 |
| 1 |  | 
On January 1, 2016, Olympic Insurance Company granted 30,000 stock options to certain executives. The options are exercisable no sooner than December 31, 2018, and expire on January 1, 2019. Each option can be exercised to acquire one share of $1 par common stock for $12. An option-pricing model estimates the fair value of the options to be $5 on the date of grant. The market price of Olympic's stock was as follows: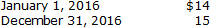 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q01.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
What amount should Olympic recognize as compensation expense for 2016? |
|  | A) | $10,000 |
|  | B) | $20,000 |
|  | C) | $30,000 |
|  | D) | $50,000 |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following statements is untrue regarding earnings per share? |
|  | A) | A company has a simple capital structure if it has no outstanding securities that could potentially dilute earnings per share. |
|  | B) | When shares are retired, they are time-weighted for the fraction of the period they were not outstanding, prior to being subtracted from the number of shares outstanding during the reporting period. |
|  | C) | Dividends paid on nonconvertible preferred stock outstanding should be subtracted from reported net income. |
|  | D) | Any new shares issued during the period in a stock dividend or stock split are time-weighted by the fraction of the period they were outstanding and then added to the number of shares outstanding for the period. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
At December 31, 2016 and 2017, Frist Company had outstanding 50 million common shares and 4 million shares of 10%, $10 par cumulative preferred stock. Net income for 2017 was $20 million. No dividends were declared in 2016 or 2017. EPS for 2017 was: |
|  | A) | $.32. |
|  | B) | $.37. |
|  | C) | $.40. |
|  | D) | $.48. |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
At December 31, 2016, the balance sheet of Goode Corporation included 80 million common shares. On October 1, 2017, Goode retired 4 million shares as part of a share repurchase program. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2017, was $400 million. Goode's 2017 EPS should be: |
|  | A) | $4.94. |
|  | B) | $5.00. |
|  | C) | $5.06. |
|  | D) | $5.26. |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
At December 31, 2016, the balance sheet of Darwin Corporation included 8 million common shares and 4 million nonconvertible preferred shares. On July 1, 2017, Darwin issued a 5 for 4 stock split on its common shares and paid $10 million cash dividends on the preferred stock. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2017, was $40 million. Darwin's 2017 EPS should be: |
|  | A) | $3.00. |
|  | B) | $4.00. |
|  | C) | $5.00. |
|  | D) | $5.55. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
When calculating basic earnings per share, net income is reduced by dividends on nonconvertible cumulative preferred stock: |
|  | A) | Whether declared or not. |
|  | B) | Only if declared. |
|  | C) | Whether dilutive or not. |
|  | D) | Under no circumstances. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
When calculating the weighted average number of shares outstanding, the number of shares are not time-weighted by the fraction of the reporting period they are (are not) outstanding for: |
|  | A) | Common shares retired. |
|  | B) | Common shares issued during the period as a stock dividend. |
|  | C) | Shares obtainable in executive stock options granted in mid-year. |
|  | D) | New common shares sold during the period. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
A business is deemed to have a complex capital structure when it has outstanding: |
|  | A) | Three types of securities or more besides common stock. |
|  | B) | Executive stock options. |
|  | C) | Bonds payable. |
|  | D) | Cumulative preferred stock. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
To incorporate the effect of outstanding stock options in the calculation of diluted EPS: |
|  | A) | Would be inappropriate because options are considered only when calculating basic EPS. |
|  | B) | We would never increase or decrease the numerator of the EPS fraction. |
|  | C) | We assume common shares are issued at the average market price and repurchased at the exercise price. |
|  | D) | We assume the options were exercised at mid-year. |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
When calculating diluted EPS, which of the following, if dilutive, would cause the weighted average number of shares to increase? <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (21.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | a |
|  | B) | b |
|  | C) | c |
|  | D) | d |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
When calculating earnings per share, the effect of after-tax interest expense paid on convertible bonds that are dilutive is to: |
|  | A) | Increase net income for diluted earnings per share and not for basic earnings per share. |
|  | B) | Decrease net income for basic earnings per share and not for diluted earnings per share. |
|  | C) | Increase net income for both basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share. |
|  | D) | Decrease net income for both basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Common stock options that are antidilutive generally affect the calculation of: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q12.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | a |
|  | B) | b |
|  | C) | c |
|  | D) | d |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Convertible bonds that are dilutive generally affect the calculation of: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q13.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q13.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (14.0K)</a>
|
|  | A) | a |
|  | B) | b |
|  | C) | c |
|  | D) | d |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Executive stock options are outstanding all year that permit executives to buy 12 million common shares at $50. The average market price of the common stock was $60. When calculating diluted earnings per share, the assumed exercise of these options will increase the weighted average number of shares outstanding by: |
|  | A) | zero shares. |
|  | B) | 2 million shares. |
|  | C) | 8 million shares. |
|  | D) | 10 million shares. |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Executive stock options are outstanding all year that permit executives to buy 12 million common shares at $60. The average market price of the common stock was $50. When calculating diluted earnings per share, the assumed exercise of these options will increase the weighted average number of shares outstanding by: |
|  | A) | zero shares. |
|  | B) | 2 million shares. |
|  | C) | 8 million shares. |
|  | D) | 10 million shares. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
Which of the following statements is true regarding diluted earnings per share? |
|  | A) | It is assumed that stock options are exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time the options are issued, if later) and the cash proceeds received are used to buy back (as treasury stock) as many of those shares as can be acquired at the closing market price for the period. |
|  | B) | To incorporate convertible bonds into the calculation, the denominator of the EPS fraction is decreased by the additional common shares assumed. |
|  | C) | To incorporate convertible securities into the calculation, the numerator is decreased by the interest (after-tax) that would have been avoided in the event of conversion. |
|  | D) | Contingently issuable shares are considered outstanding in the computation of diluted EPS when any conditions for issuance are currently being met. |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Which of the following is not disclosed regarding earnings per share? |
|  | A) | Basic EPS for income from continuing operations. |
|  | B) | Diluted EPS for net income. |
|  | C) | Cash paid per share. |
|  | D) | Reconciliation of the numerator and denominator used in the computations. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
White Company is a calendar-year firm with operations in several countries. At January 1, 2016, the company had issued 10,000 executive stock options permitting executives to buy 10,000 shares of stock for $25. The vesting schedule is 30% the first year, 30% the second year, and 40% the third year (graded-vesting). The fair value of the options is estimated as follows: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q18.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q18.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (29.0K)</a>
What is the compensation expense related to the options to be recorded in 2017? |
|  | A) | $4,500. |
|  | B) | $9,000. |
|  | C) | $9,500. |
|  | D) | $12,000. |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Blue Company is a calendar-year firm with operations in several countries. At January 1, 2016, the company had issued 40,000 executive stock options permitting executives to buy 40,000 shares of stock for $30. The vesting schedule is 20% the first year, 30% the second year, and 50% the third year (graded-vesting). The fair value of the options is estimated as follows: <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q19.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (27.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0078025834/1061248/Chapter19_q19.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (27.0K)</a>
Assuming Blue prepares its financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards, what is the compensation expense related to the options to be recorded in 2017? |
|  | A) | $48,000. |
|  | B) | $96,000. |
|  | C) | $128,000. |
|  | D) | $130,667. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Under IFRS, a deferred tax asset for stock options |
|  | A) | is created for the cumulative amount of the fair value of the options the company has recorded for compensation expense. |
|  | B) | is the portion of the options' intrinsic value earned to date times the tax rate. |
|  | C) | is the tax rate times the amount of compensation. |
|  | D) | isn't created if the award is "in the money;" that is, it has intrinsic value. |
|
|

