Please note that this quiz uses special characters. Not all browsers display special characters properly. For best results please use Internet Explorer 5.5 or newer or Netscape 6.2 or newer.
 |
| 1 |  | 
Of the three major types of bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic) which ones are based on electrostatic attractions between opposite charges? |
|  | A) | only ionic bonding |
|  | B) | only ionic and covalent bonding |
|  | C) | only ionic and metallic bonding |
|  | D) | ionic, covalent and metallic bonding |
|  | E) | none of the above |
|
|
 |
| 2 |  | 
The Lewis dot symbol for the oxide ion is |
|  | A) | 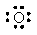 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image8.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image8.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | B) | 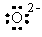 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image9.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image9.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | C) | 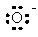 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image10.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image10.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | D) | 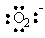 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image11.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image11.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|  | E) | 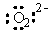 <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> <a onClick="window.open('/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=gif::::/sites/dl/free/0073402699/37547/Image12.gif','popWin', 'width=NaN,height=NaN,resizable,scrollbars');" href="#"><img valign="absmiddle" height="16" width="16" border="0" src="/olcweb/styles/shared/linkicons/image.gif"> (0.0K)</a> |
|
|
|
 |
| 3 |  | 
Which of the following is the correct formula for magnesium nitride? |
|  | A) | Mg NO3 |
|  | B) | Mg(NO3)2 |
|  | C) | MgN |
|  | D) | Mg2N3 |
|  | E) | Mg3N2 |
|
|
 |
| 4 |  | 
The electrostatic force of attraction between two charges, A and B, is proportional to |
|  | A) | (charge A) + (charge B) + (distance between the charges)2 |
|  | B) | (charge A) x (charge B) x (distance between the charges)2 |
|  | C) | (charge A) x (charge B) + (distance between the charges)2 |
|  | D) | (charge A) x (charge B) / (distance between the charges)2 |
|  | E) | (distance between the charges)2/(charge A) x (charge B) |
|
|
 |
| 5 |  | 
Predict which of the following solids has the greatest lattice energy. |
|  | A) | CsI |
|  | B) | NaF |
|  | C) | SrCl2 |
|  | D) | KF |
|  | E) | SrO |
|
|
 |
| 6 |  | 
Ionic compounds normally conduct electricity |
|  | A) | when in the solid state. |
|  | B) | only when molten. |
|  | C) | when in aqueous solution or molten. |
|  | D) | only when in aqueous solution. |
|  | E) | when a solid or in aqueous solution. |
|
|
 |
| 7 |  | 
Order the following by decreasing bond length: C≡C, C=C, C-C |
|  | A) | they are all the same |
|  | B) | C≡C, C=C, C-C |
|  | C) | C≡C, C-C, C=C |
|  | D) | C-C, C=C, C≡C |
|  | E) | C=C, C-C, C≡C |
|
|
 |
| 8 |  | 
List the following bonds in order of decreasing strength: Br-Br, Cl-Cl, F-F, I-I. |
|  | A) | F-F, Cl-Cl, I-I, Br-Br |
|  | B) | F-F, Br-Br, Cl-Cl, I-I |
|  | C) | I-I, Br-Br, Cl-Cl, F-F |
|  | D) | F-F, Cl-Cl, Br-Br, I-I |
|  | E) | I-I, Cl-Cl, Br-Br, F-F |
|
|
 |
| 9 |  | 
Which one of the following is not characteristic of substances composed of small, covalently-bonded molecules? |
|  | A) | low melting point |
|  | B) | low boiling point |
|  | C) | weak bonds |
|  | D) | poor electrical conductor when solid |
|  | E) | poor electrical conductor when molten |
|
|
 |
| 10 |  | 
Electronegativity is a measure of |
|  | A) | the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. |
|  | B) | the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. |
|  | C) | the magnitude of the negative charge on an electron. |
|  | D) | the attraction by an atom for electrons in a chemical bond. |
|  | E) | the magnitude of the negative charge on a molecule. |
|
|
 |
| 11 |  | 
Which of the following elements is the most electronegative? |
|  | A) | C |
|  | B) | Si |
|  | C) | As |
|  | D) | Cl |
|  | E) | Sr |
|
|
 |
| 12 |  | 
Consider an isolated H-C bond in an organic compound. Based on the electronegativities of the two elements, which of the following best describes the net charge on the carbon atom? |
|  | A) | no polarization of the bond, i.e. no net charge |
|  | B) | a full negative charge |
|  | C) | a full positive charge |
|  | D) | a partial negative charge |
|  | E) | a partial positive charge |
|
|
 |
| 13 |  | 
Which of the following lists orders the bonds from the most to the least covalent character? |
|  | A) | H-C, N-H, H-O |
|  | B) | H-C, H-O, N-H |
|  | C) | H-O, N-H, H-C |
|  | D) | N-H, H-O, H-C |
|  | E) | N-H, H-C, H-O |
|
|
 |
| 14 |  | 
Based on electronegativity trends in the periodic table, predict which of the following compounds will have the greatest % ionic character in its bonds. |
|  | A) | HCl |
|  | B) | CaI2 |
|  | C) | CaCl2 |
|  | D) | SrF2 |
|  | E) | SrCl2 |
|
|
 |
| 15 |  | 
Which one of the following properties is not characteristic of typical metals? |
|  | A) | moderately high melting point |
|  | B) | high boiling point |
|  | C) | brittleness |
|  | D) | good electrical conductor when solid |
|  | E) | good electrical conductor when molten |
|
|

