables sampling. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
How is the tolerable rate of deviation established by the auditor? |
|  | A) | Based on the necessary level of detection risk determined from the use of the audit risk model. |
|  | B) | Based on the level used in prior years' audits. |
|  | C) | Based on the desired level of control risk. |
|  | D) | Based on the sample rate of deviation. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
The rate of deviations that has a one minus risk of overreliance probability of equaling or exceeding the true deviation rate is the: |
|  | A) | Upper limit rate of deviation. |
|  | B) | Expected population deviation rate. |
|  | C) | Sample rate of deviation. |
|  | D) | Tolerable rate of deviation. |
|
|

