 |
| 1 |  | 
A test often performed in POLs is an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). It measures the tendency of red cells to settle together at the bottom of a column of blood. While it is not specific for any one disorder, it gives valuable information when combined with a patient's physical symptoms. Patient A had an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 39 mm/hr. Patient B had an ESR of 9 mm/hr. What does the unit "mm" signify? What is each patient's rate in meters? What is the difference in their rates? Use your school library or your own reference books to determine which patient’s result is normal and which is abnormal. |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
Mr. Dugal had a reticulocyte count that resulted in 4 reticulocytes for 500 red blood cells (RBC). Using the following formula, calculate the percent of reticulocytes on the stained blood smear:
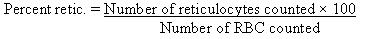 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073401951/820897/chap3_41.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::::/sites/dl/free/0073401951/820897/chap3_41.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (6.0K)</a> |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
A while ago, your laboratory supervisor assigned you the task of calibrating the spectrophotometer with a new batch of reagents. She went through the procedure with you, and you understood it at the time. The old batch of reagents is almost gone, and the supervisor has reminded you that it is time to recalibrate. You feel a little shaky about the task. What should you do? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
You have calculated a patient's data with a test formula. The answer you get for the patient's test result is abnormal. It is a very busy day. What should you do? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
In the POL where you work, you have been asked to give a tour to a group of students. You are to explain to them why the POL relies solely on metric measurements. What should you say? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
You have been instructed to take a blood sample from an infant for a microbilirubin test. The pipette measures a very small amount. You will use a heel stick to obtain the specimen. What metric unit will you use to measure the amount of blood collected? |
|  | |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::chap3_56::/sites/dl/free/0073401951/820897/chap3_56.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">chap3_56 (3.0K)</a>chap3_56 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=jpg::chap3_56::/sites/dl/free/0073401951/820897/chap3_56.JPG','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif">chap3_56 (3.0K)</a>chap3_56 |
|  | |
|
|

