 |
| 1 |  | 
Studies indicate that nondiscriminatory factors such as differences in education or occupation account for about: |
|  | A) | one fourth of earnings differences between men and women |
|  | B) | one tenth of earnings differences between African Americans and whites |
|  | C) | three fourths of earnings differences between African Americans and Hispanics |
|  | D) | half of earnings differences between men and women and whites and African Americans |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Which of the following workers is more likely to be a member of a union? |
|  | A) | Barry, an African American police officer |
|  | B) | Trina, a white office worker |
|  | C) | Zito, a Hispanic shop manager |
|  | D) | Emily, a white sales clerk in a dress shop |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
State laws which prohibit union and agency shop clauses in union contracts: |
|  | A) | were made illegal under the National Labor Relations Act |
|  | B) | do not apply to transportation and construction |
|  | C) | are known as "right-to-work" laws |
|  | D) | are found only in a few Northeastern states |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Which of the following is an example of "featherbedding?" |
|  | A) | The musicians' union bargains for an agency shop clause |
|  | B) | The carpenters' union refuses to allow members of the plumbers' union to perform simple carpentry |
|  | C) | Management locks out its union members during a wage dispute |
|  | D) | A newspaper is required to retain a union typesetter even though its typesetting is computerized |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Immigration of low-wage workers in response to wage differentials: |
|  | A) | reduces total income in both the origin and destination countries |
|  | B) | increases total income in both the origin and destination countries |
|  | C) | raises total income in the origin country while reducing it in the destination country, leaving overall income lower |
|  | D) | reduces total income in the origin country while raising it in the destination country, resulting in higher overall income |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
By removing barriers blocking some workers from higher-productivity jobs, eliminating economic discrimination would: |
|  | A) | move the economy to a point inside its production possibilities curve |
|  | B) | increase the economy's total output |
|  | C) | move the economy from one point on the production possibilities curve to a different point on the curve |
|  | D) | redistribute total output, but have no effect on its size |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Use the following diagram to answer the next question:
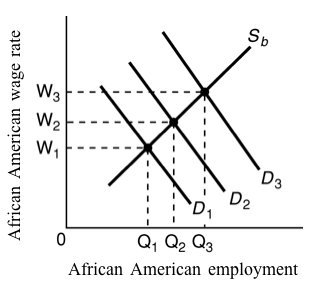 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz34a_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384260/quiz34a_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (17.0K)</a>
Refer to the diagram: Suppose demand is initially given by D2. Which of the following would shift demand to D3? |
|  | A) | A decrease in the productivity of African American workers |
|  | B) | A reduction in white employers' discrimination coefficients |
|  | C) | An increase in white employers' discrimination coefficients |
|  | D) | A reduction in employment discrimination coupled with an increase in statistical discrimination |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Assume that (1) the labor force is comprised of equal numbers of men and women workers; (2) the economy has 3 occupations, X, Y, and Z, each having identical demand curves for labor; (3) men and women workers are homogeneous with respect to their labor-market capabilities; (4) women are discriminated against by being excluded from occupations X and Y and are confined to Z; and (5) aside from discrimination, the economy is competitive. Under these circumstances: |
|  | A) | X, Y, and Z will all employ the same number of workers |
|  | B) | the value of total output will be less than if women were allowed to enter occupations X and Y |
|  | C) | elimination of discrimination will increase both men's and women's wages |
|  | D) | X, Y, and Z will pay the same wage |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
In the U.S., the unionization rate is highest in: |
|  | A) | mining |
|  | B) | manufacturing |
|  | C) | services |
|  | D) | government |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Mary and Arthur were both recently hired by the same employer to perform the same work; Mary was offered and accepted a wage 10% lower than Arthur. This is an example of: |
|  | A) | employment discrimination |
|  | B) | statistical discrimination |
|  | C) | wage discrimination |
|  | D) | human capital discrimination |
|
|

