 |
| 1 |  | 
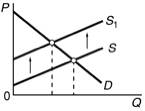
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz28b_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz28b_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram. Assume S is a market supply curve comprising all private costs of production and D is a demand curve representing all private benefits. Further assume that property rights are well defined. In which of the following circumstances is the appropriate government response most likely to be a tax that shifts the supply curve to S1? |
|  | A) | Production of this good generates a substantial external benefit and the number of affected parties is small |
|  | B) | Production of this good generates a substantial external benefit and the number of affected parties is large |
|  | C) | Production of this good generates a substantial external cost and the number of affected parties is small |
|  | D) | Production of this good generates a substantial external cost and the number of affected parties is large |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following best exemplifies the problem of moral hazard? |
|  | A) | Marsha purchases extra medical insurance because she has inherited a gene that increases the likelihood of ovarian cancer |
|  | B) | Bill talks too much on his cell phone while driving, knowing he's insured in the event of an accident |
|  | C) | Production of beer generates a negative externality |
|  | D) | Governments impose "sin taxes" on cigarettes and alcohol |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Amy, Ben, and Carol are the only three people in a community considering how big a fireworks show to put on for the 4th of July. Amy is willing to pay $3 for the tenth shell, Ben is willing to pay $2, and Carol is willing to pay $1. The tenth shell should be fired if the marginal cost of the shell is: |
|  | A) | less than $1 |
|  | B) | at least $2 |
|  | C) | at least $3 |
|  | D) | less than $6 |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Government has imposed a tax on the producers of good X and has subsidized the consumers of good Y. If these policies result in the production of the efficient amounts of both goods, it is likely the government is correcting for: |
|  | A) | external costs in producing X and external benefits in consuming Y |
|  | B) | external benefits in producing X and external costs in consuming Y |
|  | C) | external benefits in producing X and consuming Y |
|  | D) | external costs in producing X and consuming Y |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
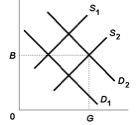
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz28b_5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz28b_5.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Suppose private marginal cost is given by S1 and private benefits are given by D1. Under what circumstances is output G the economically efficient output in this market? |
|  | A) | There are external costs to both production and consumption of this good |
|  | B) | There are external benefits to both production and consumption of this good |
|  | C) | There are external benefits to production of this good and external costs to its consumption |
|  | D) | There are external costs to production of this good and external benefits to its consumption |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
At the optimal quantity of a public good: |
|  | A) | the marginal benefit to each consumer equals the marginal cost of provision |
|  | B) | the sum of the marginal benefits to each consumer equals the marginal cost of provision |
|  | C) | the marginal benefit to each consumer equals the sum of the marginal costs of provision |
|  | D) | the sum of the marginal benefits to each consumer equals the sum of the marginal costs of provision |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Government intervention is required to correct market failures created by negative externalities. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
A premium television service transmits its signal via a stationary satellite; the scrambled signal is available to anyone with a satellite dish and descrambler who also pays a monthly service fee. This service is: |
|  | A) | both rival and excludable |
|  | B) | neither rival nor excludable |
|  | C) | rival but nonexcludable |
|  | D) | nonrival but excludable |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Provisions of the Clean Air Act of 1990 that required 30 to 60 percent reduction of tailpipe emissions in cars were an example of: |
|  | A) | market policies to correct for an external benefit |
|  | B) | direct controls to correct for an external cost |
|  | C) | an application of the Coase Theorem |
|  | D) | direct controls to correct for moral hazard |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Which of the following would be an example of an attempt to reduce the adverse selection problem? |
|  | A) | An employer requires all employees to participate in its company-subsidized health insurance plan |
|  | B) | The government subsidizes the use of recycled inputs |
|  | C) | The government imposes a tax on tailpipe emissions for automobiles |
|  | D) | An employer monitors her workers to ensure they are not shirking |
|
|

