- The Function and Primary Purpose of Financial Accounting
Concept Check
The primary focus of financial accounting is on the financial information provided by _____________________ companies to their present and potential _____________ and ________________. Concept Check
The primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through _________________________ and related _____________________. - The Economic Environment and Financial Reporting
- The capital markets provide a mechanism to help our economy allocate resources efficiently.
- Corporations, the dominant form of business organization in the United States, acquire capital from investors in exchange for ownership interest and by borrowing from creditors.
- The investment-credit decision- A cash flow perspective
- A company will be able to provide a return to investors and creditors only if it can generate cash receipts from selling a product or service that exceed the cash disbursements necessary to provide that product or service.
- The objective of financial accounting is to provide information to investors and creditors to help them predict future cash flows.
Concept Check
The _____________________ and ____________________ or ___________ of that return are key variables in the investment decision. Concept Check
Information should help investors and creditors evaluate the __________, __________, and ______________ of the enterprise's future cash receipts and disbursements. - Cash versus accrual accounting
- Over short periods of time, operating cash flow may not be an accurate predictor of future operating cash flows.
- The accrual accounting model provides a measure of periodic performance called net income.
- Net income is considered a better indicator of future operating cash flows than is current net operating cash flows.
 Illustration (34.0K) Illustration (34.0K)
- The Development of Financial Accounting and Reporting Standards
- Purpose of the Conceptual Framework
- The conceptual framework does not prescribe GAAP.
- It provides an underlying foundation for accounting standards.
- The framework consists of financial reporting objectives, qualitative characteristics of information, financial statement elements, recognition and measurement concepts, and constraints.
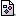 Here is an overview. (189.0K) Here is an overview. (189.0K)
- Objectives of Financial Reporting
- To provide information that is useful to present and potential investors and creditors.
- Information is useful to investors and creditors if it helps them assess the amounts, timing, and uncertainty of prospective cash flows.
- Useful cash flow information includes information about economic resources, the claims to those resources, and the effects of transactions, events, and circumstances that cause changes in resources and claims.
- Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information.
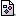 Here is an overview. (229.0K) Here is an overview. (229.0K)- Overriding objective is decision usefulness.
- Primary qualities of useful information are relevance and reliability.
- Components of relevance are:
- Predictive value
- Feedback value
- Timeliness
- Components of reliability are:
- Verifiability
- Neutrality
- Representational faithfulness
- Secondary qualities are comparability and consistency.
- Constraints are cost effectiveness and materiality.
- Elements of Financial Statements.
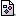 Here is a description of each of the elements. (275.0K) Here is a description of each of the elements. (275.0K)- Balance sheet elements:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Investments by owners
- Distributions to owners
- Income statement elements:
- Revenues
- Gains
- Expenses
- Losses
- Comprehensive income
- Recognition and Measurement Concepts.
 Here is an overview. (60.0K) Here is an overview. (60.0K)- Recognition- an item should be recognized in the basic financial statements when it meets certain criteria.
- Measurement
- The monetary unit used in financial statements is nominal units of money without any adjustment for changes in purchasing power.
- Different attributes are used to measure different financial statement elements.
- There are important assumptions that underlie fundamental principles.
- Economic entity assumption
- Going concern assumption
- Periodicity assumption
- Monetary unit assumption
- There are four broad accounting principles that guide accounting practice.
- Historical cost principle
 Realization Principle (37.0K) Realization Principle (37.0K)- Matching principle 34. This Real-World, Real-Time Electronic Case addresses the matching principle as it relates to the treatment of promotional expenditures made by American Online.
- Full-disclosure principle
- Ethics in Accounting
- Ethics deal with the ability to distinguish right from wrong.
- Many professions have articulated ethical standards in a code of ethics.
- There are a number of
 steps (52.0K) that provide a framework for analyzing ethical issues. steps (52.0K) that provide a framework for analyzing ethical issues.
This is a test òArte y cultura
Literatura, Teatro, Museos
Ciencia y tecnología
Animales, Informática, Ingeniería
Ciencias sociales
Economía, Psicología
Deportes y ocio
Fútbol, Deportes, Turismo
Economía y negocios
B2B, Empleo, Finanzas
Educación y formación
Primarias, Universidades
Espectáculos y diversión
Cine, Actores, Música, ChÈvere Internet y computadoras
Red mundial, Aplicaciones, Revistas
Materiales de consulta
Bibliotecas, Diccionarios
Medios de comunicación
Temas de Actualidad, PeriÛdicos, TV
Política y gobierno
Países, Derecho, Embajadas
Salud
Medicina, Enfermedades
Sociedad
Gastronomía, Culturas, Religión
Zonas geográficas
PaÌses, Regiones |




 2001 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2001 McGraw-Hill Higher Education