
(See related pages)
| The Investigation poses questions to generate interest in various mathematical topics from the text and encourages students to formulate and investigate their own conjectures. One use of the investigations is for term papers in which students report on their conjectures and the patterns they find.
Click on the Read Me file below to open the investigation in a Word file: Laboratory Investigation 11.3Pantographs A pantograph is a mechanical device for enlarging and reducing figures by producing a similarity mapping. It can be constructed by computer software programs (see footnote) or constructed from four strips of wood, metal, or posterboard that are drilled with equally spaced holes, as shown in the following figure.* The arms of the pantograph are hinged at points A, B, C, and P so that they move freely. Point O is the projection point and should be held fixed. As point P traces the original figure, a pencil at point P' (its image) traces the enlargement. In this figure the arms are set so that point P' is twice as far from the projection point O as is point P, so the scale factor for this mapping is 2. To reduce a figure, the pencil is positioned at P and P' is moved around the boundary of the original figure. With the arms set as shown in the above figure, the scale factor for such a reduction is 1/2. The pantograph can be changed to obtain different scale factors by adjusting the locations of points B and C. Build a pantograph and experiment with different settings of the arms.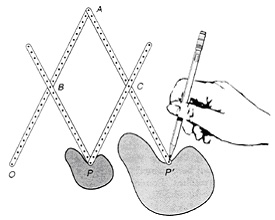
|