 |
| 1 |  | 
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
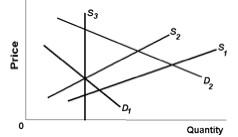 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. The total amount paid to a resource is economic rent if supply and demand are given by, respectively: |
|  | A) | S1 and D1 |
|  | B) | S2 and D1 |
|  | C) | S2 and D2 |
|  | D) | S3 and D1 |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. Assume supply and demand for land are initially given by S3 and D2, respectively. Which of the following would cause demand to shift to D1? |
|  | A) | A decrease in the interest rate |
|  | B) | An increase in the productivity of the land |
|  | C) | An increase in the demand for the goods and services produced on the land |
|  | D) | An increase in the tax rate on land |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Use the following data to answer the next question. Assume that the quantity of a certain type of farmland is 500,000 acres and the demand for this land is given by the table below.
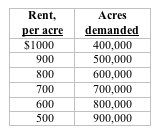 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384259/quiz27c_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (7.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. If the government imposed a $200 per acre tax on land, the equilibrium rent would be: |
|  | A) | $900 |
|  | B) | $800 |
|  | C) | $700 |
|  | D) | $600 |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
When there are alternative uses to land, economic rent is a cost, not a surplus. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Suppose there are news reports of an increase in consumer confidence and firms become optimistic about the future of the economy and expected returns on investments. Then: |
|  | A) | the demand for loanable funds will increase and the equilibrium interest rate will rise |
|  | B) | the demand for loanable funds will decrease and the equilibrium interest rate will fall |
|  | C) | the supply of loanable funds will increase and the equilibrium interest rate will fall |
|  | D) | the supply of loanable funds will decrease and the interest rate will rise |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
A firm is considering the purchase of a machine that will increase its productive capacity. The machine will cost $10,000 and has a useful life of one year. It will add $10,500 (in real terms) to its total revenue for the year, all funds received at the end of the year. The firm can borrow the money to purchase the machine at a nominal interest rate of 6%; the inflation rate is 3%. This investment: |
|  | A) | should be undertaken because the rate of return is 2 percentage points above the real interest rate |
|  | B) | should be undertaken because the rate of return is positive |
|  | C) | should not be undertaken because the rate of return is negative |
|  | D) | should not be undertaken because the rate of return is 1 percentage point below the nominal interest rate |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Suppose a firm has the option to purchase new equipment for $16,000 that can reduce its annual operating costs by $800. The firm should borrow funds for this investment if it can negotiate an annual nominal interest rate: |
|  | A) | less than 3% |
|  | B) | less than 5% |
|  | C) | less than 20% |
|  | D) | at least 10% |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
All else equal, the longer the maturity of a loan: |
|  | A) | the lower the risk |
|  | B) | lower the nominal cost of all the interest payments |
|  | C) | lower the interest rate it carries |
|  | D) | higher the interest rate it carries |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
A usury law will be ineffective if: |
|  | A) | the maximum interest rate is set below the equilibrium rate |
|  | B) | the real interest rate is negative |
|  | C) | the minimum interest rate is set below the equilibrium rate |
|  | D) | the maximum interest rate is set above the equilibrium rate |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Which of the following is an uninsurable risk an entrepreneur may have to bear? |
|  | A) | Loss of profit due to employee theft and shoplifting |
|  | B) | Loss of productive work time due to employee injury on the job |
|  | C) | Loss of profit due to higher state and local taxes |
|  | D) | Loss of a factory due to fire |
|
|

