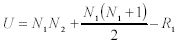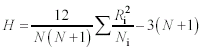SYMBOLS | Symbol | Stands For |
| | U or M–W U or U´ | statistic computed for the Mann–Whitney (M-W) test of significance | | N1, N2 | number of subjects in the first and second groups, respectively | | R1, R2 | sum of the ranks of the scores in the first and second groups, respectively | | d | differences between pairs of scores in the Wilcoxon test | | T | sum of the ranks of the scores with the less frequent sign (Wilcoxon test) | | H or K–W H | statistic computed for the Kruskal–Wallis (K–W) test | | Ni | number of observations in a particular sample | | Ri | sum of the ranks for a particular sample | | K | number of samples |
FORMULAS Formula 15-1. Computational formula for the Mann-Whitney U test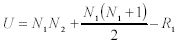 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f1.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (1.0K)</a>
N1 is the number of observations in the first sample, N2 is the number of observations in the second sample,
and R1 is the sum of the ranks of the scores in the first sample.Formula 15-2. Equation for U´U´ = N1N2 - U
The smaller of U and U´ is used in the test of significance.
Formula 15-4. Equation for converting large-sample U to a z score <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f2.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
U or U´ is converted to a z score when sample sizes are larger than N = 20.
Formula 15-5. Equation for converting a large-sample T to a z score <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f3.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
T is the sum of the ranks with the less frequently occurring sign. With samples of 25 or more, T is
converted to a z score.
Formula 15-6. Computational formula for the Kruskal-Wallis test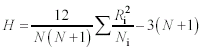 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif:: ::/sites/dl/free/0072832517/55324/c15_f4.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (2.0K)</a>
Ni is the number of observations for a particular sample, N is the total number of observations, and Ri is the
sum of the ranks for a particular sample. With sample sizes of at least 5 and at least three samples, H is
distributed approximately as c2 with df = K - 1, where K is the number of samples. |



 2003 McGraw-Hill Higher Education
2003 McGraw-Hill Higher Education