 |
| 1 |  | 
Over the past several years, the volume of world trade has: |
|  | A) | decreased because of increased government regulation of trade through tariffs and quotas |
|  | B) | decreased because of the decline in incomes brought on by global recession |
|  | C) | increased because of increased government regulation of trade through tariffs and quotas |
|  | D) | increased because of improvements in communications and transportation |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
A tariff: |
|  | A) | raises the price of imported goods, increasing the demand for domestic substitutes |
|  | B) | lowers the cost of producing domestic goods |
|  | C) | offsets the effect of a quota |
|  | D) | raises the price of domestic goods, lowering the demand for them |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
U.S. exports: |
|  | A) | average 4-6 percent of GDP, as do imports |
|  | B) | average 18-20 percent of GDP, while imports average 10-12 percent |
|  | C) | average 10-12 percent of GDP, while imports average 15-17 percent |
|  | D) | average 1-2 percent of GDP, while imports average 4-6 percent |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
A government agency requires that all agricultural goods entering the country undergo an unduly long inspection process to assure product quality. This is an example of: |
|  | A) | an export subsidy |
|  | B) | a tariff |
|  | C) | a nontariff barrier |
|  | D) | a quota |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Which of the following will tend to increase U.S. exports to Mexico and reduce Mexican exports to the U.S.? |
|  | A) | A decrease in the dollar price of the peso |
|  | B) | An appreciation of the dollar relative to the peso |
|  | C) | A depreciation of the peso relative to the dollar |
|  | D) | An increase in the dollar price of the peso |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities tables for countries Alpha and Beta:
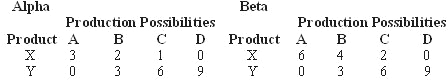 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627562/q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627562/q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a>
In Beta, the domestic opportunity cost of one unit of good X is: |
|  | A) | 1 unit of Y |
|  | B) | 1.5 units of Y |
|  | C) | 2 units of X |
|  | D) | 3 units of Y |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Answer the next question on the basis of the following production possibilities tables for countries Alpha and Beta:
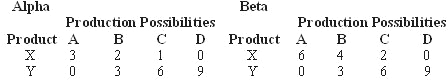 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627562/q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073365955/627562/q6.jpg','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (15.0K)</a>
According to the concept of comparative advantage: |
|  | A) | Alpha should specialize in the production of X; Beta in the production of Y |
|  | B) | Alpha should produce some of both goods X and Y |
|  | C) | Beta should produce some of both goods X and Y |
|  | D) | Beta should specialize in the production of X; Alpha in the production of Y |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
Two nations, Gamma and Delta, both produce shoes and dresses. Gamma has a comparative advantage in the production of shoes if: |
|  | A) | it can produce shoes with fewer resources than Delta |
|  | B) | its domestic opportunity cost of shoes in terms of dresses is lower than Delta's |
|  | C) | its supply of shoes is greater than Delta's |
|  | D) | it is wealthier than Delta |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
A decrease in the U.S. demand for Mexican goods will: |
|  | A) | increase the demand for the peso and increase its dollar price |
|  | B) | increase the supply of the peso and decrease its dollar price |
|  | C) | decrease the supply of the peso and increase its dollar price |
|  | D) | decrease the demand for the peso and decrease its dollar price |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
One major outcome of the North American Free Trade Agreement is: |
|  | A) | massive investment by Asian companies in Mexico to exploit reduced tariffs |
|  | B) | increased unemployment in Mexico |
|  | C) | higher average living standards in Canada, Mexico, and the U.S. |
|  | D) | reduced exports from the U.S. to Mexico and Canada |
|
|

