 |
| 1 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table showing the market shares of 6 firms in four hypothetical industries, labeled W through Z. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them.
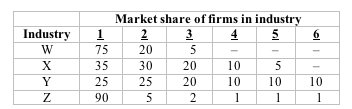 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz30c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz30c_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. A merger between firm 1 in industry W and firm 2 in industry Y would be a(n): |
|  | A) | vertical merger |
|  | B) | horizontal merger |
|  | C) | illegal merger |
|  | D) | conglomerate merger |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table showing the market shares of 6 firms in four hypothetical industries, labeled W through Z. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them.
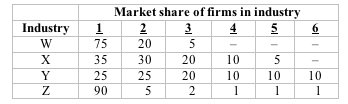 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz30c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz30c_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. As measured by the Herfindahl index, industry concentration is greatest in industry: |
|  | A) | W |
|  | B) | X |
|  | C) | Y |
|  | D) | Z |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following allows injured parties to collect triple damages from illegal monopolies? |
|  | A) | Celler-Kefauver Act |
|  | B) | Sherman Act |
|  | C) | Wheeler-Lea Act |
|  | D) | Clayton Act |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Jones is a director of ABC Company and sits on the board of its competitor, the XYZ Company, effectively reducing competition in the industry. This activity was outlawed by the: |
|  | A) | Sherman Act |
|  | B) | Federal Trade Commission Act |
|  | C) | Clayton Act |
|  | D) | Wagner Act |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
A merger between Coca Cola and Pepsico would be an example of a: |
|  | A) | vertical merger |
|  | B) | horizontal merger |
|  | C) | conglomerate merger |
|  | D) | structural merger |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The market shares of the only firms in a particular industry are 40%, 40%, and 30%. The Herfindahl index for this industry is: |
|  | A) | 33.3 |
|  | B) | 100 |
|  | C) | 1000 |
|  | D) | 4100 |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Industries characterized as natural monopolies operate most efficiently with a single seller, yet a single seller is likely to engage in monopolistic practices. Government oversight in this situation is known as: |
|  | A) | social regulation |
|  | B) | bipartisan regulation |
|  | C) | industrial regulation |
|  | D) | legal cartel theory |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Studies of the U.S. deregulation of the airline, trucking, and rail freight industries have revealed that: |
|  | A) | prices have dropped by one third to one half, adjusted for inflation |
|  | B) | industry output has decreased, adjusted for population growth |
|  | C) | these industries have "remonopolized" as firms have either merged or gone out of business |
|  | D) | deregulation ultimately harms consumers |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Among other things, social regulation addresses: |
|  | A) | pricing decisions by natural monopolies |
|  | B) | mergers that lead to industry concentration |
|  | C) | price discrimination |
|  | D) | product design |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
The initial court ruling in the Microsoft case, overturned on appeal, called for breaking the firm into two competing companies. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|

