 |
| 1 |  | 
The utility of a particular good: |
|  | A) | is the same for everyone, even if its usefulness differs from person to person |
|  | B) | measures the products usefulness |
|  | C) | increases at a constant rate |
|  | D) | increases at a decreasing rate |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility) that a consumer would get from successive quantities of products J and K.
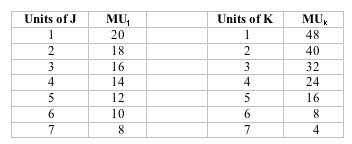 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. If this consumer has an income of $26 and the prices of J and K are $2 and $4 respectively, the consumer will maximize her utility by purchasing: |
|  | A) | 7 units of J and 3 units of K |
|  | B) | 5 units of J and 4 units of K |
|  | C) | 3 units of J and 5 units of K |
|  | D) | 1 units of J and 6 units of K |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table which shows Ann's total utility derived from drinking soft drinks.
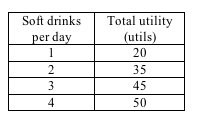 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. Ann's marginal utility of the third soft drink per day is: |
|  | A) | 45 utils |
|  | B) | 5 utils |
|  | C) | 100 utils |
|  | D) | 10 utils |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Jim enjoys both peanut butter sandwiches and bologna sandwiches in his lunch. A drop in the price of peanut butter increases the marginal utility per dollar of peanut butter and causes Jim to buy less bologna to restore maximum utility. This best illustrates the: |
|  | A) | law of diminishing marginal utility |
|  | B) | income effect |
|  | C) | substitution effect |
|  | D) | law of increasing total utility |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
If one sums the marginal utilities of each unit consumed, one obtains: |
|  | A) | the demand curve |
|  | B) | maximum marginal utility |
|  | C) | total income |
|  | D) | total utility |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The high marginal utility of water explains the diamond-water paradox. |
|  | A) | True |
|  | B) | False |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following table which shows a consumer's total utility for products A, B, C, and D.
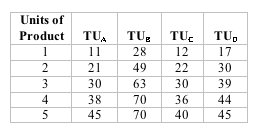 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/1113273090/384258/quiz19a_7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (9.0K)</a>
Refer to the table. Marginal utility declines most rapidly for product: |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | B |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Suppose the prices of products X and Y are $5 and $10, respectively. For a specific consumer who is currently exhausting her total income, the total utility from X is 100, while the total utility from Y is 200. The marginal utility of X and Y are both equal to 8. From this information, we can conclude: |
|  | A) | she is maximizing total utility |
|  | B) | she should purchase relatively more X |
|  | C) | she should purchase relatively more Y |
|  | D) | nothing about whether she is maximizing total utility |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Suppose the price of X is $4 and the price of Y is $2. In order to maximize total utility, a consumer should allocate purchases such that: |
|  | A) | the marginal utility of each good is the same |
|  | B) | the marginal utility of X is half that of Y |
|  | C) | the marginal utility of X is twice that of Y |
|  | D) | the total utility of X is half that of Y |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Suppose that Karen used to buy one latte every weekday, but she has cut back her purchases to just one per week. Her decision is best explained by: |
|  | A) | the income effect only |
|  | B) | the substitution effect only |
|  | C) | complementary effect only |
|  | D) | both income and substitution effects |
|
|

