 |
| 1 |  | 
Consider the following inventory activity:
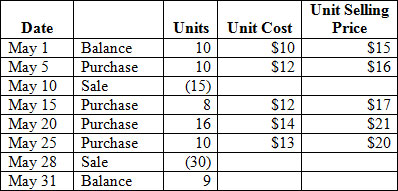 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (35.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (35.0K)</a>
The 9 units of ending inventory are identified with the purchase of May 20. Using the specific identification method, calculate the value of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold. |
|  | A) | $126 and $430, respectively |
|  | B) | $126 and $530, respectively |
|  | C) | $126 and $544, respectively |
|  | D) | $56 and $474, respectively |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Consider the following inventory activity:
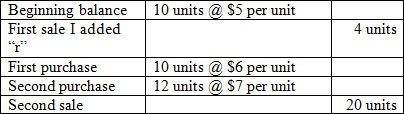 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a>
What is the value of the ending inventory, using a perpetual inventory system and a FIFO cost flow assumption? |
|  | A) | $46 |
|  | B) | $56 |
|  | C) | $36 |
|  | D) | $26 |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
During periods of inflation, the inventory method that produces the greatest income tax benefits is which of the following? |
|  | A) | FIFO method |
|  | B) | LIFO method |
|  | C) | Average cost method |
|  | D) | Specific identification method |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Consider the following:
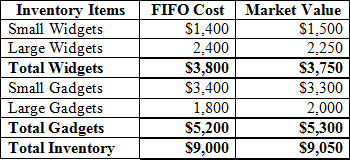 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q4.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (34.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q4.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (34.0K)</a>
Using the LCM rules on the basis of inventory category, the write-down of inventory would be |
|  | A) | $50 |
|  | B) | $250 |
|  | C) | $150 |
|  | D) | $200 |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Consider the following inventory activity:
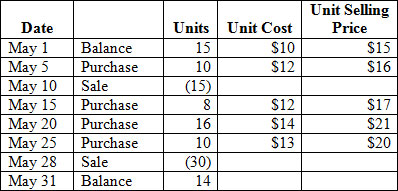 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (35.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (35.0K)</a>
The 14 units of ending inventory are identified with the purchase of May 20. Assume a periodic inventory system and use the specific identification method to calculate the value of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold. |
|  | A) | $290 and $430, respectively |
|  | B) | $190 and $530, respectively |
|  | C) | $196 and $524, respectively |
|  | D) | $196 and $474, respectively |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Consider the following inventory activity:
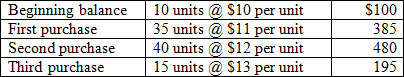 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (22.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (22.0K)</a>
If 83 units were sold, what is the value of the ending inventory under a periodic inventory system and a FIFO cost flow assumption? |
|  | A) | $219 |
|  | B) | $905 |
|  | C) | $177 |
|  | D) | $204 |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Consider the following inventory activity:
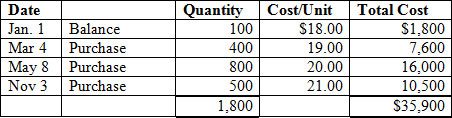 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (27.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (27.0K)</a>
Five hundred and eighty units are unsold. Using the LIFO cost flow assumption and a periodic inventory system, what is the cost assigned to the ending merchandise inventory? |
|  | A) | $10,800 |
|  | B) | $11,800 |
|  | C) | $11,970 |
|  | D) | $11,000 |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Consider the following
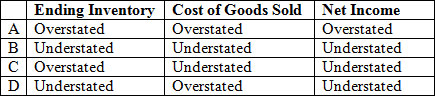 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q8.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/007802577x/1036574/CH08_Q8.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a>
Which condition is true with regard to errors in the ending inventory? |
|  | A) | Line A |
|  | B) | Line B |
|  | C) | Line C |
|  | D) | Line D |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Beginning inventory of $40,000 plus purchases of $30,000 equals which of the following? |
|  | A) | Cost of goods available for sale of $10,000 |
|  | B) | Cost of goods sold of $10,000 |
|  | C) | Net income of $70,000 |
|  | D) | Cost of goods available for sale of $70,000 |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Which one of the following is the formula for the inventory turnover rate? |
|  | A) | Net sales/Cost of goods sold |
|  | B) | Cost of goods sold/Average inventory |
|  | C) | Cost of goods sold/Ending Inventory |
|  | D) | Average inventory/Cost of goods sold |
|
|

