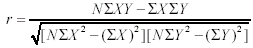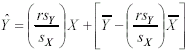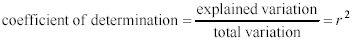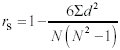|  Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 4/e Michael Thorne,
Mississippi State University -- Mississippi State
Martin Giesen,
Mississippi State University -- Mississippi State
Correlation and Regression
Symbols and FormulasSYMBOLS | Symbol | Stands For |
| | r | Pearson r, Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient | | zx, zy | z scores for the X and Y variables, respectively | | covXY | covariance of X and Y | | ρ | population correlation coefficient, read “rho” | | rcomp, rcrit | computed value of r and the critical value of r from Table E, respectively |  <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_ycaret.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_ycaret.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> | Y-caret, predicted values for Y based on the regression equation | | b | regression coefficient, slope of the regression line | | a | Y intercept, value of Y where the regression line crosses the Y axis | | sY, sX | standard deviation of the Y variable and the X variable, respectively | | r2 | coefficient of determination | | rs | Spearman rank order correlation coefficient | | d | difference between the ranks |
FORMULAS Formula 13-2. Computational formula for the Pearson r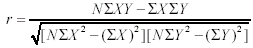 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
The values needed to compute the equation are: ∑X, ∑Y, ∑X2, ∑Y2, ∑XY, and N. ∑XY is found by
multiplying each X by each Y and summing the result.
Formula 13-3.Regression equation for predicting Y from X <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
The values needed to compute the equation are: ∑X, ∑Y, ∑X2, ∑Y2, ∑XY, and N. ∑XY is found by
multiplying each X by each Y and summing the result.
Formula 13-3.Regression equation for predicting Y from X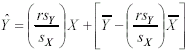 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> Formula 13-4. Equation for determining the proportion of variability in data explained by correlation <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> Formula 13-4. Equation for determining the proportion of variability in data explained by correlation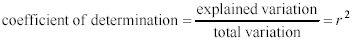 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> Formula 13-5. Equation for the Spearman rank order correlation coefficient <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (3.0K)</a> Formula 13-5. Equation for the Spearman rank order correlation coefficient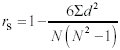 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula5.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
d is the difference between the ranks of individuals on the two variables, and N is the number of pairs of
observations. <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55322/chap13_formula5.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
d is the difference between the ranks of individuals on the two variables, and N is the number of pairs of
observations. |
|



 2003 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2003 McGraw-Hill Higher Education