 |
| 1 |  | 
Use the following diagrams to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627572/q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627572/q1.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (16.0K)</a>
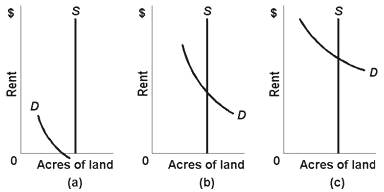
Refer to the diagrams. These diagrams illustrate three grades of land available for development of a new shopping complex. The same amount of labor, capital, and other inputs for the shopping complex would be used regardless of which land is chosen. In terms of the land's ability to generate potential revenue for the developers, we can say that: |
|  | A) | land in figure (a) is most productive |
|  | B) | land in figure (b) is most productive |
|  | C) | land in figure (c) is most productive |
|  | D) | we cannot compare the productivity of the three grades of land |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Suppose Congress, in an attempt to increase taxes on the wealthy, passes a law doubling the tax rate on interest income. The effect of this law would be most likely to: |
|  | A) | increase the supply of loanable funds and decrease the equilibrium interest rate |
|  | B) | decrease the supply of loanable funds and increase the equilibrium interest rate |
|  | C) | increase the demand for loanable funds and increase the equilibrium interest rate |
|  | D) | decrease the demand for loanable funds and decrease the equilibrium interest rate |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
In year 1, the nominal rate of interest is 7% and the inflation rate is 3%. The real rate of interest in year 1: |
|  | A) | is 4% |
|  | B) | is 7% |
|  | C) | is 10% |
|  | D) | cannot be determined from the information given |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
In the loanable funds market (all else equal): |
|  | A) | a decrease in bank lending will decrease the interest rate |
|  | B) | an increase in saving will increase the interest rate |
|  | C) | an increase in the productivity of business investments will decrease the interest rate |
|  | D) | an increase in government borrowing will increase the interest rate |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Compared to taxes on other resources, taxes on land may be preferable because they: |
|  | A) | do not lead to a reallocation of the resource |
|  | B) | are proportional to income across all income classes |
|  | C) | lead to more rapid economic growth |
|  | D) | can increase productive efficiency by reducing the cost of a key input |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
The XYZ Corporation can make a 4% real (inflation-adjusted) return on an investment. It can borrow funds to finance the investment at a nominal rate of 6% and the inflation rate is 1%. We can conclude that the: |
|  | A) | investment will be profitable |
|  | B) | investment will be unprofitable |
|  | C) | real rate of interest is 3% |
|  | D) | real rate of interest is 7% |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Use the following diagram to answer the next question.
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627572/q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627572/q7.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (11.0K)</a>
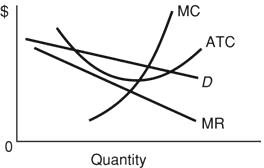
Refer to the diagram. Assuming entry into this industry is blocked, the firm represented in the diagram: |
|  | A) | can use its monopoly power to earn an economic profit |
|  | B) | will be unable to earn economic profits at any possible price |
|  | C) | is earning a normal profit |
|  | D) | is earning a normal profit but not an economic profit |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Suppose a firm has the option to purchase new equipment for $16,000 that can reduce its annual operating costs by $800. The firm should borrow funds for this investment if it can negotiate an annual nominal interest rate: |
|  | A) | less than 3% |
|  | B) | less than 5% |
|  | C) | less than 20% |
|  | D) | at least 10% |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which of the following is an uninsurable risk an entrepreneur may have to bear? |
|  | A) | Loss of profit due to employee theft and shoplifting |
|  | B) | Loss of productive work time due to employee injury on the job |
|  | C) | Loss of profit due to higher state and local taxes |
|  | D) | Loss of a factory due to fire |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Suppose Carol's uncle has left her $2000 in his will. The money is being put into a bank account earning 5% interest compounded annually. Because she has just turned 19, her uncle restricted her from accessing the account. How much money will be in the account two years from now, when she is 21, and can withdraw the funds? |
|  | A) | $2010 |
|  | B) | $2200 |
|  | C) | $2205 |
|  | D) | $2222 |
|
|

