 |
| 18 |  | 
Which of the following epidermal cells functions in immunity? |
|  | A) | Langerhans' cells |
|  | B) | Merkel's cells |
|  | C) | keratinocytes |
|  | D) | melanocytes |
|
|
 |
| 19 |  | 
Which of the following acts as the foundation for the skin? |
|  | A) | epidermis |
|  | B) | hypodermis |
|  | C) | dermis |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 20 |  | 
The subcutaneous layer in the skin is |
|  | A) | composed of loose connective tissue and adipose tissue |
|  | B) | also another term for the skin |
|  | C) | a heat insulator layer which helps to conserve body heat |
|  | D) | the site for sweat production |
|
|
 |
| 21 |  | 
The integumentary system has many functions, one of which is |
|  | A) | protection from cancer |
|  | B) | production of Vitamin E |
|  | C) | detection of painful stimuli |
|  | D) | regulation of acid-base balance |
|
|
 |
| 22 |  | 
Intact skin provides protection because |
|  | A) | it forms a physical barrier against the entry of microbes |
|  | B) | its secretions keep the skin slightly alkaline |
|  | C) | skin contains components of the excretory system |
|  | D) | skin enhances water loss from the body |
|
|
 |
| 23 |  | 
A newborn child's body hair is mostly |
|  | A) | lanugo |
|  | B) | vernix |
|  | C) | vellus |
|  | D) | alopecia |
|
|
 |
| 24 |  | 
During surgery, an anesthesiologist often checks for the presence of cyanosis at the patient's fingertips. If cyanosis is present, what would be a possible cause? |
|  | A) | too much blood flowing into the fingertips |
|  | B) | poor oxygenation in the patient |
|  | C) | reduced blood flow to the patient's fingertips |
|  | D) | both B and C |
|
|
 |
| 25 |  | 
Pattern baldness is relatively rare in women because |
|  | A) | it is inhibited by estrogen. |
|  | B) | it only occurs in people with two Y chromosomes. |
|  | C) | it only occurs in people with an X and a Y chromosome. |
|  | D) | women have lower testosterone levels than men. |
|
|
 |
| 26 |  | 
Delicate unpigmented hairs that cover the fetus in early development are called |
|  | A) | terminal hairs. |
|  | B) | primary hairs. |
|  | C) | lanugo hairs. |
|  | D) | vellus hairs. |
|
|
 |
| 27 |  | 
At birth the hairs of the scalp, eyelids, and eyebrows are replaced by coarser pigmented hairs called |
|  | A) | terminal hairs. |
|  | B) | primary hairs. |
|  | C) | lanugo hairs. |
|  | D) | vellus hairs. |
|
|
 |
| 28 |  | 
Goose-bumps on the skin are due to the contraction of the muscle called |
|  | A) | triceps. |
|  | B) | arrector pili muscle. |
|  | C) | intramuscular. |
|  | D) | biceps. |
|
|
 |
| 29 |  | 
What is the difference between a hair and a hair follicle?
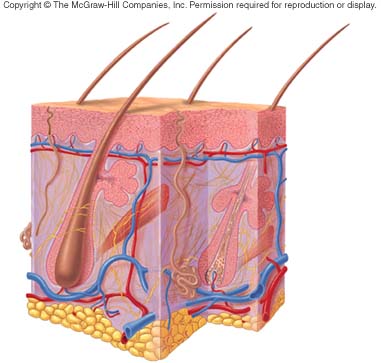 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig06.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (40.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig06.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (40.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Hair is composed of living stratified squamous tissue, whereas a hair follicle is composed of dead dermal cells. |
|  | B) | Hair originates in the subcutaneous layer, whereas a hair follicle originates from the dermis. |
|  | C) | Both of them are basically the same. |
|  | D) | Dead epidermal cells exist in the hair, whereas a hair follicle is composed of living epidermal cells. |
|
|
 |
| 30 |  | 
A hair receives its nutrition from |
|  | A) | its medulla. |
|  | B) | its cortex. |
|  | C) | the epithelial root sheath. |
|  | D) | the dermal papilla. |
|
|
 |
| 31 |  | 
The most superficial layer of the epidermis is
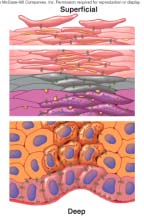 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig07.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig07.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | stratum basale. |
|  | B) | stratum lucidum. |
|  | C) | stratum granulosum. |
|  | D) | stratum corneum. |
|
|
 |
| 32 |  | 
Which of the following layers of the epidermis has no nuclei in its cells?
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig07.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0072507470/234419/mc_ch05_fig07.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (26.0K)</a> |
|  | A) | Stratum basale |
|  | B) | Stratum spinosum |
|  | C) | Stratum granulosum |
|  | D) | Stratum corneum |
|
|
 |
| 33 |  | 
Which of the following is true concerning light and dark-skinned races? |
|  | A) | Light-skinned people have fewer melanocytes than dark skinned people. |
|  | B) | Melanin production in light-skinned people is greater than in dark-skinned people |
|  | C) | Dark-skinned people have the same number of melanocytes as light-skinned people but there is greater melanin production in dark skinned-people. |
|  | D) | None of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 34 |  | 
The activity of apocrine sweat glands |
|  | A) | produces cerumen |
|  | B) | sometimes leads to body odor |
|  | C) | gives the skin a healthy glow |
|  | D) | produces sweat on the palm of the hand |
|
|
 |
| 35 |  | 
Sweat contains |
|  | A) | water, salts and wastes |
|  | B) | sebum |
|  | C) | water only |
|  | D) | dead cells, urea and sodium chloride |
|
|
 |
| 36 |  | 
Which one among the following is not a skin gland? |
|  | A) | sebaceous glands |
|  | B) | salivary glands |
|  | C) | ceruminous glands |
|  | D) | mammary glands |
|
|
 |
| 37 |  | 
The glands most responsible for cooling the skin are |
|  | A) | ceruminous |
|  | B) | sebaceous |
|  | C) | merocrine |
|  | D) | exothermic |
|
|
 |
| 38 |  | 
Eccrine sweat glands |
|  | A) | are most common in the armpits and groin. |
|  | B) | respond primarily to elevated body temperature. |
|  | C) | respond primarily to emotional stress. |
|  | D) | usually are associated with hair follicles. |
|
|
 |
| 39 |  | 
Eccrine sweat glands differ from sebaceous glands |
|  | A) | in terms of what is secreted |
|  | B) | in their location in the body |
|  | C) | because sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles, whereas sweat glands are not |
|  | D) | All of the above. |
|
|
 |
| 40 |  | 
In which of the following regions of the body are apocrine sweat glands most numerous? |
|  | A) | forehead |
|  | B) | axilla and groin |
|  | C) | neck |
|  | D) | palms of the hands |
|
|
 |
| 41 |  | 
Which of the following statements about the sebaceous gland is true? |
|  | A) | They are associated with the hair follicle. |
|  | B) | Sebaceous glands are also called holocrine glands. |
|  | C) | Secretion from sebaceous gland is called sebum. |
|  | D) | All of the above statements about the sebaceous gland are true. |
|
|
 |
| 42 |  | 
Which of the following structures in the hair would contain hard keratin? |
|  | A) | Shaft |
|  | B) | Hair bulb |
|  | C) | Medulla |
|  | D) | Cuticle |
|
|
 |
| 43 |  | 
Which of the following is true concerning hair growth? |
|  | A) | Hair grows continually until old age. |
|  | B) | Hair grows for a period of time and then rests and grows again. |
|  | C) | The period of rest before additional growth is the same for all structures in the body. |
|  | D) | Hair grows from cells called the shaft. |
|
|
 |
| 44 |  | 
When the arrector pili muscle contracts, which of the following happens? |
|  | A) | The hair shaft is pulled closer to the skin |
|  | B) | The hair shaft is pulled perpendicular to the skin surface. |
|  | C) | Movement of the hair follicle causes "goose bumps". |
|  | D) | Both B and C. |
|
|
 |
| 45 |  | 
Which of the following glands produce sweat? |
|  | A) | Apocrine |
|  | B) | Merocrine |
|  | C) | Holocrine |
|  | D) | A and B |
|
|
 |
| 46 |  | 
Which of the following is true concerning the growth of nails? |
|  | A) | Nails grow from the hyponychium outward. |
|  | B) | Nails are modified structures derived from the stratum corneum. |
|  | C) | Fingernails take about six months to grow from the matrix to the end of the nail plate. |
|  | D) | Toenails take about three months to grow from the matrix to the end of the nail plate. |
|
|
 |
| 47 |  | 
Why is it not a good idea for nail technicians to "pull back the cuticles" (eponychium) when
manicuring nails? |
|  | A) | The cuticle makes the nail look better. |
|  | B) | The cuticle is where the nail grows from. |
|  | C) | The cuticle acts as a barrier against infection. |
|  | D) | The cuticle makes the nail harder. |
|
|
 |
| 48 |  | 
The most active growing region of the nail is called |
|  | A) | nail matrix. |
|  | B) | nail bed. |
|  | C) | lunula. |
|  | D) | hyponychium. |
|
|

