 |
| 1 |  | 
Which one of the following would not be a nutrient? |
|  | A) | cholesterol |
|  | B) | water |
|  | C) | cellulose |
|  | D) | starch |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Most vitamins, minerals, and water all have this in common: |
|  | A) | They provide energy. |
|  | B) | They cannot be manufactured by the body. |
|  | C) | They are all building blocks of complex molecules used by cells. |
|  | D) | They all contain the element carbon. |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
When the body metabolizes nutrients for energy, fats yield about _______ times the energy as carbohydrates or proteins. |
|  | A) | 1/2 |
|  | B) | 2 |
|  | C) | 4 |
|  | D) | 6 |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A calorie is the amount of energy necessary to raise the temperature of one gram of _________ one degree __________. |
|  | A) | water, Fahrenheit |
|  | B) | oil, Fahrenheit |
|  | C) | oil, Centigrade |
|  | D) | water, Centigrade |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
One piece of apple pie would yield about |
|  | A) | 34.5 Cal. |
|  | B) | 345 cal. |
|  | C) | 3450 kcal. |
|  | D) | 345,000 cal. |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The disaccharide that most people think of as table sugar is |
|  | A) | sucrose. |
|  | B) | lactose. |
|  | C) | maltose. |
|  | D) | fructose. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
When lactose is digested, it yields two monosaccharides called |
|  | A) | glucose and glucose. |
|  | B) | maltose and glucose. |
|  | C) | glucose and fructose. |
|  | D) | glucose and galactose. |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
The complex carbohydrate (polysaccharide) that is digested to the monosaccharide, glucose, and is found in vegetables, fruits, and grains and is called |
|  | A) | maltose. |
|  | B) | starch. |
|  | C) | glycogen. |
|  | D) | cellulose. |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
If excess glucose is present in the body, the glucose first will be stored as __________ in muscle and the liver. |
|  | A) | starch |
|  | B) | glycogen |
|  | C) | cellulose |
|  | D) | fat |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Triglycerides that contain one or more double covalent bonds between carbon atoms of their fatty acids are called |
|  | A) | saturated fats. |
|  | B) | cholesterol. |
|  | C) | phospholipids. |
|  | D) | unsaturated fats. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Bubbling hydrogen gas through polyunsaturated vegetable oil will cause the oil to become more |
|  | A) | unsaturated and more liquid. |
|  | B) | unsaturated and more solid. |
|  | C) | saturated and more liquid. |
|  | D) | saturated and more solid. |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
The lipid that is a component of the plasma membrane and can be used to form bile salts and steroid hormones is |
|  | A) | a saturated fat. |
|  | B) | an unsaturated fat. |
|  | C) | cholesterol. |
|  | D) | a phospholipid. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
The American Heart Association recommends that saturated fats should contribute no more than 10% of total fat intake. Excess fats, especially cholesterol and saturated fat, can increase the risk of |
|  | A) | hepatitis and cardiovascular disease. |
|  | B) | cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. |
|  | C) | Type I Diabetes and colon cancer. |
|  | D) | cardiovascular disease and lung cancer |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
The proteins in the body are composed of _________ amino acids; _________ of these amino acids are termed essential amino acids. |
|  | A) | 20; 9 |
|  | B) | 20; 11 |
|  | C) | 40; 20 |
|  | D) | 40; 9 |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
A toxic waste product of protein metabolism that must be excreted from the body is |
|  | A) | ammonia. |
|  | B) | carbon dioxide. |
|  | C) | urea. |
|  | D) | uric acid. |
|
|
 |
| 16 |  | 
The daily-recommended consumption amount of protein for a healthy adult is about _____% of total kilocalorie intake per day. |
|  | A) | 1 |
|  | B) | 10 |
|  | C) | 30 |
|  | D) | 60 |
|
|
 |
| 17 |  | 
Organic molecules found in minute quantities in food but that are essential to normal metabolism are called |
|  | A) | coenzymes. |
|  | B) | provitamins. |
|  | C) | nonessential vitamins. |
|  | D) | vitamins. |
|
|
 |
| 18 |  | 
Which one of the following vitamin remains in the body for only a short time before being excreted? |
|  | A) | A |
|  | B) | K |
|  | C) | C |
|  | D) | D |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
One of the reported benefits of taking Vitamin C and Vitamin E is that they |
|  | A) | increase the formation of collagen. |
|  | B) | promote the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the small intestine. |
|  | C) | are necessary for rhodopsin synthesis in the retina. |
|  | D) | block the effect of free radicals. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
Inorganic nutrients that are necessary for normal metabolism are called |
|  | A) | minerals. |
|  | B) | vitamins. |
|  | C) | lecithin. |
|  | D) | eicosanoids. |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
The energy-requiring process by which small molecules are joined to form larger molecules is specifically called |
|  | A) | metabolism. |
|  | B) | anabolism. |
|  | C) | catabolism. |
|  | D) | enzymatic reactions. |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
The energy currency of the cell is |
|  | A) | starch. |
|  | B) | glycogen. |
|  | C) | glucose. |
|  | D) | ATP. |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
When a molecule loses an electron, that molecule is said to be ___________ and often a(n) _____________ ion is lost along with the electron. |
|  | A) | reduced; hydrogen |
|  | B) | reduced; sodium |
|  | C) | oxidized; sodium |
|  | D) | oxidized; hydrogen |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
Which of the following terms is the total of all the breakdown processes in the body? |
|  | A) | metabolism |
|  | B) | anabolism |
|  | C) | catabolism |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
When a hydrogen ion and an associated electron are lost from a nutrient molecule, which of the following happens? |
|  | A) | The molecule gains energy. |
|  | B) | The molecule loses energy. |
|  | C) | The molecule becomes oxidized. |
|  | D) | Both B and C. |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
Consider the figure. How many ATP's are generated from glucose in the absence of oxygen?
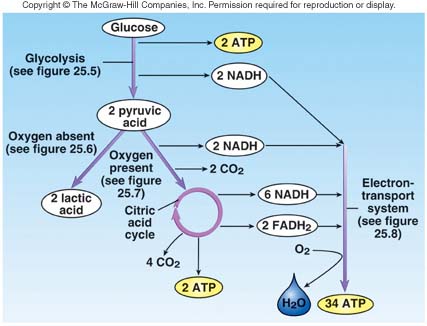 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 2 |
|  | B) | 4 |
|  | C) | 34 |
|  | D) | 38 |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
Using the figure, skeletal muscle and brain cells using aerobic respiration produce ____________ molecules of NADH which generates __________ molecules of ATP total.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 2; 4 |
|  | B) | 10; 28 |
|  | C) | 10; 30 |
|  | D) | 10; 36 |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
Refer to the figure below. In aerobic respiration, each glucose molecule forms _______ molecules of FADH2 that yields _______ molecules of ATP.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234439/mc_ch25_fig10.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (43.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | 2; 6 |
|  | B) | 10; 28 |
|  | C) | 10; 30 |
|  | D) | 2; 4 |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
In anaerobic respiration, lactic acid is released into the blood from skeletal muscle. When oxygen is available, most of the lactic acid is converted back to pyruvic acid and glucose in the |
|  | A) | liver. |
|  | B) | skeletal muscle. |
|  | C) | heart. |
|  | D) | lung. |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
In the human skeletal muscle and brain cells, the energy yield per molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration is ________ times higher than the energy yield in anaerobic respiration. |
|  | A) | 2 |
|  | B) | 16 |
|  | C) | 18 |
|  | D) | 19 |
|
|
 |
| 31 |  | 
In the liver, kidney, and heart cells, the total number of ATP molecules generated per glucose in aerobic respiration is |
|  | A) | 2 |
|  | B) | 30 |
|  | C) | 36 |
|  | D) | 38 |
|
|
 |
| 32 |  | 
The role of oxygen in aerobic respiration is to |
|  | A) | form water that is the medium of all chemical reactions. |
|  | B) | combine with free electrons and hydrogen ions from the electron transport system. |
|  | C) | provide transport of electrons from the cystol across the inner membrane of mitochondria. |
|  | D) | combine with carbon to form carbon dioxide. |
|
|
 |
| 33 |  | 
In the electron transport chain, the hydrogen ions enter the inner compartment of mitochondria through special channels formed by |
|  | A) | ATP synthase. |
|  | B) | coenzyme A. |
|  | C) | acetyl CoA. |
|  | D) | oxygen. |
|
|
 |
| 34 |  | 
Which of the following is true concerning glycolysis? |
|  | A) | It is an aerobic process. |
|  | B) | A net of 2 molecules of ATP are produced. |
|  | C) | A total of 38 ATP are produced. |
|  | D) | 4 NADH are produced. |
|
|
 |
| 35 |  | 
Which of the following processes converts lactic acid to glucose? |
|  | A) | citric acid cycle |
|  | B) | Krebs cycle |
|  | C) | Cori cycle |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 36 |  | 
Which of the following series of reactions prevents the heat given off during the citric acid cycle from burning up body cells? |
|  | A) | glycolysis |
|  | B) | Krebs cycle |
|  | C) | electron transport chain. |
|  | D) | phosphorylation |
|
|
 |
| 37 |  | 
In beta oxidation, free fatty acids are converted to |
|  | A) | glycerol. |
|  | B) | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. |
|  | C) | pyruvic acid. |
|  | D) | acetyl-CoA. |
|
|
 |
| 38 |  | 
In the liver, when large amounts of acetyl-CoA are produced, some of the acetyl-CoA is used to form |
|  | A) | pyruvic acid. |
|  | B) | citric acid. |
|  | C) | ketone bodies. |
|  | D) | lactic acid. |
|
|
 |
| 39 |  | 
In transamination, an amine group is transferred to ____________ to form a nonessential amino acid. |
|  | A) | keto acid |
|  | B) | ketone body |
|  | C) | acetyl-CoA |
|  | D) | carbon dioxide |
|
|
 |
| 40 |  | 
In oxidative deamination, an amine group is removed from an amino acid (usually glutamic acid) leaving ammonia and a keto acid. In this process ____________ is formed, which can enter the electron transport chain. |
|  | A) | NADH |
|  | B) | NAD+ |
|  | C) | FAD |
|  | D) | FADH2 |
|
|
 |
| 41 |  | 
Amino acids can be used for energy by converting them into various intermediate molecules of carbohydrate metabolism. Which intermediate molecule cannot be directly formed from an amino acid? |
|  | A) | pyruvic acid |
|  | B) | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate |
|  | C) | oxaloacetic acid |
|  | D) | acetyl-CoA |
|
|
 |
| 42 |  | 
People on strict diets or that have Type I Diabetes may check their urine periodically for ketones. Excessive production of ketones in the urine may indicate excessive |
|  | A) | carbohydrate metabolism. |
|  | B) | protein metabolism. |
|  | C) | lipid metabolism. |
|  | D) | lactic acid production. |
|
|
 |
| 43 |  | 
Which of the following processes is involved in using proteins as a source of energy? |
|  | A) | glycolysis |
|  | B) | ketogenesis |
|  | C) | beta oxidation |
|  | D) | oxidative deamination |
|
|
 |
| 44 |  | 
Which of the following substances are NOT stored in the body? |
|  | A) | amino acids |
|  | B) | glycogen |
|  | C) | triglycerides |
|  | D) | cholesterol |
|
|
 |
| 45 |  | 
Excess glucose after a meal will first form glycogen in a process called |
|  | A) | glycolysis. |
|  | B) | glycogenesis. |
|  | C) | lipogenesis. |
|  | D) | lipolyosis. |
|
|
 |
| 46 |  | 
Once glycogen stores are filled, glucose and amino acids are used to synthesize |
|  | A) | glycoproteins. |
|  | B) | proteins. |
|  | C) | lipids. |
|  | D) | lactic acid. |
|
|
 |
| 47 |  | 
When liver glycogen levels are inadequate to supply glucose, especially to the brain, amino acids and glycerol are used to produce ___________ in a process called _______________. |
|  | A) | glycogen; glycogenesis |
|  | B) | glucose; gluconeogenesis |
|  | C) | lipids; lipogenesis |
|  | D) | glucose-6-phosphate; glycogenolysis |
|
|
 |
| 48 |  | 
Which of these does not occur for about four hours after a meal? |
|  | A) | Glucose enters cells and is either used or stored as glycogen or fat. |
|  | B) | Fatty acids and glycerol combine to form fat, which when absorbed is deposited in adipose tissue. |
|  | C) | Amino acids are used in protein synthesis, some are used for energy and some are converted to fats and carbohydrates. |
|  | D) | Glycerol is converted to glucose, fatty acids are converted to acetyl-CoA, and acetyl-CoA is used to produce ketone bodies. |
|
|
 |
| 49 |  | 
Which one of the following would not be a characteristic of the postabsorptive state which occurs late in the morning, late in the afternoon or early in the morning before breakfast? |
|  | A) | Glycogen is broken down to produce glucose. |
|  | B) | Amino acids are used to synthesize proteins. |
|  | C) | Triglycerides in adipose tissue break down to glycerol and fatty acids. |
|  | D) | Lactic acid is produced and then converted to glucose in the liver. |
|
|
 |
| 50 |  | 
Which of the following processes describes the formation of glycogen from excess glucose in the blood? |
|  | A) | ketogenesis |
|  | B) | glycogenolysis |
|  | C) | lipogenesis |
|  | D) | gluconeogenesis |
|
|
 |
| 51 |  | 
Which of the following substances is produced in limited quantities in glycolysis as a result of the metabolism of excessive amounts of alcohol (ethanol)? |
|  | A) | NADH |
|  | B) | lipids |
|  | C) | glucose |
|  | D) | glycogen |
|
|
 |
| 52 |  | 
Which of the following processes is involved in converting amino acids into glucose? |
|  | A) | glycogenolysis |
|  | B) | lipogenesis |
|  | C) | gluconeogenesis |
|  | D) | transamination |
|
|
 |
| 53 |  | 
Which of the following metabolic states describes the first 4 hours after eating a meal? |
|  | A) | postabsorptive state |
|  | B) | preabsorptive state |
|  | C) | absorptive state |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 54 |  | 
Which of the following represents a normal average blood glucose level in young adults? |
|  | A) | 150-170 mgs/100ml. |
|  | B) | 60 - 90 mgs/100ml. |
|  | C) | 125-160mgs/100ml. |
|  | D) | 70 - 110 mgs/100ml. |
|
|
 |
| 55 |  | 
After glycogen has been used up in the postabsorptive state, which of the following is usually used as the next source of energy? |
|  | A) | glucose |
|  | B) | lipids |
|  | C) | proteins |
|  | D) | amino acids |
|
|
 |
| 56 |  | 
Two people who have the same weight and age are taking in the same kilocalories per day. Both people are doing the same exercise activities, but one person is gaining weight while the other is losing weight. This unfair situation can be explained because |
|  | A) | one person is male and the other person is female. |
|  | B) | the person gaining weight has more fat in the diet. |
|  | C) | the person gaining weight has more protein in the diet. |
|  | D) | the person gaining weight has more carbohydrate in the diet. |
|
|
 |
| 57 |  | 
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the energy needed to keep the resting body functional. This BMR accounts for about _____% of the energy expended during the day. |
|  | A) | 7 |
|  | B) | 20 |
|  | C) | 60 |
|  | D) | 80 |
|
|
 |
| 58 |  | 
People shiver when cold because |
|  | A) | about 40% of the total energy released by catabolism generates heat. |
|  | B) | about 60% of the total energy released by catabolism generates heat. |
|  | C) | when shivering you generate more heat per mole of glucose. |
|  | D) | shivering causes arrector pili muscles to contract releasing large amounts of heat. |
|
|
 |
| 59 |  | 
Which of the following would be a use for metabolic energy? |
|  | A) | thermic effect of food |
|  | B) | basal metabolism |
|  | C) | muscular activity |
|  | D) | All of the above |
|
|
 |
| 60 |  | 
Which of the following persons would mostly likely have a decreased BMR? |
|  | A) | a pregnant woman |
|  | B) | a thin, muscular, person |
|  | C) | a starving person |
|  | D) | a young child |
|
|
 |
| 61 |  | 
Which of the following is the usual amount of energy given off as heat during the burning of food? |
|  | A) | 40% |
|  | B) | 20% |
|  | C) | 60% |
|  | D) | 80% |
|
|
 |
| 62 |  | 
Which of the following conditions would produce malignant hyperthermia? |
|  | A) | frost bite |
|  | B) | hypothyroidism |
|  | C) | general anesthesia |
|  | D) | cancer |
|
|

