(See related pages)
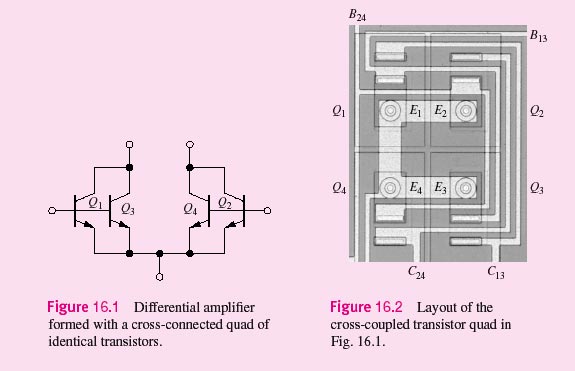
In Chapter 16, we explore several extremely clever and exciting circuits designed by two of the legends of integrated circuit design, Robert Widlar and Barrie Gilbert. Widlar developed the LM101 operational amplifier and many of the circuits that led to the design of the classic μA741 op amp. Widlar was also responsible for the bandgap reference. Gilbert invented a four-quadrant analog multiplier circuit referred to today as the Gilbert multiplier. The A741 circuit techniques spawned a broad range of follow-on designs that are still in use today. The bandgap reference forms the heart of most precision voltage references and voltage regulator circuits, and is also used as a temperature sensor in digital thermometry. Circuits related to the analog multiplier are used in RF mixers (the Gilbert mixer) and phase detectors in phase-locked loops. Integrated circuit (IC) technology allows the realization of large numbers of virtually identical transistors. Although the absolute parameter tolerances of these devices are relatively poor, device characteristics can be matched to within 1 percent or better. The ability to build devices with nearly identical characteristics has led to the development of special circuit techniques that take advantage of the tight matching of the device characteristics. Figures 16.1 and 16.2 show an example of the use of four matched transistors to improve the performance of the differential amplifier that we studied in the last chapter. The four devices are cross-connected to further improve the overall parameter matching and temperature tracking of the circuit.
Chapter 16 begins by exploring the use of matched transistors in the design of current sources, called current mirrors, in both MOS and bipolar technology. The cascode and Wilson current sources are subsequently added to our repertoire of high-output-resistance current source circuits. Circuit techniques that can be used to achieve power supply independent biasing are also introduced. We will also study the bandgap reference circuit which uses the well defined behavior of the pn junction to produce a precise output voltage that is highly independent of power supply voltage and temperature. The bandgap circuit is widely used in voltage references and voltage regulators. The current mirror is often used to bias analog circuits and to replace load resistors in differential and operational amplifiers. This active-load circuit can substantially enhance the voltage gain capability of many amplifiers, and a number of MOS and bipolar circuit examples are presented. The chapter then discusses circuit techniques used in IC operational amplifiers, including the classic 741 amplifier. This design provides a robust, high-performance, generalpurpose operational amplifier with breakdown-voltage protection of the input stage and shortcircuit protection of the output stage. The final section looks at the precision four-quadrant analog multiplier design of Gilbert. |