| Chapter 22. Perfect Competition# 1: Calculating Total Profit Using a Graph
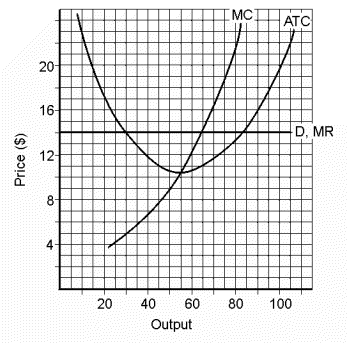
We're going to use data from Figure 22.1 to calculate the total profit of this perfect competitor. We'll be using this formula: Total Profit = Output (Price - ATC). Please look at the graph and write down the output, price, and ATC.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30186/image12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (19.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30186/image12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (19.0K)</a>
Figure 22.1
The output is 65 (where MC and MR intersect). At that output ATC = $11. And price, which is read from the demand curve, D, is $14. Now plug the numbers into the formula and solve for total profit.
Solution:| Total Profit | = | Output (Price - ATC) | | = | 65 ($14 - $11) | | = | 65 ($3) | | = | $195 |
#2: Calculating Total Loss Using a Graph
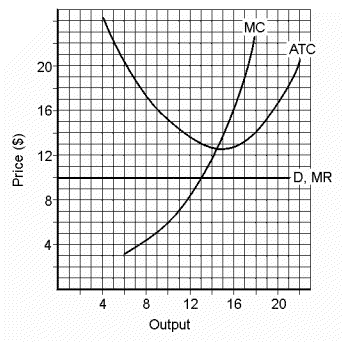
Use the data in Figure 22.2 to find this firm's total loss (i.e., negative total profit).
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30186/image13.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072237409/30186/image13.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (20.0K)</a>
Figure 22.2 | Total Profit | = | Output (Price - ATC) | | = | 13 ($10 - $13) | | = | 13 (-$3) | | = | -$39 |
|



 2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2002 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
