Please note that this quiz uses special characters. Not all browsers display special characters properly. For best results please use Internet Explorer 5.5 or newer or Netscape 6.2 or newer.
 |
| 1 |  | 
Balance the following redox equation occurring in aqueous solution:
KMnO4 + KCl + H2SO4 → MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O + Cl2
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for chlorine (Cl2) when the equation is balanced with smallest whole number coefficients?
|
|  | A) | 1 |
|  | B) | 3 |
|  | C) | 5 |
|  | D) | 8 |
|  | E) | 10 |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
In the shorthand notation for an electrochemical cell, what does a single vertical line (|) represent? |
|  | A) | the cathode |
|  | B) | the anode |
|  | C) | a salt bridge |
|  | D) | a phase boundary |
|  | E) | the external wire connecting anode to cathode |
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
A voltaic cell is based on the following two half-reactions:
Ni+2(aq) + 2e- ® Ni(s) E° = -0.25 V
Cr+3(aq) + 3e- ® Cr(s) E° = -0.74 V
Sketch the cell and then select the correct statement about it. |
|  | A) | Cr serves as the cathode. |
|  | B) | The direction of electron flow through the external wire is from the Ni to the Cr electrode. |
|  | C) | Anions in solution will migrate toward the Ni+2/Ni electrode. |
|  | D) | The net cell reaction is 3Ni+2(aq) + 2Cr(s) ® 3Ni(s) + 2Cr+3(aq) |
|  | E) | 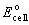 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/38224/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 0.99 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/38224/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 0.99 V |
|
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
Consider the following electrochemical cell reaction:
2Fe2+(aq) + Cu2+(aq) ® 2Fe3+(aq) + Cu(s)
Use the table of standard electrode potentials in your textbook to calculate the standard cell potential for the above reaction. |
|  | A) | -0.43 V |
|  | B) | +0.43 V |
|  | C) | +0.78 V |
|  | D) | -0.78 V |
|  | E) | +1.11 V |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Consider the following two electrode reactions and their standard electrode potentials:
Al+3(aq) + 3e- → Al(s) E° = -1.66 V
Cd+2(aq) + 2e- → Cd(s) E° = -0.40 V
Write the cell reaction for a voltaic cell based on these two electrodes, and calculate the standard cell potential, 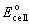 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>. <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (5.0K)</a>. |
|  | A) | 2Al+3(aq) + 3Cd+2(aq) ® 2Al(s) + 3Cd(s) 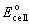 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 2.10 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 2.10 V |
|  | B) | 2Al(s) + 3Cd+2(aq) ® 2Al+3(aq) + 3Cd(s) 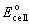 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 1.26 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 1.26 V |
|  | C) | 2Al(s) + 3Cd+2(aq) ® 2Al+3(aq) + 3Cd(s) 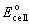 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 3.78V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 3.78V |
|  | D) | 2Al+3(aq) + 3Cd(s) ® 2Al(s) + 3Cd+2(aq) 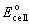 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 1.26 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 1.26 V |
|  | E) | 2Al+3(aq) + 3Cd(s) ® 2Al(s) + 3Cd+2(aq) 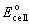 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 2.10 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 2.10 V |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Consider the following standard reduction potentials, E°, in acid solution:
Al3+(aq) + 3e- → Al(s) E° = -1.66 V
Sn4+(aq) + 2e- → Sn2+(aq) E° = +0.14 V
I2(s) + 2e- → 2I-(aq) E° = +0.53 V
Under standard conditions, which of the following species is the most likely to gain electrons in a reaction? |
|  | A) | Al3+(aq) |
|  | B) | Al(s) |
|  | C) | I-(aq) |
|  | D) | I2 (s) |
|  | E) | Sn4+(aq) |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Consult the table of standard electrode potentials in your textbook in order to decide which one of the following reagents is capable of reducing I2(s) to I-(aq, 1 M). |
|  | A) | Br-(aq) |
|  | B) | Ag(s) |
|  | C) | Sn(s) |
|  | D) | Zn2+(aq, 1 M) |
|  | E) | Sn4+(aq,1 M) |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
A redox reaction which involves the transfer of 3 electrons has an equilibrium constant Kc of
1.8 ´ 1017. What is the standard cell potential at 25°C of a voltaic cell based on this reaction?
(F = 96500 C/mol) |
|  | A) | -1.20 V |
|  | B) | -0.68 V |
|  | C) | +0.12 V |
|  | D) | +0.34 V |
|  | E) | +1.20 V |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
A voltaic cell consists of Mn/Mn2+ and Cd/Cd2+ half-cells with concentrations [Mn2+] = 0.75 M and [Cd2+] = 0.15 M. Use the Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential, Ecell, at 25° C.
(F = 96500 C/mol)
Data: Cd+2(aq) + 2e- → Cd(s) E° = -0.40 V
Mn+2(aq) + 2e- → Mn(s) E° = -1.18 V |
|  | A) | 1.60 V |
|  | B) | 1.56 V |
|  | C) | 1.54 V |
|  | D) | 0.80 V |
|  | E) | 0.76 V |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Consider the following cell reaction and its standard cell potential:
2Cr(s) + 3Pb2+(aq) ® 3Pb(s) + 2Cr3+(aq) 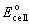 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 0.61 V <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image26.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> = 0.61 V
Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for this reaction at 25°C. (F = 96500 C/mol)
|
|  | A) | 4 ´ 1020 |
|  | B) | 8 ´ 1030 |
|  | C) | 9 ´ 1045 |
|  | D) | 3 ´ 1051 |
|  | E) | 8 ´ 1061 |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Which of the following types of electrochemical cell is most likely to find use in the future as a power source for electric vehicles? |
|  | A) | fuel cell |
|  | B) | nickel-metal hydride cell |
|  | C) | dry cell |
|  | D) | alkaline battery |
|  | E) | lithium-ion battery |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Select the incorrect statement relating to the corrosion of iron in air. |
|  | A) | Fe2+ is formed in the anodic region. |
|  | B) | O2 is oxidized in the cathodic region. |
|  | C) | Electrons travel through the iron metal between the anodic and cathodic regions. |
|  | D) | Moisture provides a pathway for ions to migrate. |
|  | E) | Rust is a hydrated form of iron(III) oxide. |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Use the following standard electrode potentials to predict the species formed at the electrodes in the electrolysis of aqueous CuSO4.
O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e- ® 2H2O(l) E° = +1.23 V
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ® Cu(s) E° = +0.34 V
SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e- ® H2SO3(aq) + H2O(l) E° = 0.20 V
2H+(aq) + 2e- ® H2(g) E° = 0.00 V
|
|  | A) | H2, O2, H+ |
|  | B) | Cu, O2, H+ |
|  | C) | Cu, H2 |
|  | D) | H2, H2SO3, H2O |
|  | E) | H2SO3, H2O, O2, H+ |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
In an electrolytic cell, a current of 3.00 A is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride for a period of 5.00 min. What volume of chlorine gas (Cl2), measured at 25°C and 1.00 atm, will be formed at the anode? (F = 96500 C/mol) |
|  | A) | 4.61 L |
|  | B) | 1.24 L |
|  | C) | 456 mL |
|  | D) | 228 mL |
|  | E) | 114 mL |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
A constant current was passed through a solution of KAuCl4 between gold electrodes. Over a period of 20.00 min, the cathode increased in mass by 2.664 g. What was the current in amperes?
(F = 96500 C/mol)
Cathode half-reaction: AuCl4-(aq) + 3e- ® Au(s) + 4Cl-(aq) |
|  | A) | 1.08 A |
|  | B) | 3.26 A |
|  | C) | 2.17 A |
|  | D) | 6.52 A |
|  | E) | 3.48 A |
|
|

