The Nuclear Reactions Test consists of 20 questions. Correct answers will be provided after your answers have been submitted. If they are available, possible solutions can be accessed by clicking an additional link at the bottom of the answer, which will open a problem solution screen. If you bring up such a solution screen be sure to close it by clicking the button in the upper left corner or upper right corner.
 |
1 |  | 
Which of the following would be attracted toward a positively charged sheet of metal? |
|  | A) | alpha particle |
|  | B) | beta particle |
|  | C) | gamma ray |
|  | D) | none of the above |
 |
 |
2 |  | 
Which of the following would be attracted toward a negatively charged sheet of metal? |
|  | A) | alpha particle |
|  | B) | beta particle |
|  | C) | gamma ray |
|  | D) | none of the above |
 |
 |
3 |  | 
The rate of radioactive decay is increased by |
|  | A) | increased heat. |
|  | B) | increased pressure. |
|  | C) | the use of a nuclear catalyst. |
|  | D) | none of the above. |
 |
 |
4 |  | 
The emission of a beta particle from a nucleus results in |
|  | A) | a decrease in the atomic number. |
|  | B) | an increase in the atomic number. |
|  | C) | no change in the atomic number. |
|  | D) | none of the above. |
 |
 |
5 |  | 
The emission of a gamma ray from a nucleus results in |
|  | A) | a decrease in the atomic number. |
|  | B) | an increase in the atomic number. |
|  | C) | no change in the atomic number. |
|  | D) | none of the above. |
 |
 |
6 |  | 
After emission and moving 2 to 12 cm through the air an alpha particle most likely becomes |
|  | A) | an ordinary helium atom. |
|  | B) | an electron. |
|  | C) | increased energy in the impacted material. |
|  | D) | none of the above |
 |
 |
7 |  | 
An element in a radioactive decay series will continue to disintegrate into various radioactive elements until it becomes a stable isotope of |
|  | A) | uranium. |
|  | B) | lead. |
|  | C) | bismuth. |
|  | D) | lawrencium. |
 |
 |
8 |  | 
The decay rate for a given number of nuclei of each radioactive isotope is observed to be |
|  | A) | an identifying characteristic of that isotope. |
|  | B) | specific for each radioactive element. |
|  | C) | dependent on external conditions of temperature, pressure, and chemical state. |
|  | D) | totally random and not dependent on any external condition. |
 |
 |
9 |  | 
The mass of a given nucleus is always __ ? __ the sum of the masses of the individual particles of which it is made. |
|  | A) | less than |
|  | B) | more than |
|  | C) | the same as |
|  | D) | sometimes less, sometimes more, but never the same as |
 |
 |
10 |  | 
When applied to E = mc2 the mass defect of a given nucleus is found to be the |
|  | A) | energy released when the nucleus formed. |
|  | B) | energy required to break the nucleus into individual particles. |
|  | C) | same as the binding energy. |
|  | D) | any of the above. |
 |
 |
11 |  | 
The nucleus of the greatest stability is found in the isotope of the element |
|  | A) | aluminum. |
|  | B) | iron. |
|  | C) | hydrogen. |
|  | D) | lead. |
 |
 |
12 |  | 
Radiation can be a hazard to living organisms because it |
|  | A) | produces ionization along its path of travel. |
|  | B) | disrupts chemical bonds. |
|  | C) | generates free polyatomic ions. |
|  | D) | all of the above. |
 |
 |
13 |  | 
In general, the public receives how much radiation exposure each year? |
|  | A) | none |
|  | B) | more than 500 millirem. |
|  | C) | between 100 and 500 millirem. |
|  | D) | about 130 rem. |
 |
 |
14 |  | 
A Geiger counter is able to provide an indirect measure of radioactivity because radiation has a property of |
|  | A) | ionization. |
|  | B) | making matter glow in the dark. |
|  | C) | fogging photographic film. |
|  | D) | attracting electrons. |
 |
 |
15 |  | 
The use of which unit would indicate radioactivity is being measured at its source? |
|  | A) | rad |
|  | B) | rem |
|  | C) | curie |
|  | D) | roentgen |
 |
 |
16 |  | 
One of the first observable effects of over exposure to very low level radioactivity is |
|  | A) | loss of hair. |
|  | B) | changes in the blood count. |
|  | C) | glowing in the dark. |
|  | D) | leukemia. |
 |
 |
17 |  | 
The U-238 isotope is most likely to emit |
|  | A) | an alpha particle. |
|  | B) | a beta particle. |
|  | C) | a gamma ray. |
|  | D) | It is not possible to predict. |
 |
 |
18 |  | 
This type of radiation is released when Rn-224 decays to Po-220: |
|  | A) | alpha. |
|  | B) | beta. |
|  | C) | gamma. |
|  | D) | all of these. |
 |
 |
19 |  | 
Which of the following correctly balances the following nuclear fission reaction?
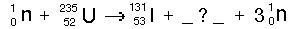 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_question19.jpg','popWin', 'width=350,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_question19.jpg','popWin', 'width=350,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 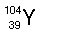 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=107,height=106,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=107,height=106,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 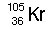 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 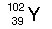 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 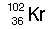 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_4.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu19_4.jpg','popWin', 'width=102,height=99,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
 |
 |
20 |  | 
Which of the following correctly balances this decay reaction?
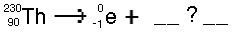 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_question20.jpg','popWin', 'width=291,height=102,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_question20.jpg','popWin', 'width=291,height=102,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 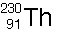 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_1.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | B) | 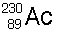 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_2.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | C) | 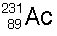 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_3.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
|  | D) | 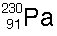 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_4.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072509783/121105/chap13_qu20_4.jpg','popWin', 'width=99,height=101,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> |
 |

